-
Review Article
Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination for Cancer Patients: Risk or Benefit?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):602-608
08-15-2022
Summary
Review ArticleCoronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination for Cancer Patients: Risk or Benefit?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):602-608
08-15-2022Views112See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of the present study is to list the published clinical trials on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines, to describe the mechanism of action of the identified vaccines, and to identify protocols regarding safety, status, and prioritization of cancer patients for vaccination.
Methods
This is a systematic review with a limited literature search conducted by an information specialist; key resources such as PubMed and websites of major cancer organizations were searched. The main search terms were COVID-19, vaccination, cancer, and breast and gynecological cancers.
Results
Cancer patients infected with the new coronavirus are at high risk of complications and death, but we still know little about the risks and benefits of vaccination for COVID-19 in these patients. In an ideal scenario, all cancer patients should have their immunization status updated before beginning treatment, but this is not always possible.
Conclusion
Patients with breast or gynecological cancers who are receiving treatment or are in the 5-year posttreatment period should be included in the priority group for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination.
-
Case Report
Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology to Identify a Rare Mimicker of Breast Cancer: Plasma Cell Mastitis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):491-493
08-01-2018
Summary
Case ReportFine-needle Aspiration Cytology to Identify a Rare Mimicker of Breast Cancer: Plasma Cell Mastitis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):491-493
08-01-2018Views108See moreAbstract
There are rare benign diseases that can mimic malignant breast neoplasms in the clinical exam and in mammography. We evaluated the contribution of an accessible procedure to most clinicians, the fine-needle aspiration cytology, to identify a rare mimicker of malignant breast neoplasms. A type 2 diabetic 85-year-old female presented with a 6-month history of a left breast lump. The physical exam and mammography were compatible with breast cancer. Nevertheless, after fine-needle aspiration cytology, the diagnosis was plasma cellmastitis. Once this rare diagnosis was established, the tumor was extirpated, and the final histologic diagnosis corroborated chronic plasma cellmastitis. The patient’s postoperative evolution was uneventful, and no other treatment was needed. Fine-needle aspiration cytology could be a valuable tool to identify rare mimickers of malignant breast neoplasms.
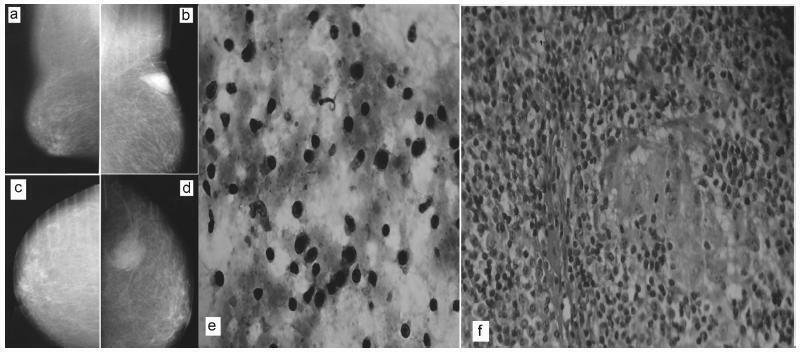
-
Review Article
Common Dysregulated Genes in Endometriosis and Malignancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):253-262
05-01-2016
Summary
Review ArticleCommon Dysregulated Genes in Endometriosis and Malignancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):253-262
05-01-2016Views107See moreAbstract
Several authors have investigated the malignant transformation of endometriosis, which supports the hypothesis of the pre-neoplastic state of endometriotic lesions, but there are few data about the pathways and molecular events related to this phenomenon. This review provides current data about deregulated genes that may function as key factors in the malignant transition of endometriotic lesions. In order to do so, we first searched for studies that have screened differential gene expression between endometriotic tissues and normal endometrial tissue of women without endometriosis, and found only two articles with 139 deregulated genes. Further, using the PubMed database, we crossed the symbol of each gene with the terms related to malignancies, such as cancer and tumor, and obtained 9,619 articles, among which 444 were studies about gene expression associated with specific types of tumor. This revealed that more than 68% of the analyzed genes are also deregulated in cancer. We have also found genes functioning as tumor suppressors and an oncogene. In this study, we present a list of 95 informative genes in order to understand the genetic components that may be responsible for endometriosis' malignant transformation.
However, future studies should be conducted to confirm these findings.
-
Case Report
Lobular Carcinoma in Situ with Atypical Mass Presentation: a Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):112-116
02-01-2016
Summary
Case ReportLobular Carcinoma in Situ with Atypical Mass Presentation: a Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):112-116
02-01-2016Views170See moreLobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and accounts for 1 to 2% of all breast cancers. LCIS diagnosis currently remains one of the major identifiable risk factors for subsequent breast cancer development. Imaging methods are becoming increasingly sensitive, and the consequent detection of small lesions and subtle abnormalities increases the chance of detection of in situ and invasive carcinomas, leading to a reduction in mortality. This report describes a case of a palpable complaint with abnormal imaging findings, including a solid LCIS mass.
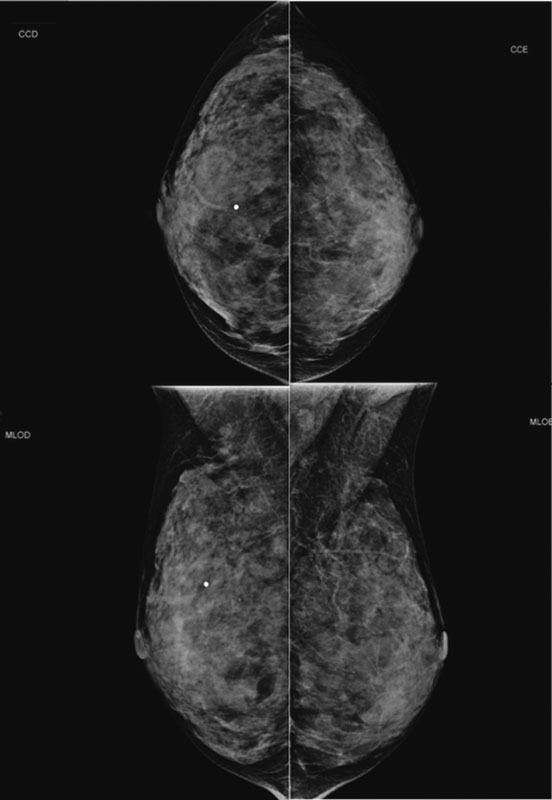
-
Trabalhos Originais
Endogenous sexual steroids and gonadotrophins in women with or without endometrial carcinoma: a comparative clinical study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):267-271
04-12-1998
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisEndogenous sexual steroids and gonadotrophins in women with or without endometrial carcinoma: a comparative clinical study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):267-271
04-12-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500006
Views87See moreObjective:To analyze the levels of endogenous sexual steroids and gonadotrophin in women with and without endometrial cancer. Methodology:We developed a clinical comparative study on 20 postmenopausal women with endometrial cancer and 20 postmenopausal women without endometrial cancer. The age, the postmenopausal time and the index of body mass were used as matching variables. The plasma levels of the endogenous sexual steroids were measured using radioimmunoassay and immunoenzymatic methods. For the statistic analysis we used the Student's t test. Results: The levels of androstenedione (A), total testosterone (t) and free testosterone (TL) were higher in the women with endometrial cancer, and those of the luteinic hormone (LH) were significantly lower values in these women. We also observed that the ratio (E1/A) showed significantly lower in the group of women with cancer, while the ratio (E2/E1) did not present any differences between groups. Conclusions: We emphasize the potentiality of sexual steroids and gonadotrophins in the genesis of endometrial adenocarcinoma in postmenopausal women.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Duration of Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Invasive Carcinoma of the Cervix in Relation to Age at Diagnosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):565-569
04-04-1998
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisDuration of Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Invasive Carcinoma of the Cervix in Relation to Age at Diagnosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):565-569
04-04-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000004
Views76See morePurpose: to estimate the duration of cervical neoplasia from human pappilomavirus (HPV) infection to advanced invasive carcinoma, using as paremeter the mean age of the women at diagnosis. Methods: this cross-sectional study included 1,177 women with HPV infection, 1,561 with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and 773 with invasive carcinoma. Results: the mean ages of CIN 1 and CIN 2 on diagnosis were not statistically different. The mean duration of CIN 2 was 2.2 years. The mean duration of CIN 3 was 10.3 years, with 4.1 years as severe dysplasia and 6.2 years as carcinoma in situ (CIS). The mean duration of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions was 12.5 years. The duration means of invasive carcinoma stages Ia, Ib and II were 3.0, 2.7 and 3.7 years, respectively. Conclusions: according to the results, CIN 1 and CIN 2 may arise directly from HPV infection and most of these lesions are transient. CIS presented the longest duration and the mean asymptomatic period of cervical neoplasia is 18.2 years. These results were discussed considering the present knowledge of the natural history of cervical carcinoma and other studies on duration of this neoplasia.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subclinical Breast Lesions
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):69-76
03-20-1999
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisCore Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subclinical Breast Lesions
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):69-76
03-20-1999DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200003
Views51See morePurpose: to evaluate core biopsy (CB) for the diagnosis of subclinical breast lesions, comparing with surgical biopsy previously identified by stereotaxic mammography. Methods: this is a cross-sectional study of 41 subclinical lesion cases over 35 years of age, between January 1995 and February 1997 at the Instituto de Ginecologia da Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro. The cases were classified mammographically as benign, probably benign, suspicious and malignant. Benign and probably benign lesions were studied together for statistical purposes. The histopathologic diagnosis of CB was classified as inadequate for diagnosis, absence of malignancy, suspicious and malignant. The histopathologic diagnosis of the surgical biopsy was classified as absence of malignancy, pre-malignant and malignant. The sensitivity, especificity and predictive values of CB were evaluated. Mammography likelihood ratio and core biopsy likelihood ratio were evaluated to predict breast cancer. Results: CB coincided with surgical biopsy in 86.2% of the 29 cases of absence of malignancy. All cases suspected by CB were malignant by surgical biopsy. All cases malignant by CB were also malignant by surgical biopsy. CB sensitivity and specificity were 36.4% and 100%, respectively. Positive predictive value was 100% and negative predictive value was 78.1%. In the group classified mammographically as malignant the likelihood ratio was 9.7; for suspicious lesions it was 1.3 and for probably benign lesions it was 0.1. Core biopsy likelihood ratio was infinite (¥) for suspicious and malignant lesions, 0.4 for cases classified as absence of malignancy and 1.4 for inadequate for diagnosis cases. Conclusions: after analysis of the results, with the use of the likelihood ratio, we conclude that CB report of absence of malignancy did not allow to rule out the diagnosis of malignancy. In these cases, we should correlate the result with mammography. If CB shows absence of malignancy and there is no correlation with mammography, the research must be continued. When the report of CB was suspicious, the probability of a breast carcinoma was very high. In these cases, we should perform a surgical biopsy to establish a definitive diagnosis, because an infiltrating carcinoma needs a different therapy when compared with carcinoma in situ and atypical hyperplasia. In the cases of histopathologic report of malignancy, the probability of breast cancer was high, since we did not observe any false positive CB. In these cases, CB allowed a quick diagnosis without the need of surgical biopsy.
-
Relato de Caso
Squamous cell carcinoma of the breast tissue: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):419-421
08-07-1999
Summary
Relato de CasoSquamous cell carcinoma of the breast tissue: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):419-421
08-07-1999DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700009
Views68See moreSquamous cell carcinoma of the mammary tissue is a very rare neoplasm, representing less than 1% of all breast carcinomas. The present study reports a case of squamous cell carcinoma of the breast, treated at the Hospital Araújo Jorge/ACCG. The tumor diagnosis, treatment and prognosis are also discussed.


