-
Original Article12-17-2021
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Depression and Sexual Function: Are Pregnant Women Affected More Adversely?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):765-774
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Depression and Sexual Function: Are Pregnant Women Affected More Adversely?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):765-774
Views209See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate depression and sexual function among pregnant and nonpregnant women throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A total of 188 women, 96 pregnant and 92 non-pregnant were included. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX) were applied to the participants after obtaining sociodemographic data.
Results
The depression scores of pregnant and non-pregnant women were similar (p = 0.846). We found that the depression scores were significantly higher among the group of participants who have lower economic status (p = 0.046). Moreover, the depression score was significantly higher among women who lost their income during the pandemic (p = 0.027). The score on the ASEX was significantly higher, and sexual dysfunction was more prevalent among women who have lower levels of schooling and income (p < 0.05). Likewise, the ASEX scores were significantly higher (p = 0.019) among the group who experienced greater income loss throughout the pandemic. Upon comparing the pregnant and non-pregnant groups, we detected that sexual dysfunction had a significantly higher rate among pregnant women (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In times of global crisis, such as the current pandemic, low-income families have an increased risk of experiencing depression and sexual dysfunction. When we compared pregnant women with non-pregnant women, depression scores were similar, but pregnant women were at a 6.2 times higher risk of developing sexual dysfunction.
-
Original Article09-25-2020
Analysis of Body Composition and Pain Intensity inWomen with Chronic Pelvic Pain Secondary to Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):486-492
Abstract
Original ArticleAnalysis of Body Composition and Pain Intensity inWomen with Chronic Pelvic Pain Secondary to Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):486-492
Views298See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine the average body composition (percentage of body fat), the anthropometric markers, and the intensity of clinical pain in women with a clinical diagnosis of chronic pelvic pain (CPP) secondary to endometriosis.
Methods
A case-control study performed with 91 women, 46 of whom with CPP secondary to endometriosis and 45 of whom with CPP secondary to other causes. They underwent an evaluation of the anthropometric parameters by means of the body mass index (BMI), the perimeters (waist, abdomen, hip), and the percentage of body fat (%BF), which were assessed on a body composition monitor by bioimpedance; the intensity of the clinical pain was evaluated using the visual analog scale (VAS), and the symptoms of anxiety and depression, using the hospital’s anxiety and depression scale (HAD).
Results
The groups did not differ in terms of mean age, BMI, %BF or regarding the available waist-to-hip ratio (WHR). The mean intensity of the clinical pain by the VAS was of 7.2 ± 2.06 in the group with CPP secondary to endometriosis, and of 5.93 ± 2.64 in the group with CPP secondary to other causes (p = 0.03), revealing significant differences between the groups.
Conclusion
We concluded that, despite the difference in the pain score assessed between the two groups, there was no difference regarding body composition and anthropometry.
-
Original Article12-01-2018
Sexual Function of Women with Infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):771-778
Abstract
Original ArticleSexual Function of Women with Infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):771-778
Views195Abstract
Objective
To assess the sexual function, anxiety, and depression of infertile women relative to a control group.
Methods
Infertile women (infertile group, IG) of reproductive age were invited to participate in this controlled study. A control group (CG) of women was recruited from the general population of the same city. Sexual function was assessed by the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and anxiety and depression were measured by the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS).
Results
A total of 280 women participated in the present study, 140 in the IG and 140 in the CG. The analysis of the FSFI scores showed that 47 women (33.57%) in the IG and 49 women (35%) in the CG had sexual dysfunction (FSFI ≤ 26.55; p = 0.90). Women with anxiety or depression had a greater risk of sexual dysfunction, and sexual dysfunction increased the risk of anxiety and depression. Married women had a lower risk of depression than single women who were living with their partners.
Conclusion
Infertilewomenhadno increased riskof sexual dysfunction relativetocontrols. Anxiety and depression increased the risk of sexual dysfunction in the studied population.
Key-words AnxietyAssisted reproductionDepressionfemale sexual dysfunctionmarital infertilitySexualitySee more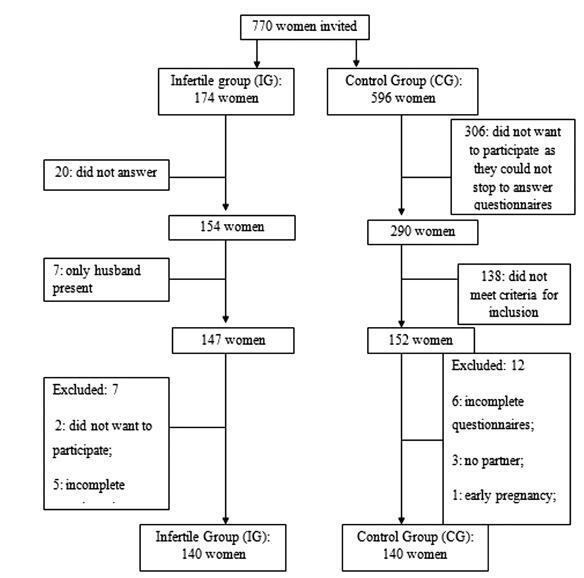
-
Original Article10-01-2017
Clinical Characteristics in a Sample of Transsexual People
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):545-551
Abstract
Original ArticleClinical Characteristics in a Sample of Transsexual People
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):545-551
Views226See moreAbstract
Purpose
To assess the clinical characteristics of subjects with gender dysphoria (GD).
Method
A cross-sectional study of adults with GD. Symptoms of anxiety and depression were measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Sociodemographic data, clinical data and life habits were recorded.
Results
Total of 44 subjects participated in the study: 36 (82%) trans women and 8 (18%) trans men. Forty-three (98%) of the GD patients had anxiety (36 [100%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men), and 36 (82%) had depression (29 [80.5%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men). Suicide had been attempted by 32 (73%) subjects. The rates of depression were lower among the subjects living with partners, parents, or other people than among those living alone (p = 0.03), and it was also lower among the subjects who were married compared to those who were dating or single (p = 0.03).
Conclusion
Improving the relationship status may reduce the prevalence of depressive symptoms in GD patients. There was a high rate of attempted suicide in this sample.
-
Original Article01-01-2016
The Influence of Education and Depression on Autonomy of Women with Chronic Pelvic Pain: A Cross-sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):47-52
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Influence of Education and Depression on Autonomy of Women with Chronic Pelvic Pain: A Cross-sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):47-52
Views118See moreObjective
Patient autonomy has great importance for a valid informed consent in clinical practice. Our objectives were to quantify thedomains of patient autonomy and to evaluate the variables that can affect patient autonomy in women with chronic pelvic pain.
Methods
This study is a cross sectional survey performed in a tertiary care University Hospital. Fifty-two consecutive women scheduled for laparoscopic management of chronic pelvic were included. Three major components of autonomy (competence, information or freedom) were evaluated using a Likert scale with 24 validated affirmatives.
Results
Competence scores (0.85 vs 0.92; p = 0.006) and information scores (0.90 vs 0.93; p = 0.02) were low for women with less than eight years of school attendance. Information scores were low in the presence of anxiety (0.91 vs 0.93; p = 0.05) or depression (0.90 vs 0.93; p = 0.01).
Conclusions
Our data show that systematic evaluation of patient autonomy can provide clinical relevant information in gynecology. Low educational level, anxiety and depression might reduce the patient autonomy in women with chronic pelvic pain.
-
Original Article04-14-2014
Sexuality and depression among pregnant women with recurrent spontaneous abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):152-156
Abstract
Original ArticleSexuality and depression among pregnant women with recurrent spontaneous abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):152-156
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0004
Views126See morePURPOSE:
It was to compare pregnant women who experienced recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) and those who did not in terms of the prevalence of depressive symptoms and sexual behavior.
METHODS:
A prospective case-control study was carried out. The first group consisted of women with RSA and the second, of primigravidae. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) and one more questionnaire, developed by the authors themselves, about emotional aspects resulting from sexual intercourse during pregnancy were applied. The Student t-test was used to compare quantitative variables with normal distribution, and categorical variables were compared by the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test. The level of significance was set at p<0.05.
RESULTS:
The BDI showed (19.9 versus 10.0%) approximately twice the incidence of depression in the RSA group. Regarding sexual function, the average scores of the FSFI were 21.1 and 16.4 (p<0.05) for the study and control groups, respectively, although no significant difference was observed only in the desire domain (average 3.4±1.3 for the RSA group and 3.7±1.1 for control group) (p=0.1). We observed that, regardless the presence or absence of an RSA history among the pregnant women, the higher the depression score, the lower the sexuality score (r=-0,3).
CONCLUSIONS:
The RSA pregnant group often experiences twice higher depression and more impaired sexual function. There is an inverse association between depression and sexual function.
-
Original Article02-01-2014
Depressive symptomsin womenwith chronic pelvic pain
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):79-83
Abstract
Original ArticleDepressive symptomsin womenwith chronic pelvic pain
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):79-83
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200006
Views121See morePURPOSE:
To investigate the presence of depressive symptoms in women with chronic pelvic
pain.METHODS:
This descriptive cross-sectional study was performed with women aged 18 years or
older, diagnosed with chronic pelvic pain, with no pregnancy history in the
previous year, and with no cancer history. The sample was established by
calculating the representative sample, estimated as 50 women. All women were
undergoing treatment at a gynecology outpatient clinic, referred by the primary
health care network of the Brazilian national health system. Data collection was
performed from October2009 to May 2010. The women's sociodemographic, economic and
clinical characteristics were analyzed. Pain intensity was evaluated using a
visual analogue scale. The depressive symptoms were investigated using Beck's
Depression Inventory. Statistical analysis was performed using position measures
(mean, median), dispersion (standard deviation) and the χ2 test. Values
of p≤ .05 were considered statistically significant.RESULTS:
The participants' mean age was 41.6±9.4 years. The following features
predominated: secondary education level; pardo (brown) skin color; Catholic
religion; and living with a steady partner. Most (98%) were economically active
and worked with general domestic services. Regarding the participants' subjective
perception of pain, 52% reported experiencing intense pain, while 48% reported
experiencing moderate pain. Most women (52%) had been living with pain for five
years or less, and 30%, for over 11 years. The mean BDI score was 17.4 (±9.4). It
was observed that 58% of the women presented mild, moderate and severe depressive
symptoms according to the BDI. The most frequent depressive symptoms were
fatigability, loss of libido, irritability, difficulty to work, somatic
preoccupations, crying, dissatisfaction, sadness, and insomnia.CONCLUSION:
Depressive symptoms were frequent among these women suffering with chronic pelvic
pain.


