-
Original Article
Hysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleHysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
04-30-2025Views14Abstract
Objective:
Analyze the hysterectomy rates per resident in graduation year in teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo (Brazil).
Methods:
We selected teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo and gathered information from two public databases to estimate the hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training between 2009 and 2019.
Results:
Between 2009 and 2019, there was a 37.5% increase in the number of residents in their final year of training, a 4.31% increase in the number of hysterectomies, and a drop in the hysterectomy rates per resident of 24.1%. The reduction of the rate of hysterectomy per resident was more pronounced for vaginal route (46.4%) followed by abdominal route (23.3%). The ratio of laparoscopic hysterectomy per resident increased 264% during the period, however, this route was used in only 7% of the surgeries in 2019.
Conclusions:
The hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training showed a notable reduction. This trend, particularly pronounced in vaginal and abdominal routes, signals a shift towards minimally invasive techniques.
Key-words Clinical competenceEducation, medicalHospitals, teachingHysterectomylearning curveMedical staff, hospitalPhysiciansStudents, medicalSurgical procedures, operativeSee more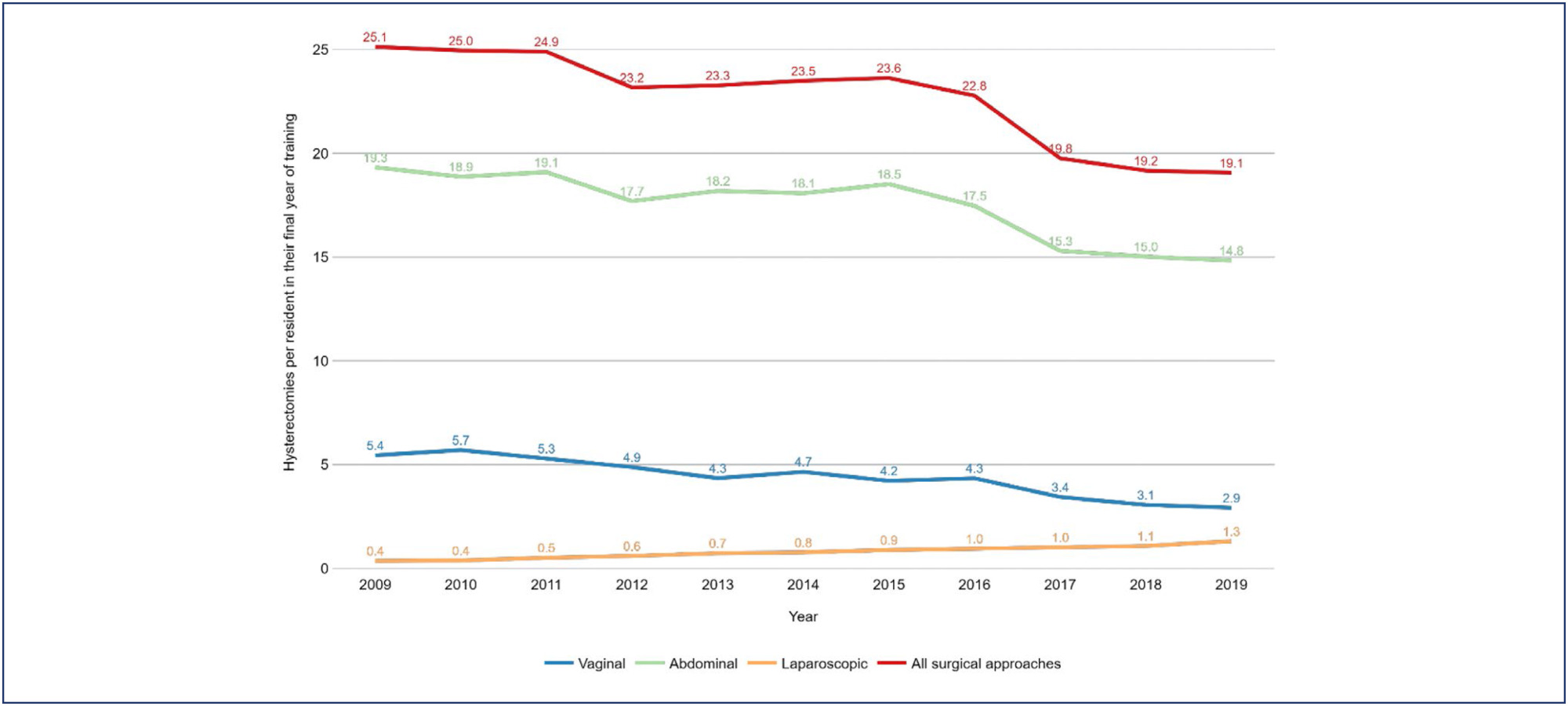
-
Review Article
Efficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
04-30-2025
Summary
Review ArticleEfficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
04-30-2025Views14Abstract
Objective:
This umbrella review aimed to synthesize evidence from systematic reviews of clinical trials on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in gynecology and obstetrics procedures.
Methods:
We searched Medline, Embase, SciELO and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews on March 11, 2024, using the term "tranexamic acid". Four reviewers independently select studies and extract data. We assessed the quality of systematic review and the quality of evidence, using AMSTAR 2 and GRADE tools, respectively.
Results:
Of 651 systematic reviews identified, 16 reviews with 96663 patients were included. The surgical procedures were cesarean section, myomectomy, hysterectomy, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia surgery. All reviews showed a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction in intraoperative and post-procedure blood loss, associated with intravenous or topical use of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid resulted in a significant reduction in the need for blood transfusions and a less pronounced drop in postoperative hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in cesarean section. Several reviews addressed the same question, but the number of included trials varied substantially, which might indicate flaws in search and selection of studies of these reviews. The quality of systematic reviews was low or critically low, and the quality of evidence was moderate.
Conclusions:
This umbrella review shows that tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and hemorrhage in gynecology and obstetrics procedures. High quality systematic reviews are still needed.
Key-words Blood transfusionCesarean sectionEfficacyGynecologic surgical procedureshematocritHemorrhageHysterectomyObstetric surgical proceduresTranexamic acidUterine cervical dysplasiauterine myomectomySee more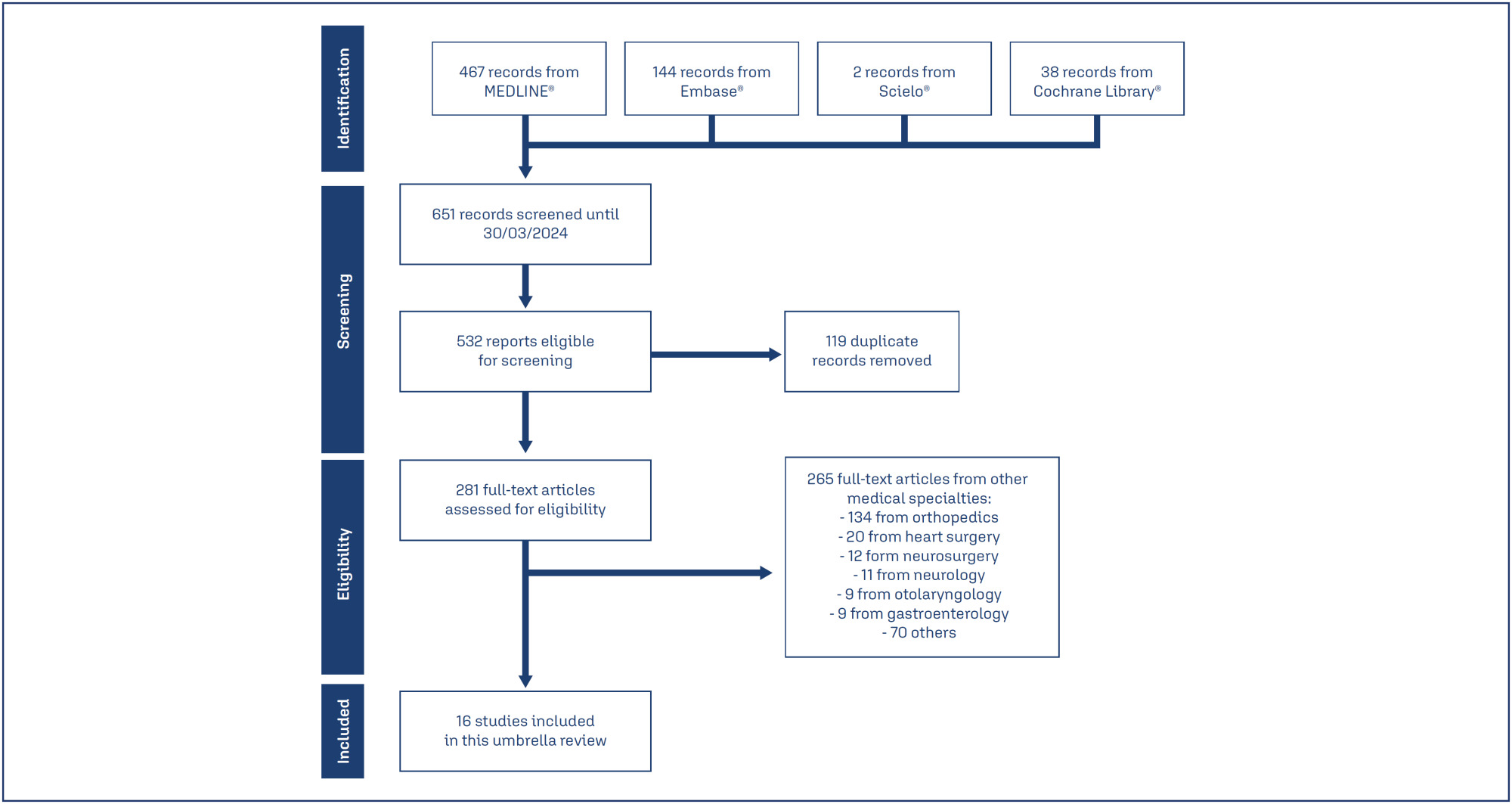
-
Original Article
A comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
01-23-2025
Summary
Original ArticleA comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
01-23-2025Views234See moreAbstract
Objective
The study investigates the influence of positive-approach counseling through both online and face-to-face group therapy on the sexual intimacy of women after benign complete abdominal hysterectomy, addressing challenges such as the loss of femininity and other psychosexual complications that disrupt the couple’s relationship post-surgery.
Methods
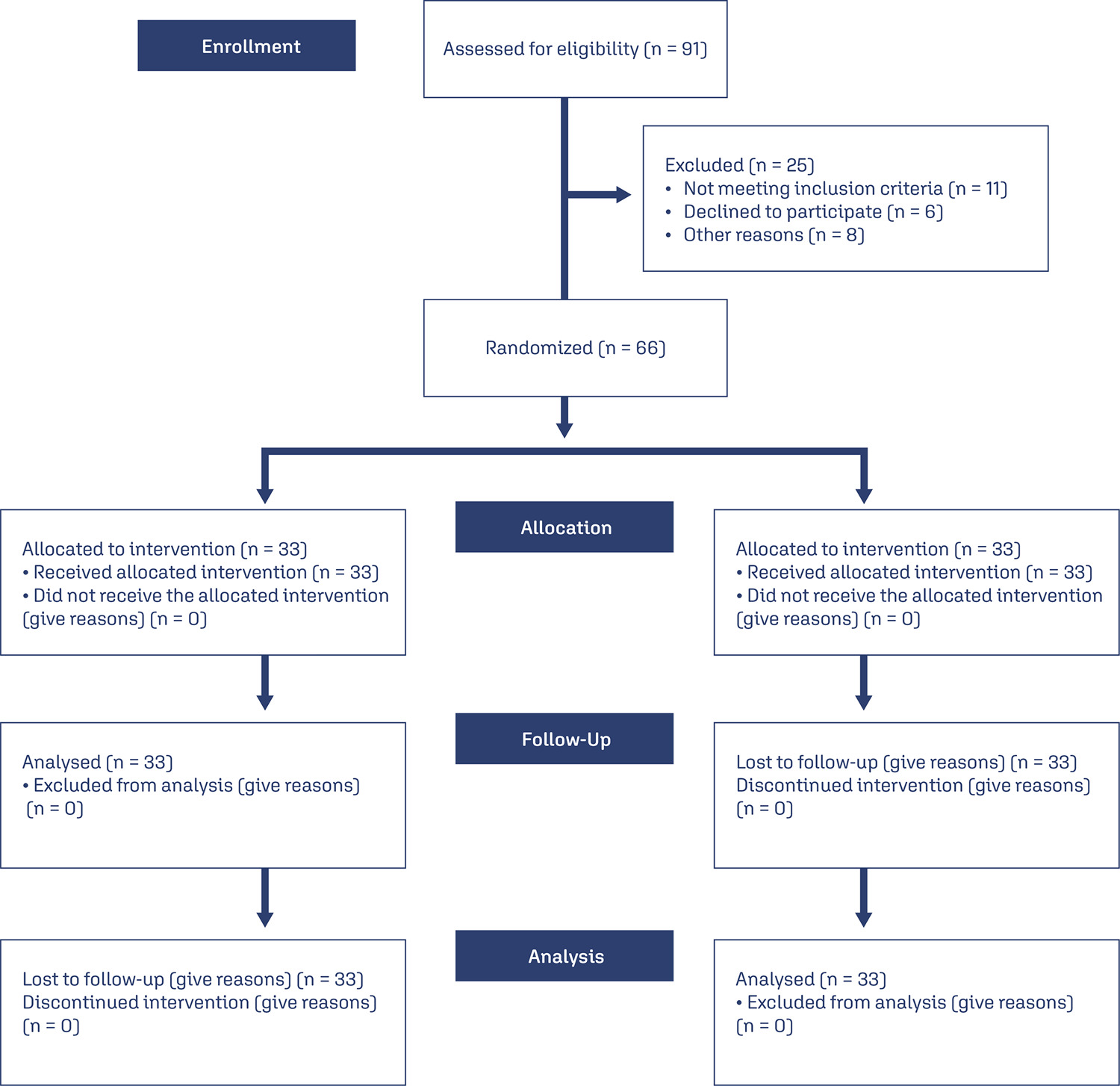
This is a parallel clinical trial, conducted in 2023 in Yazd, Iran; with sixty-six participants post- benign complete abdominal hysterectomy were randomly assigned to online and face-to-face counseling groups. Each group had eight 90-minute sessions, and data were collected using demographic and intimacy scale (IS) questionnaires at baseline, eighth week, and twelfth week follow-up. Statistical analysis used SPSS version 23 (P < 0.05).
Results
In the Online Group, the mean sexual intimacy score significantly increased from 72.42 ± 9.05 to 87.06 ± 7.98 at eight weeks and 90.30 ± 8.23 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). In the Face-to-Face Group, the mean score increased from 70.21 ± 6.75 to 81.24 ± 5.55 at eight weeks and 85.03 ± 5.40 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). Online counseling proved more effective than face-to-face counseling in enhancing sexual intimacy (P = 0.043).
Conclusion
Online and face-to-face counseling based on the positive approach improved sexual intimacy in women with a history of benign hysterectomy. Moreover, it seems that online counseling was more effective, so it is recommended that this method be employed in follow-up sessions after hysterectomy. Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials - IRCT20230209057373N1
-
Review Article
The Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):790-796
10-07-2022
Summary
Review ArticleThe Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):790-796
10-07-2022Views218See moreAbstract
Objective
This systematic review aims at describing the prevalence of urinary and sexual symptoms among women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods
A systematic search in six electronic databases was performed, in September 2019, by two researchers. The text search was limited to the investigation of prevalence or occurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and sexual dysfunctions in women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer. For search strategies, specific combinations of terms were used.
Results
A total of 8 studies, published between 2010 and 2018, were included in the sample. The average age of the participants ranged from 40 to 56 years, and the dysfunctions predominantly investigated in the articles were urinary symptoms (n= 8). The rates of urinary incontinence due to radical abdominal hysterectomy ranged from 7 to 31%. The same dysfunction related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 35% and to laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 47%. Nocturia ranged from 13%, before treatment, to 30%, after radical hysterectomy. The prevalence rates of dyspareunia related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy ranged from 5 to 16% and 7 to 19% respectively. The difficulty in having orgasm was related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (10 to 14%) and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy (9 to 19%).
Conclusion
Urinary and sexual dysfunctions after radical hysterectomy to treat cervical cancer are frequent events. The main reported disorders were urinary incontinence and dyspareunia.
-
Case Report
A Scary Complication: Single-center Study on Management and Outcome of Cesarean Scar Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):311-316
06-18-2021
Summary
Case ReportA Scary Complication: Single-center Study on Management and Outcome of Cesarean Scar Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):311-316
06-18-2021Views84See moreAbstract
A cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) is a scary and life-threatening complication of cesarean section (CS). Nevertheless, the incidence of CS is constantly growing. The CSP incidence is 0,15% of pregnancies after CS which represents 6,1% of all ectopic pregnancies in women with condition after CS. Therefore, it should be more present in the clinical daily routine. From mild nonspecific symptoms to hypovolemic shock, diagnosis and therapy must be performed quickly. With the progressive growth of the scar pregnancy, a uterine rupture involves the risk of severe bleeding, and an emergency hysterectomy could be necessary. Prolongation of pregnancy has been successful only in a few cases.We report 11 cases from our hospital in the past 10 years. In the discussion, treatment options of this complication with an increasing incidence, which is associated with serious morbidity and mortality, are presented based on the current literature. Treatment options include drug therapy, but also surgical or combined procedures with radiological intervention.
-
Original Article
Analysis of Conization Results in Patients undergoing Hysterectomy for Uterine Adenocarcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):266-271
06-22-2020
Summary
Original ArticleAnalysis of Conization Results in Patients undergoing Hysterectomy for Uterine Adenocarcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):266-271
06-22-2020Views195See moreAbstract
Objective
To observe if the histopathological result of a conization performed after cervical adenocarcinoma in situ diagnosis is compatible with the histopathological analysis of a subsequent hysterectomy.
Methods
The present descriptive and observational research consisted of the analysis of the medical records of 42 patients who were diagnosed with in situ adenocarcinoma postconization. The analysis consisted of whether there was compatibility between the histopathological reports of conization and hysterectomy and if there was an association between adenocarcinoma in situ and another neoplasia (squamous disease). Interpretation of any immunohistochemistry reports obtained was also performed. In addition, clinical and epidemiological data were also analyzed.
Results
A total of 42 conizations were performed, 33 (79%) were cold knife conizations and 9 (21%) were loop electrosurgical excision procedures (LEEPs). Of the patients analyzed, 5 (10%) chose not to undergo subsequent hysterectomy to preserve fertility or were < 25 years old. Out of the 37 patients with adenocarcinoma in situ who underwent subsequent hysterectomy, 6 (16%) presented with residual disease. This findingprovedincompatiblewiththe finding of the conizations, which had ruled out invasive cancer.
Conclusion
The prevalence of adenocarcinoma in situ increased in the past years. There is still a large part of the medical literature that advocates the use of conservative treatment for this disease, even though it is common knowledge that it is a multifocal disease. However, the majority of studies advocate that hysterectomy should remain the preferred treatment for women who have already completed their reproductive purpose.
-
Original Articles
The Impact of Systematic Laparoscopic Skills and Suture Training on Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Outcomes in a Brazilian Teaching Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(12):718-725
02-03-2019
Summary
Original ArticlesThe Impact of Systematic Laparoscopic Skills and Suture Training on Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Outcomes in a Brazilian Teaching Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(12):718-725
02-03-2019Views153See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the impact of systematic laparoscopic skills and suture training (SLSST) on the total laparoscopic hysterectomy intra- and postoperative outcomes in a Brazilian teaching hospital.
Methods
A cross-sectional observational study in which 244 charts of total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) patients operated from 2008 to 2014 were reviewed. Patient-specific (age, parity, previous cesarean sections, abdominal surgeries and endometriosis) and surgery-related variables (hospital stay, operative time, uterine volume and operative complications) were analyzed in three different time-frame groups: 2008-09 (I-1) - TLHs performed by senior attending physicians; 2010-11 (I-2) - TLHs performed by residents before the implementation of the SLSST program; and 2012-14 (I-3) - TLHs performed by residents after the implementation of the SLSST program.
Results
A total of 244 TLH patients (mean age: 45.93 years) were included: 24 (I-1), 55 (I-2), and 165 (I-3). The main indication for TLH was uterine myoma (66.4%). Group I-3 presented a decrease in surgical time compared to group I-2 (p=0.010). Hospital stay longer than 2 days decreased in group I-3 compared to group I-2 (p=0.010). Although we observed decreased uterine volume (154.2 cm3) in group I-2 compared to group I-1 (217.8 cm3) (p=0.030), logistic regression did not find any association between uterine volume and surgical time (p=0.103).
Conclusion
The total operative time for laparoscopic hysterectomy was significantly shorter in the group of patients (I-3) operated after the systematic laparoscopic skills and suture training was introduced in our hospital.
-
Original Article
Laparoscopic Approach in Surgical Staging of Endometrial Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):306-311
06-27-2019
Summary
Original ArticleLaparoscopic Approach in Surgical Staging of Endometrial Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):306-311
06-27-2019Views153See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare laparoscopy with laparotomy for surgical staging of endometrial cancer.
Methods
A cohort of women with preoperative diagnosis of endometrial cancer who underwent surgical staging was retrospectively evaluated. The main study end points were: morbidity and mortality, hospital length of stay, perioperative adverse events and recurrence rate. Data analysis was performed with the software SPSS v25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA), categorical variables using a Chi-square and Fisher test, and continuous variables using the Student t-test.
Results
Atotal of 162 patientswere analyzed. 138 patientsmet the inclusion criteria, 41of whom underwent staging by laparoscopy and 97 by laparotomy. Conversions from laparoscopy to laparotomy happened in 2 patients (4.9%) and were secondary to technical difficulties and poor exposure. Laparoscopy had fewer postoperative adverse events when compared with laparotomy (7.3% vs 23.7%, respectively; p = 0.005), but similar rates of intraoperative complications, despite having a significantly longer operative time (median, 175 vs 130 minutes, respectively; p < 0.001). Hospital stay was significantly lower in laparoscopy versus laparotomy patients (median, 3 vs 7 days, respectively; p < 0.001). No difference in recurrence or mortality rates were observed.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgical staging for endometrial cancer is feasible and safe. Patients have lower postoperative complication rates and shorter hospital stays when compared with the approach by laparotomy.


