Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):729-744
12-05-2023
To review the current state of knowledge on the impact of the surgical treatment on the sexual function and dyspareunia of deep endometriosis patients.
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. We conducted systematic searches in the PubMed, EMBASE, LILACS, and Web of Science databases from inception until December 2022. The eligibility criteria were studies including: preoperative and postoperative comparative analyses; patients with a diagnosis of deep endometriosis; and questionnaires to measure sexual quality of life.
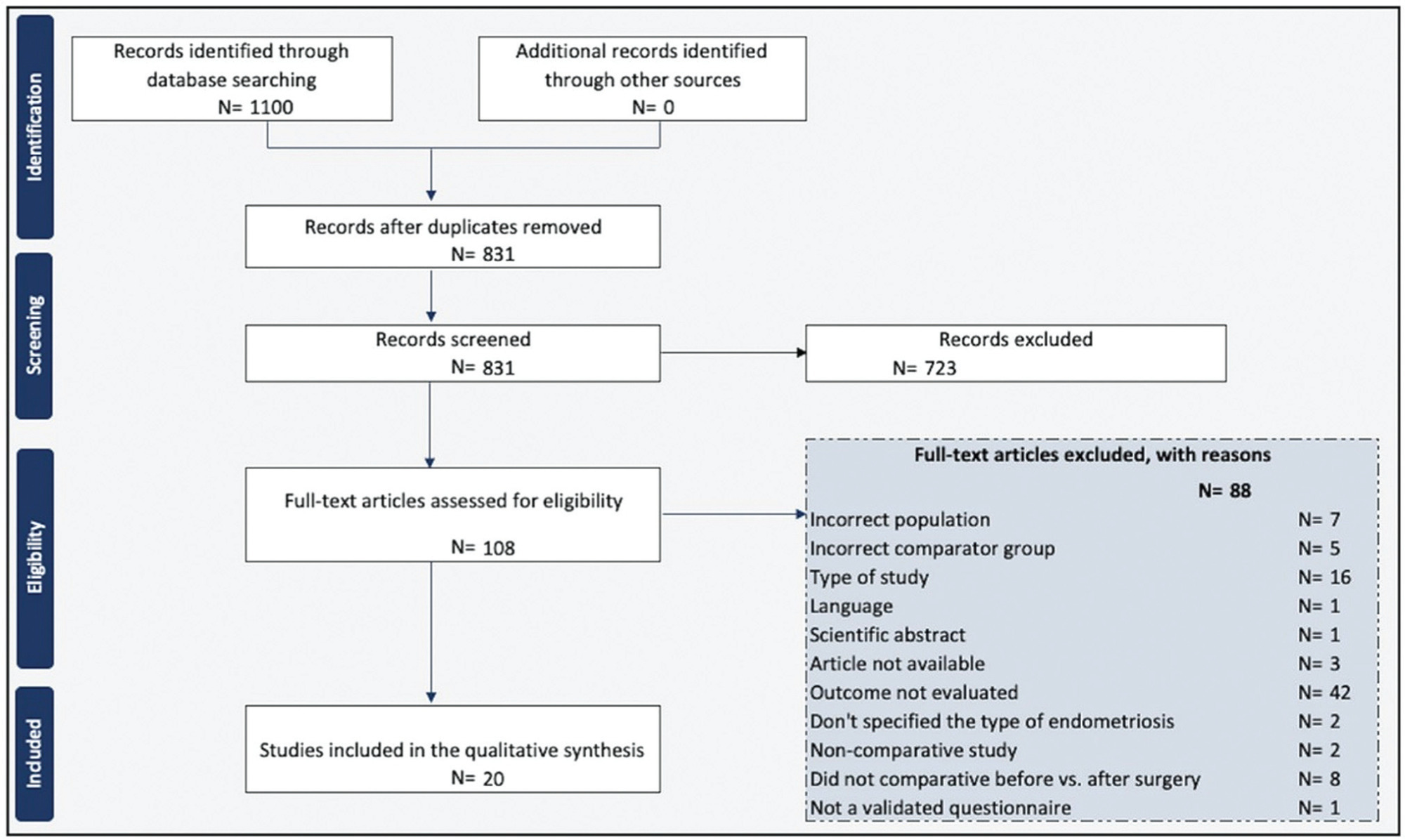
Two reviewers screened and reviewed 1,100 full-text articles to analyze sexual function after the surgical treatment for deep endometriosis. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational studies and the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for randomized controlled trials. The present study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration CRD42021289742).
General variables about the studies, the surgical technique, complementary treatments, and questionnaires were inserted in an Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, United States) spreadsheet.
We included 20 studies in which the videolaparoscopy technique was used for the excision of deep infiltrating endometriosis. A meta-analysis could not be performed due to the substantial heterogeneity among the studies. Classes III and IV of the revised American Fertility Society classification were predominant and multiple surgical techniques for the treatment of endometriosis were performed. Standardized and validated questionnaires were applied to evaluate sexual function.
Laparoscopic surgery is a complex procedure that involves multiple organs, and it has been proved to be effective in improving sexual function and dyspareunia in women with deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):986-994
01-23-2022
To evaluate the efficacy of the hormonal and nonhormonal approaches to symptoms of sexual dysfunction and vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women.
We conducted a search on the PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, SciELO, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) databases, as well as on clinical trial databases. We analyzed studies published between 1996 and May 30, 2020. No language restrictions were applied.
We selected randomized clinical trials that evaluated the treatment of sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women.
Three authors (ACAS, APFC, and JL) reviewed each article based on its title and abstract. Relevant data were subsequently taken from the full-text article. Any discrepancies during the review were resolved by consensus between all the listed authors.
A total of 55 studies were included in the systematic review. The approaches tested to treat sexual dysfunction were as follows: lubricants and moisturizers (18 studies); phytoestrogens (14 studies); dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; 8 studies); ospemifene (5 studies); vaginal testosterone (4 studies); pelvic floor muscle exercises (2 studies); oxytocin (2 studies); vaginal CO2 laser (2 studies); lidocaine (1 study); and vitamin E vaginal suppository (1 study).
We identified literature that lacks coherence in terms of the proposed treatments and selected outcome measures. Despite the great diversity in treatment modalities and outcome measures, the present systematic review can shed light on potential targets for the treatment, which is deemed necessary for sexual dysfunction, assuming that most randomized trials were evaluated with a low risk of bias according to the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool. The present review is registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42018100488).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):170-175
05-16-2019
Endometriosis is a complex disease, and pain is an important component of the syndrome. One of the most used methods to assess pain is the visual analogue scale (VAS). The aim of the present research was to study the pain experienced by patients who referred to our unit for endometriosis, using the VAS to understand the variables that could influence it.
We have conducted a prospective study from February 2012 to December 2016, enrolling 388 patients who referred to a university hospital, in Florence, Italy. We have included in the present study patients during their follow-up for endometriosis; we have also included patients who underwent surgery with a histological diagnosis of endometriosis. We have collected sociodemographic and clinical information regarding age, body mass index (BMI), smoking habit, number of pregnancies, and endometriosis staging. Finally, we have administered the VAS for several symptoms.
Dysmenorrhea was the symptom associated with the highest perception of pain (mean VAS score of 5.76). The logistic regression showed that the stage of endometriosis could influence the pain associated to constipation and to dysuria. The linear regression showed that age couldinfluencethe pain associated to constipation, to dyspareunia,and to dysmenorrhea. A positive correlation was found between dysmenorrhea and chronic pelvic pain(CPP), between dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia, and between constipation and dysuria.
Using a validated method, the VAS, we have studied the pain experienced by a group of patients with a history of endometriosis and observed that smoking habit and BMI did not influence the VAS scores, and that dysmenorrhea was associated with the highest perception of pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):787-793
12-01-2018
Genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder (GPPPD) can be an extremely bothersome condition for patients, and a tough challenge for professionals regarding its assessment and treatment. The goal of the present paper is to review the etiology, assessment, and treatment of GPPPD, especially focusing on the cognitive aspects of the disease and cognitive-behavioral treatment options, through a non-systematic review of articles indexed to the Medline, Scopus and Web of Science databases, using the following MeSH queries: pelvic pain; dyspareunia; vaginismus; vulvodynia; and cognitive therapy. Altogether, 36 articles discussing the etiology, diagnosis and management of GPPPD were selected. We provide an overview of GPPPD based on biological, psychological and relational factors, emphasizing the last two. We also summarize the available medical treatments and provide strategies to approach the psychological trigger and persisting factors for the patient and the partner. Professionals should be familiarized with the factors underlining the problem, and should be able to provide helpful suggestions to guide the couple out of the GPPPD fear-avoidance circle.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):26-30
01-01-2017
To evaluate the long-term effectiveness of perineal Thiele massage in the treatment of women with dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles.
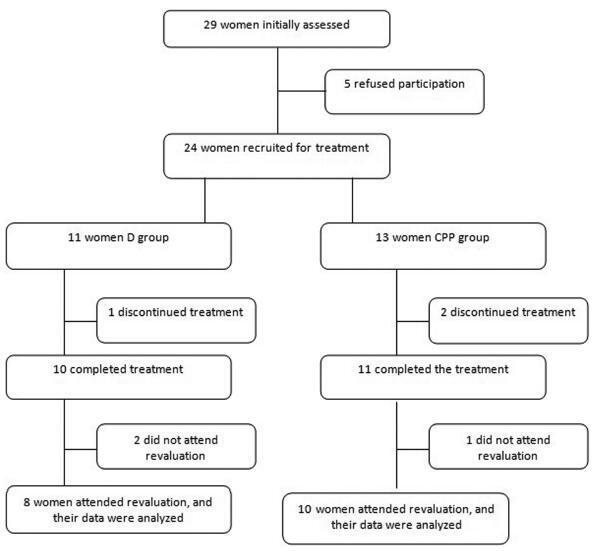
A total of 18 women with diagnoses of dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles were included in the study. The women were divided in two groups: the dyspareunia (D) group - 8 women with dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles; and the chronic pelvic pain group (CPP) group - 10 women with dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles associated with CPP. Each patient filled out the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), the McGill Pain Index, the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). After an evaluation, the women underwent transvaginal massage using the Thiele technique over a period of 5 minutes, once a week for 4 weeks.
All women had significant improvements in their dyspareunia according the VAS and the McGill Pain Index (p < 0,001), but the HADS scores did not show significant differences. Regarding sexual function, the D group showed improvements on all aspects of sexual function, while the CPP group showed differences only in the pain domain.
Thiele massage is effective in the treatment of dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles with a long-term pain relief.