Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo39i
This study aims to create a new screening for preterm birth < 34 weeks after gestation with a cervical length (CL) ≤ 30 mm, based on clinical, demographic, and sonographic characteristics.
This is a post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial (RCT), which included pregnancies, in middle-gestation, screened with transvaginal ultrasound. After observing inclusion criteria, the patient was invited to compare pessary plus progesterone (PP) versus progesterone only (P) (1:1). The objective was to determine which variables were associated with severe preterm birth using logistic regression (LR). The area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for both groups after applying LR, with a false positive rate (FPR) set at 10%.
The RCT included 936 patients, 475 in PP and 461 in P. The LR selected: ethnics white, absence of previous curettage, previous preterm birth, singleton gestation, precocious identification of short cervix, CL < 14.7 mm, CL in curve > 21.0 mm. The AUC (CI95%), sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and PNV, with 10% of FPR, were respectively 0.978 (0.961-0.995), 83.4%, 98.1%, 83.4% and 98.1% for PP < 34 weeks; and 0.765 (0.665-0.864), 38.7%, 92.1%, 26.1% and 95.4%, for P < 28 weeks.
Logistic regression can be effective to screen preterm birth < 34 weeks in patients in the PP Group and all pregnancies with CL ≤ 30 mm.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo44
To describe Top-hat results and their association with margin status and disease relapse in a referral facility in Brazil.
A retrospective study of 440 women submitted to LEEP to treat HSIL, in which 80 cases were complemented immediately by the top hat procedure (Top-hat Group - TH). TH Group was compared to women not submitted to Top-hat (NTH). The sample by convenience included all women that underwent LEEP from January 2017 to July 2020. The main outcome was the histological result. Other variables were margins, age, transformation zone (TZ), depth, and relapse. The analysis used the Chi-square test and logistic regression.
The TH Group was predominantly 40 and older (NTH 23.1% vs. TH 65.0%, p<0.001). No difference was found in having CIN2/CIN3 as the final diagnosis (NTH 17.0% vs. TH 21.3%, p=0.362), or in the prevalence of relapse (NTH 12.0% vs. TH 9.0%, p=0.482). Of the 80 patients submitted to top hat, the histological result was CIN2/CIN3 in eight. A negative top hat result was related to a negative endocervical margin of 83.3%. A CIN2/CIN3 Top-hat result was related to CIN2/CIN3 margin in 62.5% (p=0.009). The chance of obtaining a top hat negative result was 22.4 times higher (2.4-211.0) when the endocervical margin was negative and 14.5 times higher (1.5-140.7) when the ectocervical margin was negative.
The top hat procedure did not alter the final diagnosis of LEEP. No impact on relapse was observed. The procedure should be avoided in women of reproductive age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):178-186
To determine the accuracy of colposcopy findings in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in women with an atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H) pap smear result and analyze whether the prevalence of HSIL and cancer correlates with sociodemographic risk factors and specific colposcopic findings.
Colposcopic findings and sociodemographic risk factors were analyzed as possible predictors of a CIN 2 or worse diagnosis in women with an ASC-H pap smear result.
Accuracy of the colposcopic impression was 92%, sensitivity was 91.6%, and specificity was 93.1%, with a positive predictive value of 96.4% and negative predictive value of 84.3%. Diagnosis of CIN 2 or worse was more frequent in patients with a previous history of cervical dysplasia and pre-menopausal patients. Identification of major colposcopic findings, dense acetowhite epithelium, coarse mosaicism, and punctuation correlated significantly with CIN 2 or worse.
Colposcopy performed by an experienced examiner can accurately differentiate patients with CIN 1 or less from patients with CIN 2 or worse. Diagnosis of CIN 2 or worse was more frequent in patients with a previous history of cervical dysplasia and pre-menopausal patients. The degree of acetowhite changes was the best colposcopic feature to predict CIN2 or worse.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):540-546
The aim of the present study was to compare the obstetric history and both two- and tri-dimensional ultrasound parameters according to different cervical lengths.
The present cross-sectional study analyzed 248 midtrimester pregnant women according to cervical length and compared the data with the obstetric history and 2D/3D ultrasound parameters. Patients were divided into 3 groups according to cervical length: The Short Cervix group for cervical lengths ≥ 15mm and< 25mm(n= 68), the Very Short Cervix group for cervical lengths< 15mm (n = 18) and the Control group, composed of 162 pregnant women with uterine cervical lengths ≥ 25mm.
When analyzing the obstetric history of only non-nulliparous patients, a significant association between the presence of a short cervix in the current pregnancy and at least one previous preterm birth was reported (p = 0.021). Cervical length and volume were positively correlated (Pearson coefficient = 0.587, p < 0.0001). The flow index (FI) parameter of cervical vascularization was significantly different between the Control and Very Short Cervix groups. However, after linear regression, in the presence of volume information, we found no association between the groups and FI. Uterine artery Doppler was also not related to cervical shortening.
The present study showed a significant association between the presence of a short cervix in the current pregnancy and at least one previous preterm birth. None of the vascularization indexes correlate with cervical length as an independent parameter. Uterine artery Doppler findings do not correlate with cervical length.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):476-484
Labor induction does not always result in vaginal delivery, and can expose both the mother and the fetus to the risks inherent to the induction procedure or a possible cesarean section. Transvaginal sonography (TVS) of the cervix is a useful tool to predict prematurity; in the present study, this tool was used to evaluate postterm induction.
We evaluated the ultrasound characteristics of the cervix (cervical length, cervical funneling, internal os dilation, the presence or absence of the cervical gland area [CGA], and the morphological changes of the cervix as a result of applying fundal pressure) before the onset of labor induction among women with postterm pregnancy to identify the possible predictors of failed labor induction. The Bishop score (BS) was used for comparison purposes. Three groups were evaluated: successful versus unsuccessful induction; vaginal delivery versus cesarean delivery (excluding cases of acute fetal distress [AFD]); and vaginal delivery versus cesarean delivery (including cases of AFD). A fourth group including only the primiparous women from the three previous groups was also evaluated.
Based on the studied characteristics and combinations of variables, a cervical length ≥ 3.0 cm and a BS ≤ 2 were the best predictors of induction failure.
Although TVS is useful for screening for induction failure, this tool should not be used as an indication for cesarean section.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):86-91
To compare the quality of cervicovaginal samples obtained from basic health units (BHUs) of the Unified Health System (SUS) and those obtained fromprivate clinics to screen precursor lesions of cervical cancer.
It was an intervention study whose investigated variables were: adequacy of the samples; presence of epithelia in the samples, and cytopathological results. A total of 940 forms containing the analysis of the biological samples were examined: 470 forms of women attended at BHUs of the SUS and 470 forms of women examined in private clinics in January and February of 2016.
All the unsatisfactory samples were collected at BHUs and corresponded to 4% of the total in this sector (p < 0.0001). There was a higher percentage of samples containing only squamous cells in the SUS (43.9%). There was squamocolumnar junction (SJC) representativeness in 82.1% of the samples from the private clinics (p < 0.0001). Regarding negative results for intraepithelial lesions and/or malignancies, the percentages obtained were 95.9% and 99.1% (p < 0.0049) in the exams collected in the private system and SUS, respectively. Less serious lesions corresponded to 0.89% of the samples from the SUS and 2.56% of the tests from the private sector; more serious lesions were not represented in the samples obtained from BHUs, whereas the percentage was 1.49% in private institutions.
Unsatisfactory cervical samples were observed only in exams performed at the SUS. There is a need for guidance and training of professionals who perform this procedure to achieve higher reliability in the results and more safety for women who undergo this preventive test.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):408-414
the aim of this study was to evaluate the pattern of human papillomavirus (HPV) detection in an 11.3-year post-vaccination period in a cohort of adolescent and young women vaccinated or not against HPV 16/18.
a subset of 91 women from a single center participating in a randomized clinical trial (2001-2010, NCT00689741/00120848/00518336) with HPV 16/18 AS04- adjuvanted vaccine was evaluated. All women received three doses of the HPV vaccine (n = 48) or a placebo (n = 43), and cervical samples were collected at 6-month intervals. Only in this center, one additional evaluation was performed in 2012. Up to 1,492 cervical samples were tested for HPV-DNA and genotyped with polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The vaccine group characteristics were compared by Chi-square or Fisher exact or Mann-Whitney test. The high-risk (HR)-HPV 6-month-persistent infection rate was calculated. The cumulative infection by HPV group was evaluated by the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test.
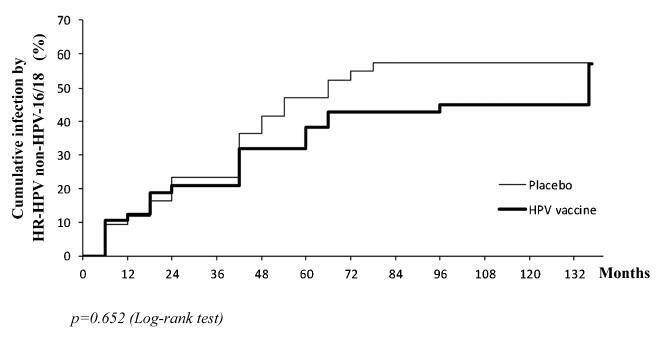
the cumulative infection with any type of HPV in an 11.3-year period was 67% in the HPV vaccine group and 72% in the placebo group (p = 0.408). The longitudinal analysis showed an increase of 4% per year at risk for detection of HR-HPV (non-HPV 16/ 18) over time (p = 0.015), unrelated to vaccination. The cumulative infection with HPV 16/18 was 4% for the HPV vaccine group and 29% for the placebo group (p = 0.003). There were 43 episodes of HR-HPV 6-month persistent infection, unrelated to vaccination.
this study showed themaintenance of viral detection rate accumulating HR-HPV (non-HPV-16-18) positive tests during a long period post-vaccination, regardless of prior vaccination. This signalizes that the high number of HPV-positive testsmay be maintained after vaccination.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):559-564
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005462
To analyze the relation between the cytological findings and telomerase activity (TA).
Cervical samples were evaluated and classified according to the Bethesda System. Telomerase activity was measured total product generated values (TPG) using the TRAP assay (telomeric repeat amplification protocol); data were analyzed statistically using the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
The study was conducted on 102 patients. Of these, 3.9% showed normal cytological findings, 8.8% showed cervicitis; 2% showed Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASCUS); 67.6% showed Low Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (LSIL); 11.8% showed High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (H-SIL) and 5.9% showed Squamous Carcinoma. Among telomerase-positive samples, the TPG values were cervicitis Results show increased telomerase activity with increasing severity of lesion, supporting the association between TA and type of lesion.CONCLUSION