Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):972-985
01-23-2022
Different drugs are used to treat mastalgia, such as danazol and bromocriptine, and both are associated with side effects, due to which most of women and healthcare providers are interested in herbal medicines. Therefore we aim to study the effectiveness of phytoestrogens on the severity of cyclic mastalgia.
To carry out the present study, English electronic resources such as the Cochrane Library, ISI Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed were used systematically and with no time limitation up to February 10, 2020.
In total, 20 studies were included in the present meta-analysis. The results of the meta-analysis showed that herbal medicines versus the control group (standard mean difference [SMD] = - 0.585; 95% confidence interval [CI]: - 0.728–- 0.44; heterogeneity; p = 0.02; I2 = 42%), herbal medicines versus the B group (SMD = - 0.59; 95%CI: - 0.75–- 0.44; heterogeneity; p = 0.03; I2 = 42%), and its subgroups, such as phytoestrogen (SMD = - 0.691; 95%CI: - 0.82–- 0.55; heterogeneity; p = 0.669; I2 = 0%), Vitex-agnus-castus (SMD = - 0.642; 95%CI: - 0.84–- 0.44; p < 0.001; p = 203; I2 = 32%), flaxseed (SMD = - 0.63; 95%CI: - 0.901–- 0.367; p = 0.871; I2 = 0%), and evening primrose (SMD= - 0.485; 95%CI:- 0.84–- 0.12; p = 0.008; heterogeneity; p = 0.06; I2 = 56%] may have effective and helpful effects on improving cyclic breast mastalgia. Also, chamomile, isoflavone, cinnamon, and nigella sativa significantly reduced mastalgia symptoms.
Herbal medicines and their subgroups may have effective and helpful effects on improving cyclic breast mastalgia. The findings of our meta-analysis must be done cautiously because low methodological quality in some evaluated studies of this systematic review.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):968-979
01-24-2021
The aim of the present systematic review meta-analysis is to assess the effect of olfactory stimulation on reducing dysmenorrhea.
Systematic search was conducted in several databases, such as PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Scopus, to identify relevant research up to October 26, 2019. The identified studies were evaluated based on a modified Jadad scale. The intervention involves aromatherapy alone or in combination with essential oils. There was no restriction for the control group such as a placebo group or other common treatments. The Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 2 (Bio stat, Englewood, NJ, USA) was used for meta-analysis. Cochran’s Q and I2 tests were utilized.
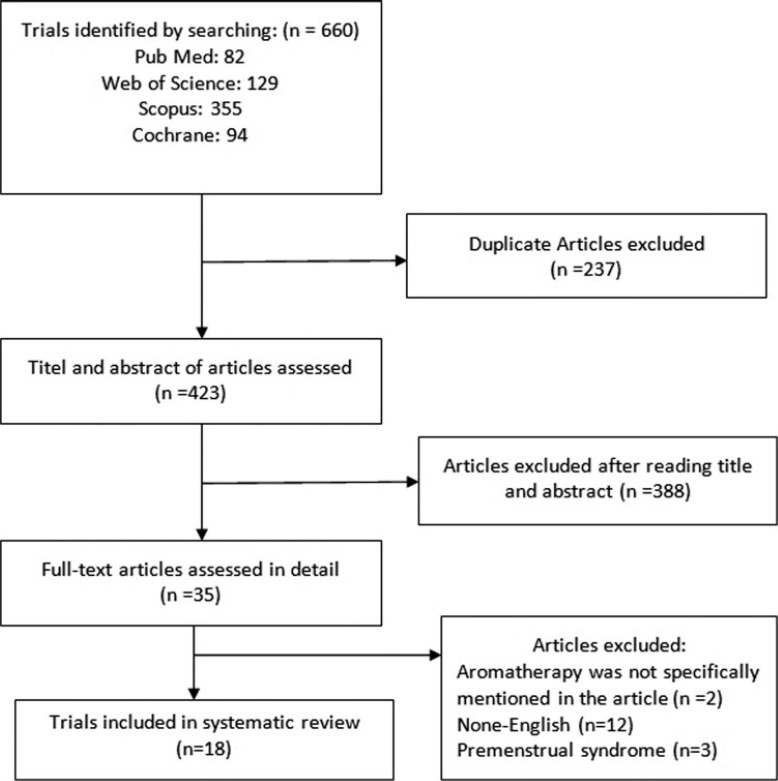
The findings of our meta-analysis, which contained 13 trials (15 data), showed that dysmenorrhea decreased significantly in the group receiving aromatherapy with herbal compared with the control group (standardized mean difference [SMD] =-0.795; 95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.922 to- 0.667; 17 trials O < 0.001); heterogeneity; I2 = 19.47%; p = 0.236). In addition, four studies with insufficient data were not included in our meta-analysis. The results of all studies suggested that aromatherapy with herbal medicine group compared with control group is effective.
Aromatherapy with herbal medicine decreased dysmenorrhea. This treatment was particularly effective when aroma oil was combined with massage or when a mixture of aroma oil was used for the treatment of dysmenorrhea.