Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):829-833
01-11-2020
Thyroid diseases are relatively common in women in the reproductive period. It is currently understood that clinically-evident thyroid disorders may impair ovulation and, consequently, fertility. However, to date it has not been proven that high serum levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone and/or positivity for antithyroid antibodies are associated to a reduction in fertility, mainly in the absence of altered thyroxine levels. The present comprehensive review aims to present current data on the association between subclinical hypothyroidism and/or thyroid autoimmunity and reproductive outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):752-758
12-21-2020
To identify whether the effects of thyroid disease during pregnancy and lactation affect the nutritional composition of human milk.
Systematic review of the scientific literature using the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online/MedLine databases to evaluate the association of thyroid diseases during pregnancy and lactation with the nutritional composition of human milk. There was no delimitation by period or by language, and the searches were completed in March 2019. The following descriptors were applied: human milk AND thyroid AND composition, using the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) protocol for data search, selection, and extraction. The flowchart proposed for bibliographic search resulted in 12 articles and, of these, four were selected.
The articles elected for this review were published between 1976 and 2018. Two studies found significant differences in the nutritional composition of mothers' milk with hypothyroidism or overweight compared with the milk of those without hypothyroidism. Studies have shown that the presence of the disease led to changes in the nutritional composition of human milk, especially a higher concentration of human milk fat.
It is extremely important that these women have continuous nutritional follow-up to minimize the impact of these morbidities on the nutritional composition of human milk.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):224-228
05-01-2017
This study analyzed the effectiveness of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as a predictor of insulin resistance (IR) and its association with the clinical and metabolic parameters of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) without overt hypothyroidism.
A cross-sectional study was performed. Women with PCOS and without overt hypothyroidism (n = 168) were included.
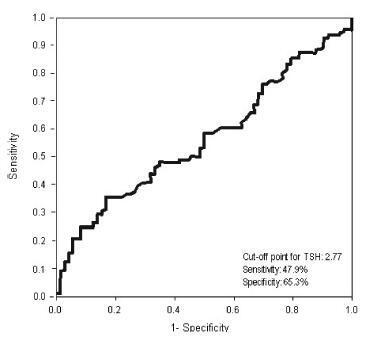
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to determine the cut-off point for TSH that would maximize sensitivity and specificity for a diagnosis of IR using homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)≥ 2.71. Clinical and metabolic parameters were compared as a function of the TSH cut-off limit and the presence of IR.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone ≥ 2.77 mIU/L was associated with a diagnosis of IR, with sensitivity of 47.9% and specificity of 65.3%. There were no differences in clinical, hormonal or metabolic parameters between TSH < 2.77 and TSH of 2.77 - 10 mIU/L.
In women with PCOS without overt hypothyroidism, TSH ≥2.77 mIU/L is associated with IR; however, with poor sensibility, showing TSH to be a poor predictor of IR in this population. No clinical or metabolic alterations were found that would justify a change in clinical management. Thus, the IR should be investigated in all women with PCOS irrespective of TSH level.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(7):321-326
12-03-2010
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000700003
PURPOSE: to study the association between hypothyroidism and depression and anxiety symptoms. METHODS: a case-control study was carried out from July 2006 to March 2008 on 100 patients (50 patients with primary hypothyroidism and 50 euthyroid controls) aged 18 to 65 years. Age, race/skin color, marital status, education level, alcohol use, working status, body mass index and menopausal status were evaluated. TSH levels were determined and the Beck Depression and Beck Anxiety Scales were applied to all cases and controls. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS software version 14.0. The level of significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: there was no demographic or epidemiologic difference between groups. The concomitant presence of anxiety and depression was five times greater among cases than among controls (20.0 versus 4.0%, p=0.01). Anxiety symptoms were approximately three times more frequent among cases (40.0%) than among controls (14.0%) (p=0.003), while the prevalence of depressive symptoms was 75% higher among cases (28.0%) than among controls (16.0%), but this did not reach statistical significance (p=0.15). We found no association between TSH levels and the prevalence of anxiety or depression symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: this case-control study showed a greater probability for hypothyroid patients to develop anxiety and depression symptoms when compared to euthyroid controls. Due to the high prevalence of hypothyroidism and depression observed in clinical practice, depressive symptoms must be considered in patients with thyroid dysfunction and depressed patients should be tested for TSH.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):96-102
05-02-2007
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the classification and the etiology of girls attended in a Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology Clinic. METHODS: The hospital charts of 58 female patients attended from 2000 to 2005 with diagnosis of probable precocious puberty were reviewed and relevant data analyzed. Inclusion criteria were breast and/or pubic hair growth before eight years old. The girls were classified according to the clinic aspects and the supplementary exams they had been submitted to, into one of the categories: central precocious puberty (CPP), precocious pseudopuberty, premature thelarche and premature pubarche. RESULTS: from the 58 reviewed cases, 28 girls were diagnosed as CPP, one as precocious pseudopuberty, ten as premature thelarche and 19 as premature pubarche. All the cases of CPP had an idiopathic etiology, except for one girl whose activation of the ypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis was secondary to congenital adrenal hyperplasia. There was one case of precocious pseudopuberty due to McCune-Albright syndrome. All the cases of premature thelarche had an idiopathic etiology, except for one girl who had primary hypothyroidism. All the cases of premature pubarche had an idiopathic etiology. CONCLUSIONS: among the cases diagnosed as precocious puberty, CPP was the leading diagnosis and most cases had an idiopathic etiology. Organic causes leading to precocious puberty were infrequent.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):467-472
11-28-2005
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism and its effects on lipidic profile and bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal women. METHODS: a cross-sectional study with survey of data from medical records of patients attended at a climacteric outpatient clinic. Inclusion criteria: postmenopausal women with measured thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxin (T4-L). Exclusion criteria: hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer. Values of TSH >5.0 mIU/ml and normal T4-L were considered to be subclinical hypothyroidism. The 329 selected women (55.2±6.4 years) were divided into three groups: normal thyroid function (control) (n=208), subclinical hypothyroidism (n=53) and clinical hypothyroidism under treatment (n=59). Clinical data, hormonal therapy use, body mass index (BMI=kg/m²), lipid profile (total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, triglycerides) and BMD of lumbar column and femur were obtained. RESULTS: subclinical hypothyroidism was diagnosed in 16.1% of the cases. The groups were homogeneous regarding clinical features, BMI or lipidic profile. BMD in lumbar column and femur was lower in subclinical and clinical hypothyroidism than in euthyroidism (p<0.001). There was a negative correlation between values of TSH and BMD of lumbar column and femur (p<0.001). There was no correlation between TSH values and age, menopause time, BMI, and lipid profile. The total of hormonal therapy users was 65.1%, mean duration of 3.43±2.42 years, not differing between the groups. CONCLUSION: subclinical hypothyroidism with prevalence of 16.1% in postmenopausal women was associated with lower BMD, with no effects on lipid profile.