Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):242-252
Evaluate the effect of combined training on body image (BI), body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer. As also the relationship of BI with body composition and functional capacity.
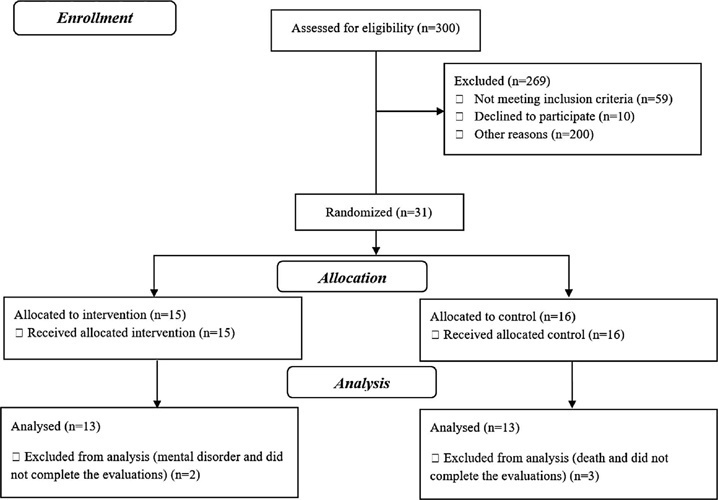
This was a Controlled Clinical Trial study, this study including 26 patients with breast cancer (30 to 59 years). The training group (n = 13) underwent 12 weeks of training, including three 60-min sessions of aerobic exercise and resistance training, and two sessions of flexibility training per week; each flexibility exercise lasted 20s. The Control Group (n = 13) received only the standard hospital treatment. Participants were evaluated at baseline and after 12 weeks. BI (primary outcomes) was assessed using the Body Image After Breast Cancer Questionnaire; Body composition was estimated with the indicators: Body mass index; Weight, Waist hip Ratio; Waist height ratio; Conicity index; Reciprocal ponderal index; Percentage of fat; Circumference of the abdomen and waist; Functional capacity by cardiorespiratory fitness (cycle ergometer) and strength (manual dynamometer). The statistic was performed in the Biostatistics and Stata 14.0 (α = 5%).
The patients in the training group showed a reduction in the limitation dimension (p = 0.036) on BI, However, an increase in waist circumference was observed in both groups. In addition an increase in VO2max (p < 0.001) and strength in the right (p = 0.005) and left arms (p = 0.033).
Combined training demonstrates to be an effective and non-pharmacological strategy to patients with breast cancer, with improvement on BI and functional capacity, changing related variables negatively when there is no physical training.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):531-538
To determine the effect of treadmill walking on maternal heart rate (MHR) and cardiotocographic parameters (basal fetal heart rate [FHR], active fetal movements [AFM], number of accelerations and decelerations, and short-term variation [STV] and long-term variation [LTV] of fetal heart rate) in pregnant women at 36 weeks.
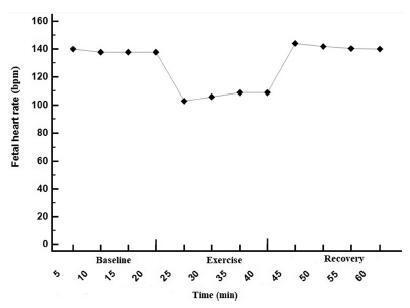
A nonrandomized, open clinical trial involving 88 healthy pregnant women submitted to moderate intensity walking and computed cardiotocography in 3 20- minute periods (resting, treadmill walking, and postexercise recovery).
The mean FHR decreased during walking (resting: 137 bpm; treadmill: 98 bpm; recovery: 140 bpm; p<0.001), with bradycardia occurring in 56% of the fetuses in the first 10minutes of exercise, and in 47% after 20minutes. Bradycardia was not detected in the other phases. The mean STV and HV were 7.9, 17.0, and 8.0 milliseconds (p<0.001) and 7.6, 10.8 and 7.6 bpm (p=0.002) in the resting, walking and recovery phases, respectively. Themean number of fetalmovements in 1 hour was 29.9, 22.2 and 45.5, respectively, in the 3 periods (p<0.001). In overweight/obese women, the mean FHR was lower (p=0.02). Following the logistic regression analysis, two variables remained significantly associated with bradycardia: maternal fitness in the 28th week of pregnancy (protective effect) and maternal weight (increased risk).
In healthy fetuses, physical exercise proved to be safe, since, although FHR and AFM decreased during treadmill walking, an increase in SVT and LTV was observed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):68-75
To access the benefits or harms of an exercise program, based on the current American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines, on the mode of delivery, duration and onset of labor.
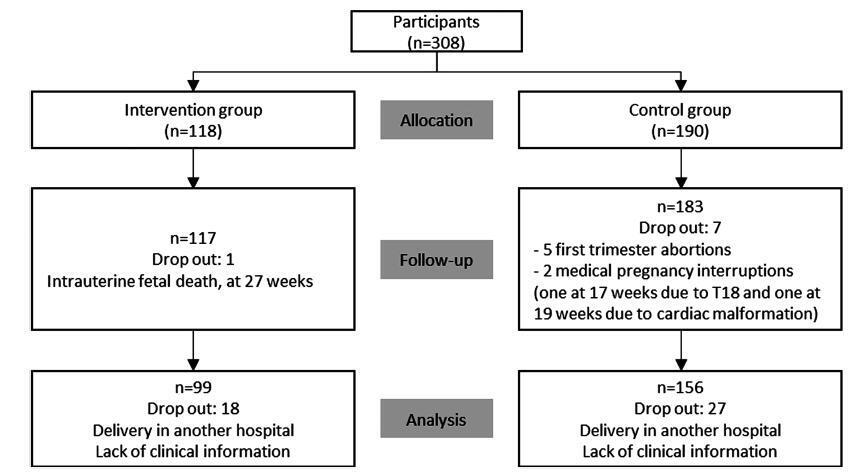
A study performed at the Hospital Senhora da Oliveira between October 2015 and February 2017. This was a quasi-experimental study involving 255 women divided into two groups: an intervention group engaged in a controlled and supervised exercise program during pregnancy (n = 99), and a control group that did not participate in the exercise program (n = 156). Data were collected in two stages: during the 1st trimester biochemical screening (before the beginning of the program), through a written questionnaire, and after delivery, from the medical files of the patients. The significance level in the present study was 5% (p = 0.05).
The control group had higher odds of induced labor (odds ratio [OR] 2.71; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.42-5.17; p = 0.003), when compared with women who underwent the intervention. No differences were found between the groups in instrumental vaginal deliveries, cesarean rate, time until the beginning of the active phase, duration of the active phase, and duration of the second stage of labor.
The implementation of a controlled and supervised exercise program in pregnancy was associated with significantly lower odds of induced deliveries.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):278-282
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005326
to analize the level of functional fitness of a group of postmenopausal women in
the city of Presidente Prudente using the set of functional fitness tests of the
American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance and to
check whether there are differences between groups of women in the fifth and sixth
decade of life.
This was a cross-sectional study conducted on 175 postmenopausal women (follicle
stimulating hormone level>26.72 mIU/L) in the city of Presidente Prudente in
2013. The inclusion criteria were not being part of any type of systematic motor
intervention for at least six months before the collection of research data;
absence of motor or cognitive impairment that would prevent the evaluation
protocols, and absence of chronic or degenerative disease, musculoskeletal injury
or comorbidity that could prevent or limit the evaluations. The women were
evaluated by the same trained examiners. The 50 to 59 year group showed a mean age
of 55.3±4.5 years, mean FSH values of 53.5±21.1 mIU/mL, mean coordination of
11.4±2.2 seconds, mean strength of 20.1±3.9 repetitions, mean flexibility of
51.7±11.8 cm, mean 23.2±2.8 seconds agility and mean aerobic resistance of
500±43/2 . The 60 to 69 year group had a mean age of 65.1±4.1 years with FSH
54.9±15.9, 11.6±2.6 seconds coordination, strength 20.3±4.7 repetitions, 54.6±11.2
cm flexibility, agility 24.7±4.3 seconds, and aerobic resistance of 508±51
seconds.
It was possible to analyze the functional fitness of postmenopausal women through
the set of the American Alliance testing for Health, Physical Education,
Recreation and Dance with no significant differences between groups for the
variables strength, flexibility, aerobic capacity and coordination, and with only
the speed variable showing significant differences. We recommend further studies
seeking to formulate normative values for the population in question.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):82-86
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005040
To analyze the risk factors for urinary incontinence (UI) in older women practicing physical exercises (PE).
A total of 152 older women with a mean age of 68.6±5.8 years who regularly practiced PE participated in the study. The presence of UI and gynecological, obstetric, clinical, behavioral, hereditary and anthropometric risk factors was determined identified. It was also applied the Domain 4 of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) to determine the level of physical activity and body mass index and waist circumference were measured. Data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics, with the level of significance set at 5%.
The prevalence of UI in the sample was 32.2%. Among the factors evaluated, only the use of diuretics (OR=2.7; 95%CI 1.0-7.0) and a positive family history of urinary incontinence (OR=2.3; 95%CI 1.1-4.8) were associated with UI symptoms.
The use of diuretics is considered to be a modifiable risk factor for UI, whereas a family history is not considered to be a modifiable risk factor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(9):404-409
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005073
To evaluate the effect of 8 weeks of functional training on body composition in postmenopausal women.
The study was conducted on 38 postmenopausal women, divided into two groups: Training Group (TG) and Control Group (CG). TG women (n=21) performed a program of physical exercise for a period of 8 weeks, 3 times a week on nonconsecutive days, with 90 minutes per session. For the same period, CG women (n=17) did not perform any systematic physical activity. All participants were assessed at baseline and after 8 weeks. The evaluations were performed by the same trained raters. Analysis of body composition was performed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), which allows estimation of body composition in the whole body and by segment. TG participants performed a functional exercise program 3 days a week (non-consecutive), with 11 stations consisting of exercises developed in circuit format sessions. The objectives of the exercises were the development of strength, agility, coordination and proprioception, followed by aerobic exercise (walking). After normality of the data was determined by the Shapiro-Wilk test (p<0.05), we applied the Student t-test for independent samples to check for possible differences in anthropometric variables and body composition between groups at both times of intervention (pre and post-test). All analyses were performed using the SPSS software v. 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) with the level of significance set at 5%.
At baseline, no significant difference was observed between groups regarding anthropometric body variables or age composition, indicating homogeneity of the groups. After 8 weeks of training, significant differences were observed between TG and CG regarding fat - CG=0.2±0.7 and TG=-0.4±0.5, total body fat (kg) - CG=0.2±1.3 and TG=-0.7±0.8, and total weight - CG=0.4±1.4 and TG=-0.6±1.1. Percent body fat was reduced in terms of absolute values, although without significance: CG=0.1±1.5 and TG=-0.8±1.5.
Functional training in circuit format can be used as a strategy to alter body composition in postmenopausal women, particularly in terms of reduction of adipose tissue. This is a model that promotes high adhesion on the part of the participants, suggesting that it is an attractive proposal for the investigated age group.