-
Case Report03-30-2021
Cervical Mesonephric Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report of a Rare Gynecological Tumor from Embryological Remains of the Female Genital Tract
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):329-333
Abstract
Case ReportCervical Mesonephric Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report of a Rare Gynecological Tumor from Embryological Remains of the Female Genital Tract
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):329-333
Views114See moreAbstract
Introduction
Malignant mesonephric tumors are uncommon in the female genital tract, and they are usually located where embryonic remnants of Wolffian ducts are detected, such as the uterine cervix. The information about these tumors, their treatment protocol, and prognosis are scarce.
Case report
A 60-year-old woman with postmenopausal vaginal bleeding was initially diagnosed with endometrial carcinoma. After suspicion co-testing, the patient underwent a loop electrosurgical excision of the cervix and was eventually diagnosed with mesonephric adenocarcinoma. She was subjected to a radical hysterectomy, which revealed International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) IB1 stage, and adjuvant radiotherapy. The follow-up showed no evidence of recurrence after 60 months.
Conclusion
We present the case of a woman with cervical mesonephric adenocarcinoma. When compared with the literature, this case had the longest clinical follow-up without evidence of recurrence, which reinforces the concept that these tumors are associated with a favorable prognosis if managed according to the guidelines defined for the treatment of patients with cervical adenocarcinomas. Though a rare entity, it should be kept in mind as a differential diagnosis for other cervical cancers.
-
Original Article01-01-2017
Immunohistochemical Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein p16 INK4a in Cervical Adenocarcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):21-25
Abstract
Original ArticleImmunohistochemical Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein p16 INK4a in Cervical Adenocarcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):21-25
Views172See moreABSTRACT
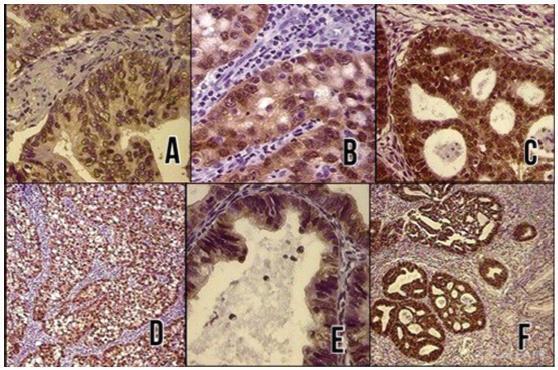
Objective:
To evaluate the diagnostic utility of the p16ink4a protein expression as a marker for adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
Methods:
In a cross-sectional study, p16ink4a expression was evaluated in 30 cervical biopsies from patients diagnosed with invasive adenocarcinoma from 2 reference clinics in Brazil, and compared with 18 biopsies of endocervical polyps (control cases). The performance of the tests for p16ink4a was evaluated using a conventional contingency table, and the Kappa (k) index was used to evaluate the agreement of the marker with the tissue diagnosis.
Results:
In total, 66% of the invasive adenocarcinoma cases were positive for p16ink4a. All of the adenomatous polyps cases used as negative controls were shown to be negative for p16ink4a. The marker showed a high sensitivity and a high negative predictive value. The Kappa index was good for p16ink4a (k 1/4 0.6).
Conclusion:
Considering the strong association between the p16ink4a marker and the cervical adenocarcinoma, its use represents an important tool for reducing incorrect diagnoses of adenocarcinoma and thereby avoiding overtreatment.
-
Original Article11-06-2013
Preterm birth prediction: sequential evaluation of the cervix and the test for phosphorylated protein-1 linked to insulin-like growth factor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):394-400
Abstract
Original ArticlePreterm birth prediction: sequential evaluation of the cervix and the test for phosphorylated protein-1 linked to insulin-like growth factor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):394-400
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900003
Views62PURPOSE: To investigate the usefulness of the measurement of cervical length and of the test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) performed sequentially in the prediction of preterm birth and the correlation between tests. METHODS: We analyzed data from 101 asymptomatic pregnant women with a history of premature delivery. The ultrasound measurement of cervical length and phIGFBP-1 test were performed in parallel every three weeks, between 24 and 34 week. The best cutoff value for each cervical evaluation was established by the ROC curve, and the two tests were compared using nonparametric tests. We determined the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of each test and of the association of the exams for the occurrence of delivery before the 37th weeks. RESULTS: There were 25 preterm births (24.8%). The cervix length showed the highest sensitivity and was able to predict preterm birth in all evaluations, with similar accuracy at different gestational ages. The test for phIGFBP-1 was not helpful at 24 weeks, but was able to predict prematurity when performed at 27, 30 and 33 weeks. The combination of tests increased the sensitivity (81.8%) and negative predictive value (93.7%) when compared to the separate use of each test. The mean cervical length was lower in women with a positive test. CONCLUSIONS: Both cervical length and the test for phIGFBP-1 were able to predict premature delivery, and sequential combination of both tests showed a high sensitivity and high negative predictive value.
Key-words Biological markersCervical length measurementCervixInsulin-like growth factor binding protein-1Premature birthRisk assessmentSee more -
Original Article03-14-1999
Validity of cytology and colposcopy – guided biopsy for the diagnosis of preclinical cervical carcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):193-200
Abstract
Original ArticleValidity of cytology and colposcopy – guided biopsy for the diagnosis of preclinical cervical carcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):193-200
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400003
Views92See morePurpose: to evaluate the efficacy of cytology and colposcopy-directed biopsy to distinguish preclinical invasive cervical carcinoma from intraepithelial lesions. Patients and Methods: 441 patients submitted to conization, hysterectomy and Wertheim-Meigs operation from 1978 to 1995 in the University Hospital "Clementino Fraga Filho", Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Cervical Pathology Outpatient Clinic. We estimated sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, likelihood ratio and confidence intervals of each study, which were divided into four classes: 1) normal and inflammatory; 2) mild and moderate dysplasias; 3) severe dysplasia and carcinoma in situ; 4) microcarcinoma and invasive carcinoma. Biopsies were analyzed as a whole and separated in accordance with the type of the colposcopic result (satisfactory and unsatisfactory). Results: cytology has shown sensitivity of 50%, specificity of 89%, positive predictive value of 63% and negative predictive value of 82%. The likelihood ratios were 4.4 for stromal invasion diagnosis, 0.7 for severe dysplasia and carcinoma in situ, 0.1 for mild and moderate dysplasia, 2.2 for normal and inflammatory report and 0.6 for the negative results for invasion as a whole. Satisfactory colposcopic guided biopsy white a visible lesion showed sensitivity of 59%, specificity of 100% positive predictive value of 100% and negative predictive value of 83%. Likelyohood ratios were: tending to infinity for invasion, 0.5 for severe dysplasia and carcinoma in situ, zero for mild and moderate dysplasia, zero for negative and inflammatory and 0.4 for all negative results for invasion.
-
Original Article12-05-2006
Factors associated with false-negative cervical cytopathological results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):479-485
Abstract
Original ArticleFactors associated with false-negative cervical cytopathological results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):479-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800007
Views68See morePURPOSE: to evaluate whether factors related to the adequacy of the sample, cell pattern and cytomorphological criteria are associated with false-negative (FN) results of cervical cytopathology during routine examinations. METHODS: this is a case-control study in which the study group included 100 cytopathologic smears with FN results detected during systematic internal quality control consisting of 100% rapid review. For each FN result detected, two smears with a true-positive diagnosis were identified by the same cytotechnician and these constituted the control group, making a total sample size of 300 smears. The variables were established in accordance with the criteria defined for the analysis of sample adequacy, cell pattern and cytomorphological analyzed criteria. The results were evaluated using bivariate analysis and logistic regression with stepwise variable selection criteria expressed in OR (95%). RESULTS: the number of atypical cells, the appearance of nuclear chromatin, and the distribution and presentation of atypical cells in the smear were the variables that showed the greatest risk for FN results with OR of 9.6, 4.2, 4.4, and 3.6, respectively. Inflammatory processes and the presence of blood in the smear were also identified as variables that influence the risk of FN results. CONCLUSIONS: the majority of the factors associated with FN results are dependent on the conditions and techniques of sample collection, since in the majority of cases, the lesion may not be adequately represented in the smear. Confounding factors such as blood and inflammatory processes may also impair analysis. With respect to cytomorphological alterations, thin chromatin strand was the variable that indicated the greatest risk of FN results.
-
Original Article07-06-2005
Cervical visual inspection after application of acetic acid in screening intraepithelial neoplasia and HPV-induced lesions
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):51-57
Abstract
Original ArticleCervical visual inspection after application of acetic acid in screening intraepithelial neoplasia and HPV-induced lesions
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):51-57
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000200002
Views126See morePURPOSE: to estimate the validity of visual inspection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and HPV-induced lesion screening, after acetic acid application (VIA), and to compare its performance with that of colpocytology and colposcopy. METHODS: a diagnostic test validation study involving 893 women aged 18 to 65 years, simultaneously screened with colpocytology, VIA and colposcopy was carried out at a public health unit in Recife, PE. VIA was performed by applying 5% acetic acid onto the cervix and observing it with the help of a clinical spotlight. The finding of any aceto-white lesion on the cervix was considered positive. The gold standard was the histopathology of cervical biopsy, carried out whenever any of the three test results was abnormal. Validity indicators were estimated for each test, within 95% confidence intervals. The analysis of agreement between test results was done by the kappa coefficient. RESULTS: of 303 women submitted to biopsy, the histopathological study was abnormal in 24. Among this total, VIA was positive in 22, yielding an estimated 91.7% sensibility, 68.9% specificity, and 7.5% positive predictive value and 99.7% negative predictive value. Comparing 95% confidence intervals, VIA was more sensitive than colpocytology, despite a lower specificity and positive predictive value. There was poor agreement between VIA and colpocytology (k=0.02) and excellent agreement with colposcopy (k=0.93). CONCLUSION: VIA was much more sensitive than colpocytology in the screening of CIN and HPV-induced lesions and presented a performance similar to colposcopy. Its low specificity determined a high number of false-positive results.
-
Original Article01-19-2004
Bacterial vaginosis and high-risk HPV-DNA in women submitted to diathermic conization for the treatment of high-grade cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(9):721-725
Abstract
Original ArticleBacterial vaginosis and high-risk HPV-DNA in women submitted to diathermic conization for the treatment of high-grade cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(9):721-725
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900008
Views124See morePURPOSE: to analyze the association between bacterial vaginosis (BV), high-risk HPV DNA, and Pap smear abnormalities in women submitted to diathermic conization for the treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN 2 or 3). METHODS: a descriptive clinical study with 81 women submitted to diathermic conization for the treatment of CIN 2 or 3. Initial Pap smear was performed by the time of the biopsy and was also used to verify the presence of BV. Prior to conization, samples for the detection of high-risk HPV DNA through hybrid capture II (HC II) were collected. A control visit was scheduled for four months after the conization to repeat these tests. Twenty-seven women were found to have BV and 54 were not. Statistical analysis comprised odds ratios (OR) to assess the correlations between BV and HPV detection before and after diathermic conization and cytological abnormalities. All analyses were performed with a 95% confidence interval (95% CI). RESULTS: high-risk HPV DNA detection before conization was identical in both groups (89%). After conization, HPV DNA detection decreased to 26 and 18% in the groups with and without BV, respectively (OR=1.5; 95% CI 0.5 to 4.6). In addition, 41% of the women with BV and 20% without BV showed Pap smear abnormalities (OR=2.7; 95% CI 1.0 to 7.4). Regarding these 22 women with Pap smear abnormalities approximately four months after the diathermic conization, 83% of the BV group tested positive for HPV DNA compared with 50% in the group without BV (OR=5.0; IC 95% 0.5 a 52.9). CONCLUSION: women with BV presented more Pap smear abnormalities after conization when compared to the women without BV, although this was not statistically significant. This association was not related to high-risk HPV DNA.
-
Original Article07-20-2004
Evaluation of alternative methods in cervical screening: HPV DNA detection and visual inspection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):269-275
Abstract
Original ArticleEvaluation of alternative methods in cervical screening: HPV DNA detection and visual inspection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):269-275
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400002
Views16See moreOBJECTIVE: to evaluate the performance of Pap smear, hybrid capture II (HC II), and visual inspection with acetic acid in the detection of pre-invasive and invasive cervical lesions. METHODS: a total of 2281 women were submitted to a clinical exam, including Pap smear, HC II for HPV DNA detection and visual inspection with 5% acetic acid (VIA). When at least one of the tests was positive, colposcopy was performed and targeted biopsies were taken from suspicious lesions. Colposcopy was also performed in 420 women with negative results. Test performance was evaluated, using colposcopy as the gold standard, with or without biopsy. RESULTS: Pap smear, VIA and HC II were positive in 9.2, 10.9 and 17.5% of all women screened, respectively. Although at least one positive test was found in 671 women (29.4%), only 82 (3.6%) presented histologically confirmed disease (50 NIC1, 20 NIC2, 7 NIC3, and 5 invasive carcinoma). VIA and HC II sensitivities were similar and significantly higher than Pap smear. Pap smear showed better specificity than VIA and than HC II. In women with a negative Pap smear result, VIA showed better performance than HC II. CONCLUSION: Pap smear combined with VIA performed better than Pap smear combined with HC II or than Pap smear alone.


