-
Original Article
Association between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Endometriosis in a Brazilian Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):146-151
04-22-2020
Summary
Original ArticleAssociation between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Endometriosis in a Brazilian Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):146-151
04-22-2020Views255See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate the association between genetic polymorphisms in candidate genes or candidate regions and the development of endometriosis in Brazilian women.
Methods
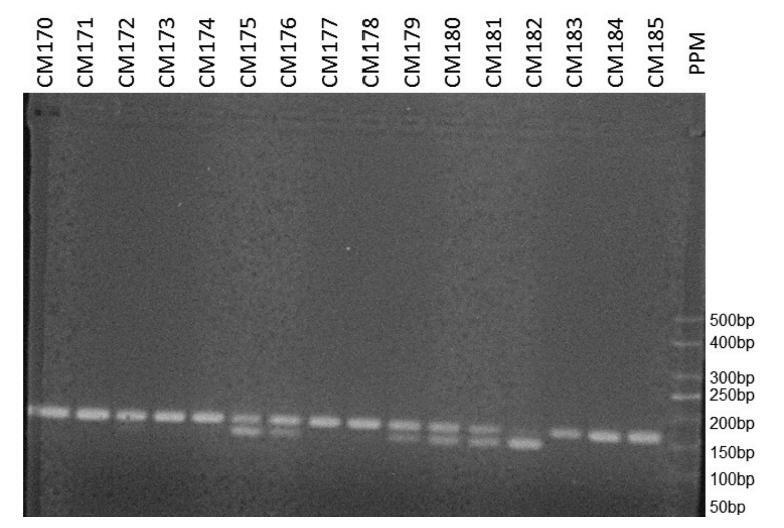
A total of 30 women between 25 and 64 years old with a diagnosis of endometriosis participated in the present study, as well as 30 matched control women from the same age group, asymptomatic and without family history of the disease. The patients genotypic and allelic frequencies of polymorphisms in the GREB1 gene (rs13394619) and in the intergenic region at position 7p15.2 (rs12700667) were analyzed and compared.
Results
There was no significant difference in the frequency of genotypes for the A > G polymorphism (rs13394619) in the GREB1 gene between the two groups. However, the distribution frequencies of the genotypes for the A > G polymorphism (rs12700667) in an intergenic region on chromosome 7 were different for control patients and for patients with endometriosis, with higher frequency of the AG genotype compared to the GG between patients with the disease (odds ratio [OR] = 3.49; confidence interval [CI] = 1.47–8.26).
Conclusion
The present study suggests that the polymorphism in the intergenic region of chromosome 7 is associated with the risk of developing endometriosis in a population of Brazilian women from Juiz de Fora.
-
Original Articles
The Influence of CYP3A4 Polymorphism in Sex Steroids as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):699-704
11-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticlesThe Influence of CYP3A4 Polymorphism in Sex Steroids as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):699-704
11-01-2018Views190See moreAbstract
Objective
Epidemiological studies have shown evidence of the effect of sex hormones in the pathogenesis of breast cancer, and have suggested a relationship of the disease with variations in genes involved in estrogen synthesis and/or metabolism. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the association between the CYP3A4*1B gene polymorphism (rs2740574) and the risk of developing breast cancer.
Methods
In the present case-control study, the frequency of the CYP3A4*1B gene polymorphism was determined in 148 women with breast cancer and in 245 women without the disease. The DNA of the participants was extracted from plasma samples, and the gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction. The presence of the polymorphism was determined using restriction enzymes.
Results
After adjusting for confounding variables, we have found that the polymorphism was not associated with the occurrence of breast cancer (odds ratio = 1.151; 95% confidence interval: 0.714–1.856; p= 0.564). We have also found no association with the presence of hormone receptors, with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression, or with the rate of tumor cell proliferation.
Conclusion
We have not observed a relationship between the CYP3A4*1B gene polymorphism and the occurrence of breast cancer.