Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo12
Endometriosis is a complex disease that affects 10-15% of women of reproductive age. Familial studies show that relatives of affected patients have a higher risk of developing the disease, implicating a genetic role for this disorder. Little is known about the impact of germline genomic copy number variant (CNV) polymorphisms on the heredity of the disease. In this study, we describe a rare CNV identified in two sisters with familial endometriosis, which contain genes that may increase the susceptibility and progression of this disease. We investigated the presence of CNVs from the endometrium and blood of the sisters with endometriosis and normal endometrium of five women as controls without the disease using array-CGH through the Agilent 2x400K platform. We excluded common CNVs that were present in the database of genomic variation. We identified, in both sisters, a rare CNV gain affecting 113kb at band 3q12.2 involving two candidate genes: ADGRG7 and TFG. The CNV gain was validated by qPCR. ADGRG7 is located at 3q12.2 and encodes a G protein-coupled receptor influencing the NF-kappaβ pathway. TFG participates in chromosomal translocations associated with hematologic tumor and soft tissue sarcomas, and is also involved in the NF-kappa B pathway. The CNV gain in this family provides a new candidate genetic marker for future familial endometriosis studies. Additional longitudinal studies of affected families must confirm any associations between this rare CNV gain and genes involved in the NF-kappaβ pathway in predisposition to endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo42
To evaluate the effects of surgical treatment of deep endometriosis on the metabolic profile, quality of life and psychological aspects.
Prospective observational study, carried out with women of reproductive age diagnosed with deep endometriosis, treated in a specialized outpatient clinic, from October/2020 to September/2022, at a University Hospital in Fortaleza - Brazil. Standardized questionnaires were applied to collect data on quality of life and mental health, in addition to laboratory tests to evaluate dyslipidemia and dysglycemia, at two moments, preoperatively and six months after surgery. The results were presented using tables, averages and percentages.
Thirty women with an average age of 38.5 years were evaluated. Seven quality of life domains showed improved scores: pain, control and impotence, well-being, social support, self-image, work life and sexual relations after surgery (ES ≥ 0.80). There was an improvement in mental health status with a significant reduction in anxiety and depression postoperatively. With the metabolic profile, all average levels were lower after surgery: total cholesterol 8.2% lower, LDL 12.8% lower, triglycerides 10.9% lower, and fasting blood glucose 7.3% lower (p < 0.001).
Surgical treatment of deep endometriosis improved the quality of life and psychological aspects of patients. The lipid profile of patients after laparoscopy was favorable when compared to the preoperative lipid profile.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo40
To evaluate and compare the sexual function and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) function of women with endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain (CPP) with and without Myofascial Pelvic Pain Syndrome (MPPS).
Cross-sectional study conducted between January 2018 and December 2020. Women with deep endometriosis underwent assessments for trigger points (TP) and PFM function using the PERFECT scale. Electromyographic activity (EMG) and sexual function through Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) were assessed. Statistical analyses included chi-square and Mann-Whitney tests.
There were 46 women. 47% had increased muscle tone and 67% related TP in levator ani muscle (LAM). Weakness in PFM, with P≤2 was noted in 82% and P≥3 in only 17%. Incomplete relaxation of PFM presented in 30%. EMG results were resting 6.0, maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) 61.9 and Endurance 14.2; FSFI mean total score 24.7. We observed an association between increased muscle tone (P<.001), difficulty in relaxation (P=.019), and lower Endurance on EMG (P=.04) in women with TP in LAM. Participants with TP presented lower total FSFI score (P=.02). TP in the right OIM presented increased muscle tone (P=.01). TP in the left OIM presented lower values to function of PFM by PERFECT (P=.005), and in MVIC (P=.03) on EMG.
Trigger points (TP) in pelvic floor muscles (PFM) and obturator internus muscle (OIM) correlates with poorer PFM and sexual function, particularly in left OIM TP cases. Endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain raise muscle tone, weaken muscles, hinder relaxation, elevate resting electrical activity, lower maximum voluntary isometric contraction, and reduce PFM endurance.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo1
To evaluate the association between clinical and imaging with surgical and pathological findings in patients with suspected neuroendocrine tumor of appendix and/or appendix endometriosis.
Retrospective descriptive study conducted at the Teaching and Research Institute of Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, in which medical records and databases of patients with suspected neuroendocrine tumor of appendix and/or endometriosis of appendix were analyzed by imaging.
Twenty-eight patients were included, all of which had some type of appendix alteration on the ultrasound examination. The pathological outcome of the appendix found 25 (89.3%) lesions compatible with endometriosis and three (10.7%) neuroendocrine tumors. The clinical findings of imaging and surgery were compared with the result of pathological anatomy by means of relative frequency.
It was possible to observe a higher prevalence of appendix endometriosis when the patient presented more intense pain symptoms. The image observed on ultrasound obtained a high positive predictive value for appendicular endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):729-744
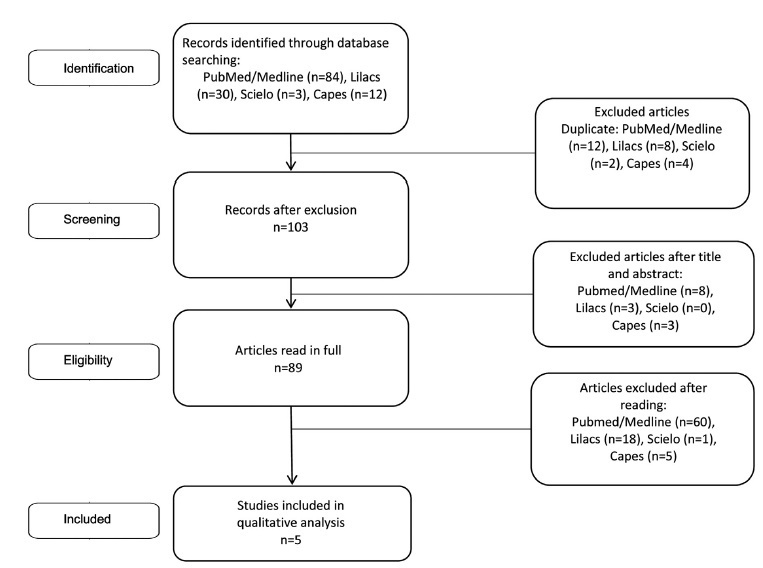
To review the current state of knowledge on the impact of the surgical treatment on the sexual function and dyspareunia of deep endometriosis patients.
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. We conducted systematic searches in the PubMed, EMBASE, LILACS, and Web of Science databases from inception until December 2022. The eligibility criteria were studies including: preoperative and postoperative comparative analyses; patients with a diagnosis of deep endometriosis; and questionnaires to measure sexual quality of life.
Two reviewers screened and reviewed 1,100 full-text articles to analyze sexual function after the surgical treatment for deep endometriosis. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational studies and the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for randomized controlled trials. The present study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration CRD42021289742).
General variables about the studies, the surgical technique, complementary treatments, and questionnaires were inserted in an Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, United States) spreadsheet.
We included 20 studies in which the videolaparoscopy technique was used for the excision of deep infiltrating endometriosis. A meta-analysis could not be performed due to the substantial heterogeneity among the studies. Classes III and IV of the revised American Fertility Society classification were predominant and multiple surgical techniques for the treatment of endometriosis were performed. Standardized and validated questionnaires were applied to evaluate sexual function.
Laparoscopic surgery is a complex procedure that involves multiple organs, and it has been proved to be effective in improving sexual function and dyspareunia in women with deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):393-400
Endometriosis causes a decrease in oocyte quality. However, this mechanism is not fully understood. The present study aimed to analyze the effect of endometriosis on cumulus cell adenosine triphosphate ATP level, the number of mitochondria, and the oocyte maturity level.
A true experimental study with a post-test only control group design on experimental animals. Thirty-two mice were divided into control and endometriosis groups. Cumulus oocyte complex (COC) was obtained from all groups. Adenosine triphosphate level on cumulus cells was examined using the Elisa technique, the number of mitochondria was evaluated with a confocal laser scanning microscope and the oocyte maturity level was evaluated with an inverted microscope.
The ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondria in the endometriosis group increased significantly (p < 0.05; p < 0.05) while the oocyte maturity level was significantly lower (p < 0.05). There was a significant relationship between ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondrial oocyte (p < 0.01). There was no significant relationship between cumulus cell ATP level and the number of mitochondrial oocytes with oocyte maturity level (p > 0.01; p > 0.01). The ROC curve showed that the number of mitochondrial oocytes (AUC = 0.672) tended to be more accurate than cumulus cell ATP level (AUC = 0.656) in determining the oocyte maturity level.
In endometriosis model mice, the ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondrial oocytes increased while the oocyte maturity level decreased. There was a correlation between the increase in ATP level of cumulus cells and an increase in the number of mitochondrial oocytes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1040-1046
The purpose was to assess the rates of postoperative complications and the need of temporary stoma of laparoscopic surgical treatment for bowel endometriosis in a referral center.
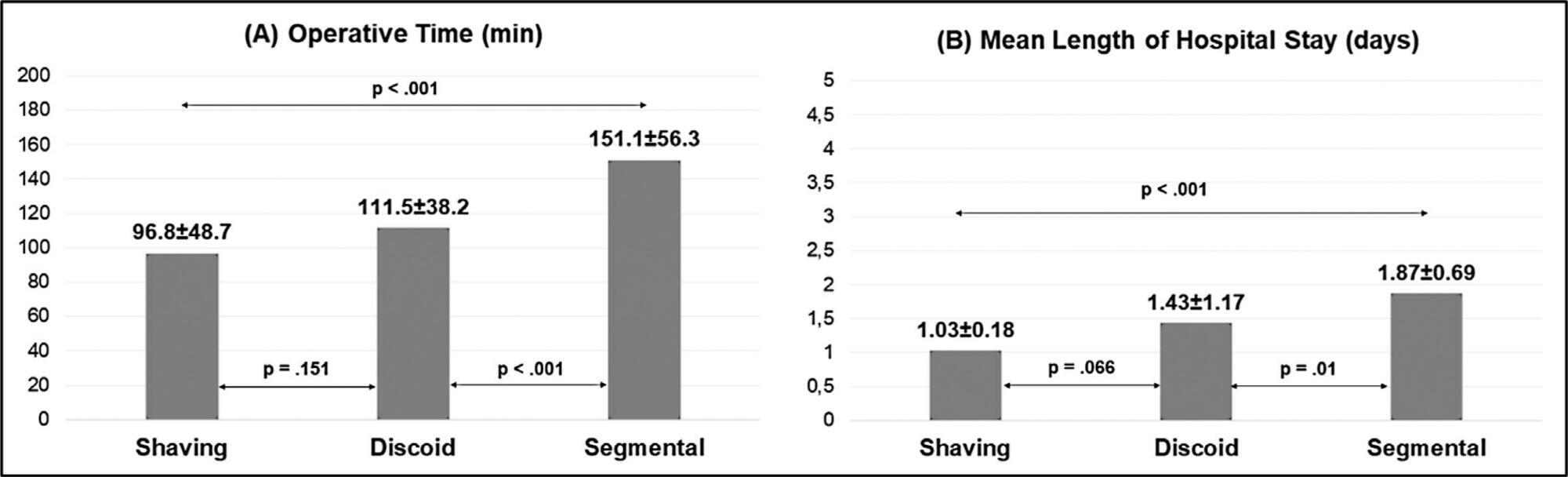
The surgical indication, type of operation, operative time, length of hospital stay, need for a temporary stoma, rate of conversion to open surgery, postoperative complications were evaluated.
One-hundred and fifty patients were included. The average duration of surgery was significantly longer for segmental resection (151 minutes) than for disc excision (111.5 minutes, p < 0.001) and shaving (96.8 minutes, p < 0.001). Patients with segmental resection had longer postoperative lengths of hospital stay (1.87 days) compared with patients with disc excision (1.43 days, p < 0.001) and shaving (1.03 days, p < 0.001). A temporary stoma was performed in 2.7% of patients. Grade II and III postoperative complications occurred in 6.7% and 4.7% patients, respectively.
Laparoscopic intestinal resection has an acceptable postoperative complication rate and a low need for a temporary stoma.
Summary
. ;