Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):184-190
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400006
PURPOSE: to analyze the clinical and epidemiological profile, the outcome of pregnancy and the vertical transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected pregnant women receiving prenatal care at the University Hospital of Santa Maria (HUSM). METHODS: A prospective study was conducted on 139 HIV-infected pregnant women attended at the High-Risk Prenatal Care Outpatient Clinic of HUSM, during the period from August 2002 to August 2007, with at least two prenatal visits in this service. Data were collected by an interview and by filling out a research protocol during a prenatal visit. The protocol was attached to the medical records of the patient and kept until the outcome of gestation. Descriptive analysis of quantitative variables was performed using the SPSS software, version 15.0. RESULTS: The mean age of the 139 pregnant women studied was 25.6 years (±5.8), 79 (56.8%) were white, 81 (58.5%) were married or lived in a stable union, and 90 (65.0%) had less than eight years of schooling. Fifty-one percent of the pregnant women already had two or more children, with a number of children higher than the mean for the state. The infection was diagnosed during the present or a previous pregnancy in more than 70.0% cases. Sexual exposure occurred in 97.0%, and in 59.6% of cases the partner was known to be infected. During the study period, among the cases properly monitored, only one newborn (0.7%) was infected with HIV. CONCLUSIONS: Young women in a socioeconomic situation of vulnerability, with low schooling and multiparous represent the majority of HIV-positive pregnant women attended at the service. Evaluations performed during the prenatal period were relevant for the diagnosis of infection in most cases. An early diagnosis associated with proper clinical, obstetrical and psychological monitoring and with nursing care is important to provide appropriate treatment compliance and a reduction of the rates of vertical transmission.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):176-183
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400005
PURPOSE: to estimate the prevalence infection of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), human T-cell lymphotropic vírus (HTLV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), Chlamydia trachomatis (C. trachomatis) and syphilis in pregnant women, as well as risk factors associated with these infections, in Fundação de Medicina Tropical do Amazonas (FMTAM). METHODS: a cross-sectional study was carried including 674 pregnant women consecutively attended of the spontaneous demand of FMTAM between March and September 2008. Demographic, epidemiologic, socioeconomic, clinical and obstetric information have been collected through specific questionnaires. Patients had blood sample collected by peripheral venous for accomplishment of serological tests of HIV, HTLV, HBV and syphilis. Cervical secretion sample has been collected for C. trachomatis antigens detection test. The Odds Ratio has been used to evaluate risk factors associated to infections. Statistical analysis has been done with the t-Student, χ2 and Fisher's exact tests. RESULTS: the average age was 23.9 years old (SD 6.3). The observed prevalence was 0.6% to infection by HIV; 0.7% by HBsAg; 1.0% of syphilis and 2.7% by C. trachomatis. All the samples went negatives to HTLV. There were no variables associated with infection by HIV, HBV and syphilis. Significative statistically association was observed between pregnant woman with age under 20 years and of first pregnancy with C. trachomatis infection. CONCLUSIONS: the study evidenced that the prevalence infection by HIV in pregnant women assisted in FMTAM is similar to the values described in the Brazilian literature, while the prevalence by HTLV, HBV, syphilis and C. trachomatis in the studied population are below found by other authors. The main risk factor for the infection by C. trachomatis was being under 20 years old.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):171-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400003
PURPOSE: the propose of this study was to analyze the clinical and laboratorial parameters of patients submitted to human assisted reproduction techniques with association of sperm processing techniques, in order to remove virus particles from semen samples of couples in which men was infected by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). METHODS: it was assessed 11 intracytoplasmatic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles from couples whose men were HIV seropositive (HIV Group), and 35 cycles in which semen donors' samples were used in ICSI procedures (Control Group). Semen samples from Control Group were submitted to routine semen analysis, sperm wash and cryopreservation. The man from HIV Group received previous antibiotic therapy; the semen samples were analyzed routinely and prepared by sperm wash and density gradient method before cryopreservation. Those samples were evaluated to viral load and ICSI was performed when no HIV was detected. RESULTS: regards to semen analysis the groups were similar to sperm concentration and progressive motility. Nevertheless, the percentage of sperm with normal morphology were higher on Control Group (14.3%) than HIV (5.8%; p=0.002). On embryo parameters assessment, the normal fertilization (CT: 74.7% and HIV: 71.7; p=0.838, respectively) and good embryos rate (CT: 42.4% and HIV: 65.1%; p=0.312, respectively) were comparable. On the other hand, the Control Group presented better clinic results than HIV Group (ongoing pregnancy rate: 52.9% versus 12.5%; p=0.054, and implantation rate: 42.6 versus 10.4%; p=0.059, respectively), however the differences were not statistically significant. After delivery, no seroconversion was observed on mother and child. CONCLUSIONS: the association of sperm processing techniques in order to remove HIV from semen samples does not influence in laboratorial parameters of assisted reproduction techniques cycles. On the other hand, it has been demonstrated excellent results getting safety gametes to serodiscordant couples.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):121-126
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000002
PURPOSE: to compare the frequency of vulvovaginitis in women infected with human imunnodeficiency virus (HIV) with the frequency in non-infected women. METHODS: a transversal study including 64 HIV infected women and 76 non-infected ones. The frequencies of bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and trichomoniasis, diagnosed by Amsel's criteria, culture and fresh exam, respectively, were calculated. Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test and multiple regressions to verify the independence of associations were used to analyze the data. RESULTS: the vaginal infection was more prevalent in HIV infected patients, as compared to the control group (59.4 versus 28.9%, p<0,001; Odds Ratio=2.7, IC95%=1.33-5.83, p=0.007). Bacterial vaginosis occurred in 26.6% of the positive-HIV women; vaginal candidiasis, in 29.7% and trichomoniasis, in 12.5% of them. All the infections were significantly more frequent in the group of HIV infected women (p=0.04, 0.02 e 0.04, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: vulvovaginitis is more frequent in HIV infected women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):539-544
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900007
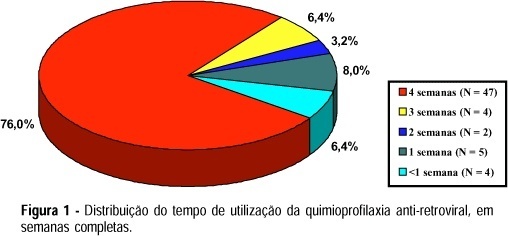
Purpose: some medical institutions have been prophylactically ministrating anti-HIV therapy in cases of sexual violence, although there are no appropriate basic facts to establish its efficacy. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the acceptance, tolerance and adhesion of these women under a chemoprophylaxis plan for HIV. Methods: sixty-two women victims of rape and/or anal intercourse with unknown aggressors have been evaluated. Prophylaxis has been started within the first 48 h after violence and maintained for 4 weeks, with daily administration of zidovudine, 600 mg; indinavir, 2,400 mg and lamivudine, 300 mg. Results: the discontinuance rate was 24.2%, withe 12 cases (80%) due to gastric intolerance. The side effects were present in 43 cases (69.4%), including nausea and vomitting as the most frequent. Complex dosage and time of administration were factors possibly related to the inadequate use of the drugs in 10.6% of the cases. Conclusion: the authors concluded that the chemoprophylaxis discontinuance rate was similar to that observed in other indications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):407-414
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of vulval squamous intraepithelial lesions and associated factors in HIV-infected patients attended at the public health services of Rio de Janeiro city. METHOD: a total of 374 HIV-infected patients were attended at public services in Rio de Janeiro city and submitted to gynecological examination, Pap smear and colposcopic examination of the cervix and vulva. The association of vulval intraepithelial lesion was analyzed according to the results of clinical (age and cervical lesions), laboratorial (CD4 count) and behavioral (number of partners and smoking habit) variables. The study (independent) variables were the epidemiological data, the immunologic status and the results of gynecological propaedeutic. Thus, age, the smoking habit, number of sexual partners, count of T CD4 lymphocites, and cervical intraepithelial lesion were selected. In the beginning, a bivariate analysis was performed, aiming at assessing the association between the presence of vulval intraepithelial lesion (ultimate variable) and the independent variables (age, smoking habits, number of sexual partners, cytology, colposcopy and CD4 count). Thereafter, the results with statistical significance (p<0.05) were submitted to a multiple logistic regression, and the probability ratio with the respective 95% confidence interval was established. RESULTS: the prevalence of vulval intraepithelial lesions was 40%. In the multivariate analysis CD4 count below 500 cells/mm³ OR=2.69 [IC 95%: 1.61-4.52], abnormal colposcopy OR=1.64 [IC 95%: 1.01-2.67] and age under 26 OR=1.98 [IC 95%: 1.18-3.30] were significant. In the vulval and cervical simultaneous lesion subgroup, age under 26 OR=3.30 [IC 95%: 1.65-6.59] and CD4 count below 500 cells/mm³ OR=4.15 [IC 95%: 1.92-8.96], were significant on analysis. CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of vulval squamous intraepithelial lesions in HIV-infected patients is high. Immunodeficiency, presence of cervical intraepithelial lesions and age under 26 were associated with the presence of vulval intraepithelial lesions.