-
Case Report08-01-2018
Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology to Identify a Rare Mimicker of Breast Cancer: Plasma Cell Mastitis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):491-493
Abstract
Case ReportFine-needle Aspiration Cytology to Identify a Rare Mimicker of Breast Cancer: Plasma Cell Mastitis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):491-493
Views191See moreAbstract
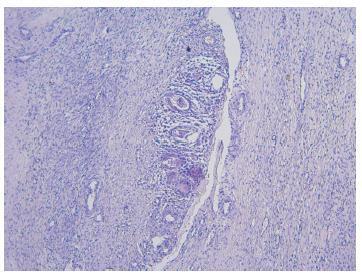
There are rare benign diseases that can mimic malignant breast neoplasms in the clinical exam and in mammography. We evaluated the contribution of an accessible procedure to most clinicians, the fine-needle aspiration cytology, to identify a rare mimicker of malignant breast neoplasms. A type 2 diabetic 85-year-old female presented with a 6-month history of a left breast lump. The physical exam and mammography were compatible with breast cancer. Nevertheless, after fine-needle aspiration cytology, the diagnosis was plasma cellmastitis. Once this rare diagnosis was established, the tumor was extirpated, and the final histologic diagnosis corroborated chronic plasma cellmastitis. The patient’s postoperative evolution was uneventful, and no other treatment was needed. Fine-needle aspiration cytology could be a valuable tool to identify rare mimickers of malignant breast neoplasms.
-
Case Report05-01-2017
Ovarian Manson’s Schistosomiasis: Rare Diagnosis or Underestimated Prevalence?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):249-254
Abstract
Case ReportOvarian Manson’s Schistosomiasis: Rare Diagnosis or Underestimated Prevalence?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):249-254
Views139See moreAbstract
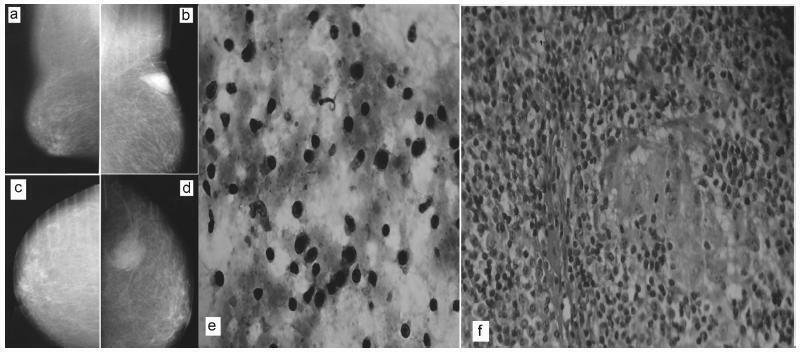
The occurrence of Manson’s schistosomiasis in organs of the female reproductive tract is an uncommon event, given that the etiological agent for this disease is a blood parasite that inhabits the mesenteric veins. In this case report, a 45-year-old female patient reported that her first symptoms had been strong pain in the left iliac region around two years earlier. An endovaginal pelvic ultrasonography showed that the left ovary was enlarged, and the report suggested that this finding might be correlated with clinical data and tumor markers. After being examined at several healthcare services, the patient was referred to an oncology service due to suspected neoplasia, where she underwent a left ovariectomy. The result from the histopathological examination showed the presence of granulomatous inflammatory processes surrounding both viable and calcified eggs of Schistosoma mansoni. There was no evidence of any neoplastic tissue. The patient was medicated and followed-up as an outpatient.