Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1134-1140
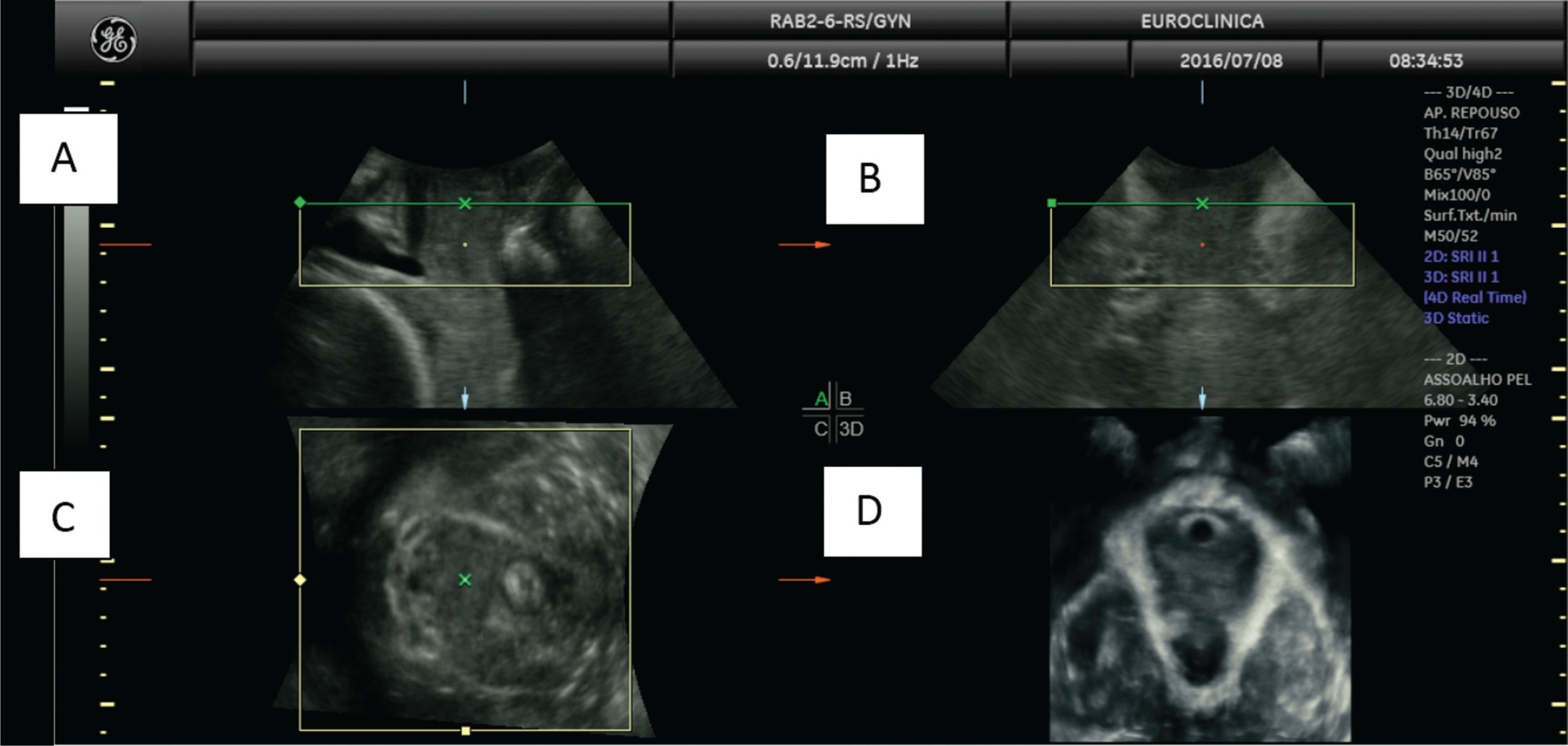
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)is an entity with evolving conceptual nuances that deserve full consideration. Gestational diabetes leads to complications and adverse effects on the mother's and infants' health during and after pregnancy. Women also have a higher prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) related to the hyperglycemic status during pregnancy. However, the exact pathophysiological mechanism is still uncertain. We conducted a narrative review discussing the impact of GDM on the women's pelvic floor and performed image assessment using three-dimensional ultrasonography to evaluate and predict future UI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(10):473-477
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001000007
PURPOSES: To evaluate the hemodynamic patterns of the ophthalmic artery by Doppler analysis in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), comparing them to normal pregnant women. METHODS: A prospective case-control study that analyzed the ophthalmic artery Doppler indices in two groups: one consisting of 40 women diagnosed with GDM and the other of 40 normal pregnant women. Included were pregnant women with GDM criteria of the American Diabetes Association - 2012, with 27 weeks of pregnancy to term, and excluded were women with hypertension, use of vasoactive drugs on or previous diagnosis of diabetes. Doppler analysis was performed in one eye with a 10 MHz linear transducer and the Sonoace 8000 Live Medison® equipment . The following variables were analyzed: pulsatility index (PI), resistance index (RI), peak velocity ratio (PVR), peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV). To analyze the normality of the samples we used the Lillefors test, and to compare means and medians we used the Student's t-test and Mann-Whitney test according to data normality, with the level of significance set at 95%. RESULTS: The median and mean values with standard deviation of the variables of the ophthalmic artery Dopplervelocimetry group GDM and normal pregnant women were: IP=1.7±0.6 and 1.6±0.4 (p=0.7); IR=0.7 and 0.7 (p=0.9); RPV=0.5±0.1 and 0.5±0.1 (p=0.1), PSV=33.6 and 31.9 cm/sec (p=0.7); VDF=6.3 and 7.9 cm/sec (p=0.4). There was no significant difference in the means and medians of these variables between the two groups of pregnant women. CONCLUSIONS: The ophthalmic artery hemodynamic patterns, analyzed by means of a Doppler technique remained unchanged in the group of pregnant women with GDM compared to the group of normal pregnant women, suggesting that the time of exposure to the disease during pregnancy was too short to cause significant vascular disorders in the central territory.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):19-24
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100004
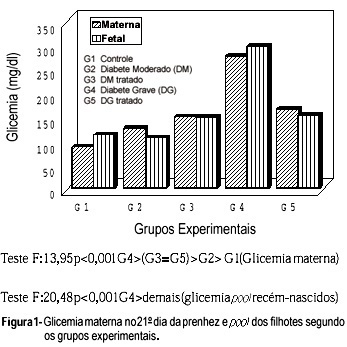
Fetal and placental effects of insulin therapy on pregnancy of diabetic rats were studied. Alloxan was administered intravenously at the dose of 42 mg/kg of body weight. Five experimental groups were formed: control (G1, n=12), non-treated rats with moderate diabetes (G2, n=10), insulin-treated rats with moderate diabetes (G3, n=11),non-treated rats with severe diabetes (G4, n=12) and insulin-treated rats with severe diabetes (G5, n=10). Six hundred and thirty-four newborn rats and placentas wereprocured. The perinatal result of insulin therapy was directly related to the quality of glycemia control. Thus, inadequate control of moderate diabetes produced levels of moderate hyperglycemia, did not interfere with the newborn rats' body weight and decreased the proportion of LGA newborn rats. Adequate control of severe diabetes brought the newborn rat glycemia to normal levels, increased the newborn rats' body weight and decreased the proportion of SGA newborn rats. Adequate insulin therapy for severe diabetes diminished the weight of the placentas, but did not change the placental index.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):315-321
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600004
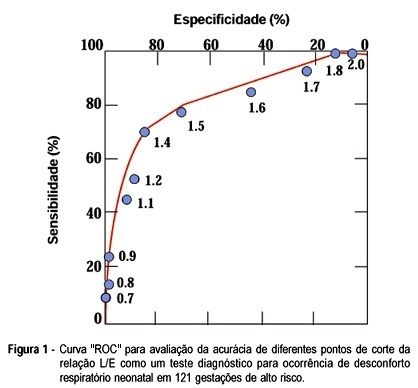
The objective was to evaluate the accuracy of the foam stability test, lecithin/sphingomyelin (LS) ratio, presence of phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and lung profile (L/S ratio > 1.7 and PG present simultaneously) in 121 consecutive high-risk gestations at the São Paulo Hospital from January 1990 to January 1995. Delivery occurred within 3 days of fetal lung maturation testing. This is a prospective study in which the sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of all the tests were determined. Neonatal respiratory outcome and amniocentesis results were stratified by gestational age for comparison. The distribution of the studied population according to maternal pathology was diabetes mellitus (48), hypertensive disorders (41), Rh isoimmunization (14) and miscellaneous (18). Respiratory distress (RD) was present in 33 infants (27.2%), mainly in the diabetic group. There was no false negative using lung profile (all patients) and foam stability tests among hypertensive pregnancies (specificity 100%), but there were about 20% to 50% false positives in the other tests. Overall, all four tests had a low PPV: 23% for foam test, 51% for L/S ratio, 63% for PG, 61% for lung profile, and high NPV: 92% for foam test, 88% for L/S ratio, 89% for PG and 100% for lung profile. All tests had less accuracy in the diabetic pregnant women. This study shows that the presence of PG and L/S ratio > 1.7 in the amniotic fluid of high-risk pregnancies confirms maturity with a very low risk to develop RD and that the foam stability test was useful as a first-line test to predict the absence of surfactant-deficient respiratory distress syndrome, particularly in hypertensive pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):519-525
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900004
Purpose: to present the perinatal outcomes resulting from the use of a protocol for assistance to diabetic pregnant women used at the Center for Integral Assistance to Women's Health (CAISM), of the University of Campinas. Methods: ninety diabetic pregnant women, who were assisted at the institution with this protocol, were compared with two control grups: the first consisted of 180 pregnant women with equal number of gestations and same age (control A) and the second consisted of 180 randomly selected pregnant women (control B). The study variables were route of delivery, indication for cesarean section, gestational age, Apgar score at first and fifth minute, weight, adequacy of weight for gestational age and perinatal morbidity and mortality. For the statistical analysis Student's t-test and the chi2 test were used. Results: there was a higher incidence of cesarean sections, prematures and large to gestational age (LGA) babies among diabetic women, as well as higher occurrence of neonatal morbidity such as hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress and neonatal depression. The incidence of low Apgar score and perinatal mortality was significantly higher than in the randomly selected group, but the same as in the group matched regarding age and number of pregnancies. Conclusions: although this protocol intends to obtain a perfect metabolic control among diabetic pregnant women, the perinatal outcomes are still unfavorable in comparison to nondiabetic pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):401-411
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700002
Purpose: to analyze the relationship between White's classification and the histopathological, changes occurring in the placentas of diabetic pregnant women, performing a qualitative comparison of histopathological changes in the placentas of nondiabetic pregnant women with those in diabetic ones (classes A and A/B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH), studying the influence of the quality of glycemic control and of gestational age on placental changes in the three groups of diabetic pregnant women. Patients and methods: specimens of placentas were collected from all diabetic pregnant women seen between 1991 and 1996 in the Maternity Section of the Hospital das Clínicas, Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, stained using the hematoxylin-eosin technique, and submitted to a histopathological examination. The quality of glycemic control was analyzed by the glycemia average of gestation and classified as adequate or inadequate, with a limit of 120 mg/dl. Gestational age was individualized as term and preterm. Results: forty-two newborns (43.3%) were born at term and the remaining were preterm (56.7%). The prematurity rate was higher for women with clinical diabetes (classes B and C; D to FRH). Some histopathological alterations were observed only in placentas from diabetic pregnant women: cystoid degeneration, chorial edema, intima edema, dysmaturity, Hofbauer cell hyperplasia, villitis, ghost cells, two vessels in the umbilical cord, and endarteritis. Conclusions: histopathological changes in the placentas of pregnant women with gestational diabetes (classes A and A/B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH) were similar to those in the nondiabetic ones, and, therefore, were independent of White's clinical classification. The histopathological changes in the placentas of pregnant women with gestational diabetes (classes A and A and B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH) were not related to gestational age at birth and to the quality of glycemic control of the mother. The comparison between histopathological changes and the increased number of preterm newborns in clinical diabetes, class D to FRH, suggest early placental ageing in clinical diabetes patients.