Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):258-263
To identify the age when individuals first perceive gender incongruence (GI) and to compare sociodemographic data of female-to-male (FtM) and male-tofemale (MtF) transgender individuals assisted at an outpatient service.
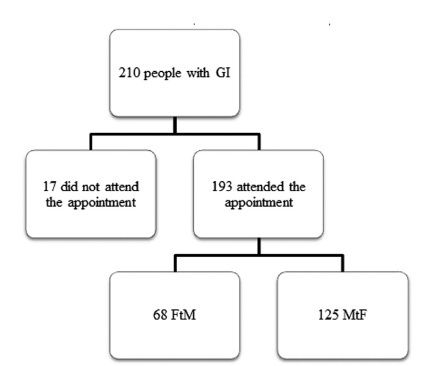
The present cross-sectional study was conducted through a review of the medical records of individuals diagnosed with GI at a single specialized outpatient service in the city of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil.
A total of 193 medical records from 2010 to 2018 were evaluated, and 109 (56.5%) patients had GI since childhood. The FtM transgender individuals perceived GI in childhood more often than the MtF transgender individuals (odds ratio [OR]: 2.06, 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.11-3.81) Unattended hormone use was highest among the MtF group (69.6% versus 32.3%; OR: 4.78, 95%CI: 2.53-9.03). All of the individuals who were engaged in prostitution or were diagnosed with a sexuallytransmitted infection, including HIV, were in the MtF group.
Despite the more prevalent perception of GI in childhood among the FtM group, social issues were more prevalent among the MtF group, which may be the result of social marginalization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):275-280
Gender incongruence is defined as a condition in which an individual self-identifies and desires to have physical characteristics and social roles that connote the opposite biological sex. Gender dysphoria is when an individual displays the anxiety and/or depression disorders that result from the incongruity between the gender identity and the biological sex. The gender affirmation process must be performed by a multidisciplinary team. The main goal of the hormone treatment is to start the development of male physical characteristics by means of testosterone administration that may be offered to transgender men who are 18 years old or over. The use of testosterone is usually well tolerated and improves the quality of life. However, there is still lack of evidence regarding the effects and risks of the long-term use of this hormone. Many different pharmacological formulations have been used in the transsexualization process. The most commonly used formulation is the intramuscular testosterone esters in a short-term release injection, followed by testosterone cypionate or testosterone enanthate. In the majority of testosterone therapy protocols, the male physical characteristics can be seen in almost all users after 6 months of therapy, and themaximum virilization effects are usually achieved after 3 to 5 years of regular use of the hormone. To minimize risks, plasmatic testosterone levels should be kept within male physiological ranges (300 to 1,000 ng/dl) during hormonal treatment. It is recommended that transgender men under androgen therapy be monitored every 3 months during the 1st year of treatment and then, every 6 to 12 months.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):545-551
To assess the clinical characteristics of subjects with gender dysphoria (GD).
A cross-sectional study of adults with GD. Symptoms of anxiety and depression were measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Sociodemographic data, clinical data and life habits were recorded.
Total of 44 subjects participated in the study: 36 (82%) trans women and 8 (18%) trans men. Forty-three (98%) of the GD patients had anxiety (36 [100%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men), and 36 (82%) had depression (29 [80.5%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men). Suicide had been attempted by 32 (73%) subjects. The rates of depression were lower among the subjects living with partners, parents, or other people than among those living alone (p = 0.03), and it was also lower among the subjects who were married compared to those who were dating or single (p = 0.03).
Improving the relationship status may reduce the prevalence of depressive symptoms in GD patients. There was a high rate of attempted suicide in this sample.