-
Review Article
Timing of semen cryopreservation: before or after processing?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo36
04-09-2024
Summary
Review ArticleTiming of semen cryopreservation: before or after processing?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo36
04-09-2024Views372Abstract
Objective:
Seminal cryopreservation causes significant damage to the sperm; therefore, different methods of cryopreservation have been studied. The aim of the study was to compare the effects of density gradient processing and washing/centrifugation with seminal plasma removal for cryopreservation in semen parameters.
Methods:
Seminal samples of 26 normozoospermic patients were divided into 3 parts: with seminal plasma; after washing/centrifugation; and after selection through density gradient. The samples were cryopreserved for at least two weeks. Motility, sperm count, morphology and viability were evaluated before cryopreservation and after thawing.
Results:
Density gradient processing selected motile and viable sperm with normal morphology in fresh samples (p<0.05). Cryopreservation negatively affected all sperm parameters regardless of the processing performed, and even if the sperm recovery was lower in the density gradient after the thawing, progressive motility, total motility, viability and morphology remained higher (p<0.05).
Conclusion:
Cryopreservation significantly compromises sperm parameters (motility, morphology, viability). In normozoospermic patients, the density gradients select better quality spermatozoa compared to other processing methods; this benefit was kept after thawing.
Key-words CentrifugationCryopreservationDensity gradientSemenSeminal plasmaSperm countSperm washSpermatozoaSee more -
Case Report
Ex vivo Retrieval of Mature Oocytes for Fertility Preservation in a Patient with Bilateral Borderline Ovarian Tumor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):225-231
01-19-2021
Summary
Case ReportEx vivo Retrieval of Mature Oocytes for Fertility Preservation in a Patient with Bilateral Borderline Ovarian Tumor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):225-231
01-19-2021Views208Abstract
We report a case of ultrasound-guided ex vivo oocyte retrieval for fertility preservation in a woman with bilateral borderline ovarian tumor, for whom conventional transvaginal oocyte retrieval was deemed unsafe because of the increased risk of malignant cell spillage. Ovarian stimulation with gonadotropins was performed. Surgery was scheduled according to the ovarian response to exogenous gonadotropic stimulation; oophorectomized specimens were obtained by laparoscopy, and oocyte retrieval was performed ~ 37 hours after the ovulatory trigger. The sum of 20 ovarian follicles were aspirated, and 16 oocytes were obtained.We performed vitrification of 12 metaphase II oocytes and 3 oocytes matured in vitro. Our result emphasizes the viability of ex vivo mature oocyte retrieval after controlled ovarian stimulation for those with high risk of malignant dissemination by conventional approach.
Key-words borderline ovarian tumorCryopreservationex vivo oocyte retrievalFertility preservationOvarian cancerVitrificationSee more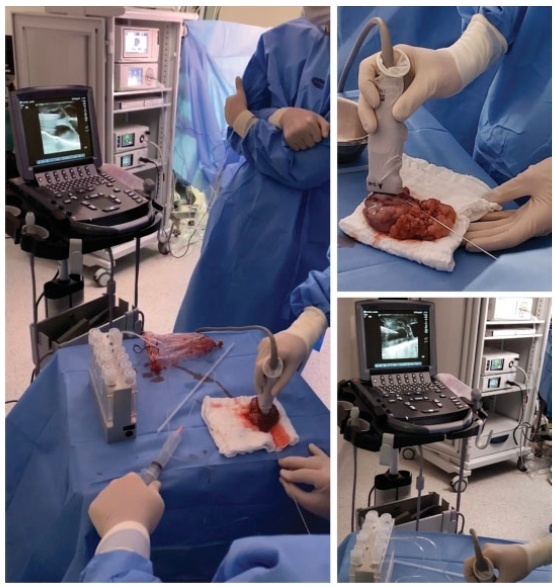
-
Artigos Originais
Cryopreservation of human semen: comparison between methods of freezing and types of storage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):708-714
03-19-2006
Summary
Artigos OriginaisCryopreservation of human semen: comparison between methods of freezing and types of storage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):708-714
03-19-2006DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001200004
Views132See morePURPOSE: to compare two different methods of freezing and two types of human semen storage during cryopreservation process. METHODS: experimental research in which the cryopreservation of 18 semen samples from 18 volunteers was studied. Following the addition of the cryoprotectant medium, Test-yolk buffer, the semen samples were packaged into 0.25 mL straws or into 2 mL cryotubes and submitted to cryopreservation by slow or rapid methods, in four different treatments: RS (cryopreservation by rapid method and packaged in straws), RT (rapid-cryotubes), SS (slow-straws), and ST (slow-cryotubes). Samples were thawed after 24 hand then maintained at 37ºC. Data collected were analyzed by the Student t-test, with p<0.05, using the SPSS computer program for Windows®, version 11.0.0. RESULTS: the motility of spermatozoa decreased after the cryopreservation process. The initial motility rate was 58.1% and motilities after the different methods of cryopreservation were 19.2% (RS), 27% (RT), 21.1% (SS) and 30.3% (ST). There was a significant decrease of the normal morphology. The initial normal morphology was 14.2% and morphologies after the different methods of cryopreservation were 12.8% (RS), 12.6% (RT), 12.6% (SS) and 12.4% (ST). CONCLUSIONS: the slow method of cryopreservation with storage in cryotubes showed the best recovery of motile cells after freezing and thawing. There was no difference among the methods when appraised the morphology.
-
Revisão
Fertility preservation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):365-372
10-20-2006
Summary
RevisãoFertility preservation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):365-372
10-20-2006DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600008
Views66See moreAs therapeutic approaches for oncologic diseases are being improved and an increase in the survival rates are being achieved, long-term complications of these therapies, initially infrequent, assume these days an important place when considering life quality. Among the long term repercussions appears the premature ovarian failure. According to the recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology recently published, the only procedures available nowadays considered to be effective for female fertility preservation are: embryo cryopreservation, conservative gynecological surgery and oophoropexy in cases of local radiotherapy. All the other proposed techniques, surch as: ovarian suppression and oocyte and ovarian tissue cryopreservation, although present promising results, are still considered as experimental options. The best choice for fertility preservation in each specific case depends on patient's age, type of treatment, existence of a partner, time available until chemo- or radiotherapy beginning, and the ovarian metastatic potential of the tumor. In the present manuscript, the available and experimental techniques for fertility preservation are revised and discussed.
-
Artigos Originais
Characterization of unviable embryos suitable for donation to stem-cell research
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):665-671
04-10-2005
Summary
Artigos OriginaisCharacterization of unviable embryos suitable for donation to stem-cell research
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):665-671
04-10-2005DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100006
Views60See morePURPOSE: to define the characteristics of unviable embryos that may be donated for stem-cell research. METHODS: a retrospective evaluation of in vitro fertilzation cycles between January 1995 and January 2005 was structured. Cycles were chosen in which the embryos transferred to the uterine cavity had the same morphological characteristics. Subsequently, the rates of pregnancy, implantation, and involution of the gestational sacs of the fresh embryos as well as of those cryopreserved were analyzed and distributed into groups according to their morphology. Embryos that were symmetric and with 0% of fragmentation were designated type A; asymmetric with up to 25% of fragmentation were designated type B; between 25 and 50% of volume occupied were designated type C, and those with 50% or more of fragmentation were designated type D. RESULTS: one hundred and seventy-two type D embryos transferred in 87 cycles presented low rates of implantation (11%) with 50% of those implanted persisting in development. Embryos with the same morphology, after cryopreservation and thawing, did not show the capacity to evolve. In 36 cycles, 113 thawed type D embryos were transferred, resulting in only one implantation, presenting a minute 3% pregnancy rate. The implanted gestational sac did not evolve, showing a 100% rate of involution. CONCLUSION: embryos with low morphological scores cannot be considered unviable because they are capable, even though with a very low frequency, of supporting gestation. However, these same embryos, after cryopreservation, thawing and transfer showed an insignificant rate of pregnancy, that did not result in viable pregnancy. Therefore, when in excess to requirements, type D embryos should not be cryopreserved; instead, rather than discarded, they should be donated for embryo stem-cell research.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Viability and in vitro fertilization of bovine oocytes after vitrification
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):553-559
12-12-2003
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisViability and in vitro fertilization of bovine oocytes after vitrification
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):553-559
12-12-2003DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800003
Views57See morePURPOSE: to verify vitrification techniques using 6 M DMSO to cryopreserve in vitro matured bovine oocytes, and to assess the effects of the time of exposure to vitrification solutions (VS). METHODS: dilutions of VS were prepared from the stock VS (VS 100%) consisting of 6 M DMSO to give 25 and 65% DMSO solutions. Bovine oocytes were in vitro matured for 18-22 h. Matured oocytes were placed first into 25% VS, at room temperature for 5 min, then transferred to 65% VS, before being pipetted into the 100% VS in plastic straws. Three experimental groups were formed: in the first group, time of pipetting through 65% VS and loading the straw took up to 60 s, in the second group it did not exceed 30 s. For thawing, straws were held in air for 10 s and then in a water bath for 10 s. The contents of each straw were expelled in sucrose solution and held for 5 min. In the third experimental group, oocytes went through all VS, but were not vitrified. All retrieved oocytes were inseminated. For control, fresh, in vitro matured oocytes were inseminated. RESULTS: after vitrification, 69.1 and 59.8% of the oocytes were retrieved from the 30 s and 60 s groups, respectively, and 93 and 89% of these oocytes appeared morphologically normal 24 h after insemination, respectively. In the group of oocytes exposed without vitrification, 75.6% were retrieved and 84.7% were morphologically viable, 24 h after insemination. No fertilization was observed in the experimental groups. Among controls, 65.4% were fertilized. CONCLUSIONS: the vitrification technique using 6 M DMSO is not a feasible approach to cryopreserve in vitro matured bovine oocytes. Decreasing the time of exposure to VS did not overcome deleterious effects of the procedure on the fertilizability of oocytes. Improvements in the technique are needed to protect the zona pellucida and oolemma.


