-
Original Article
Immunological Characteristics between αβ TDC and γδ TDC Cells in the Spleen of Breast Cancer-Induced Mice
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):368-373
07-30-2021
Summary
Original ArticleImmunological Characteristics between αβ TDC and γδ TDC Cells in the Spleen of Breast Cancer-Induced Mice
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):368-373
07-30-2021Views126See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the antitumoral role of γδ TDC cells and αβ TDC cells in an experimental model of breast cancer.
Methods
Thirty female Balb/c mice were divided into 2 groups: control group (n=15) and induced-4T1 group (n=15), in which the mice received 2 x 105 4T1 mammary tumor cell line. Following the 28-day experimental period, immune cells were collected from the spleen and analyzed by flow cytometry for comparison of αβ TDC (TCRαβ+ CD11c+MHCII+) and γδ TDC (TCRγδ+CD11c+MHCII+) cells regarding surface markers (CD4+ and C8+) and cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-12 and IL-17).
Results
A total of 26.53% of γδ TDC- control group (p<0.0001) - the proportion of αβ TDC was lower in splenic cells than γδ TDC; however, these 2 cell types were reduced in tumor conditions (p<0.0001), and the proportion of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-12 and IL-17 cytokines produced by γδ TDC was higher than those produced by αβ TDC, but it decreased under conditions of tumor-related immune system response (p<0.0001).
Conclusion
Healthy mice engrafted with malignant cells 4T1 breast tumor presented TDC with γδ TCR repertoire. These cells express cytotoxic molecules of lymphocytes T, producing anti-tumor proinflammatory cytokines.
-
Original Article
Sociodemographic and Clinical-pathological Study of Molecular Subtitles of Breast Carcinoma in a Reference Unit of Maranhão
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):820-828
01-11-2020
Summary
Original ArticleSociodemographic and Clinical-pathological Study of Molecular Subtitles of Breast Carcinoma in a Reference Unit of Maranhão
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):820-828
01-11-2020Views225See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the distribution of the main sociodemographic and clinicalpathological characteristics in women with breast cancer according to the molecular profile by immunohistochemistry.
Methods
A cross-sectional, retrospective, analytical and quantitative study was performed, with an analysis of 137 medical records from January 2015 to December 2018 of women attending the High Complexity in Oncology Unit of the city of Imperatriz, state of Maranhão, Brazil. The immunohistochemical profile of tumors based on the estrogen and progesterone receptor, Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor-type 2 (HER2) overexpression and Ki67 cell proliferation indexwas defined, fromwhich six molecular subtypes were determined: luminal A, luminal B-HER2 negative, luminal B-HER2 positive, triple negative, overexpression of HER2 and inconclusive.
Results
A total of 52.6% of the patients were postmenopausal, mean age 52.1 years old, brown (56.2%), had a schooling level < 9 years (40%), staging > IIB (52.6%) and 23.4% hadmetastasis. Invasive ductal carcinoma accounted for 84.7%, tumor size was 2 to 5 cm (48.9%), with lymph node involvement (56.2%), axillary lymphadenectomy in 67.2%, andmastectomy in 73.7% of the patients. Themost frequentmolecular subtype was the luminal B-HER2 negative (36.5%), and the luminal A subtype showed characteristics of better prognosis when compared with the others.
Conclusion
It was concluded that in the association of molecular subtypes with sociodemographic and clinical-pathological characteristics, there were no statistically significant results obtained, except for complementary therapy, referring to hormone therapy, and there was a high index of metastasis at diagnosis, which was a worrying factor and indicative of failures in the screening and early diagnosis of this population.
-
Original Articles
Association of Menopausal Status, Expression of Progesterone Receptor and Ki67 to the Clinical Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Luminal Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(12):710-717
02-03-2019
Summary
Original ArticlesAssociation of Menopausal Status, Expression of Progesterone Receptor and Ki67 to the Clinical Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Luminal Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(12):710-717
02-03-2019Views97Abstract
Objective
To identify the biomarkers of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in early luminal breast cancer.
Methods
A cross-sectional study that included all patients with early or locallyadvanced luminal breast cancer submitted to neoadjuvant chemotherapy between 2013 and 2014. Demographic, clinic and pathologic data were retrieved from patient records. The expressions of the estrogen receptor (ER), the progesterone receptor (PR), and Ki67 were analyzed by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The status of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) was evaluated by IHC and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). Independent predictors of clinic and pathologic response were evaluated by stepwise logistic regression models and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results
Out of 298 patients identified, 115 were included in the analysis. Clinical complete response (cCR) was observed in 43.4% of the patients (49/113), and pathologic complete response (pCR) was observed in 7.1% (8/115) of the patients. The independent predictors of cCR were premenopausal status (p < 0.001), low PR expression (≤ 50% versus > 50%; p = 0.048), and Ki67 expression ≥ 14% (versus < 14%; p = 0.01). Patients with cCR were more commonly submitted to breast conserving surgery (34.7% versus 7.8%; p < 0.001). Increasing cut-off points for Ki67 expression were associated with an increase in specificity and a decrease in sensitivity to identify patients with cCR.
Conclusion
Premenopausal status, lower PR expression and higher Ki67 expression were associated with a higher rate of cCR to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in luminal breast cancer.
Key-words antineoplastic agentsBreast neoplasmsestrogen receptorsNeoadjuvant therapysegmental mastectomySee more -
Review Articles
Impacts of Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) Genetic Polymorphism in Tamoxifen Therapy for Breast Cancer Impactos do polimorfismo genético do citocromo P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) na terapia com tamoxifeno para câncer de mama
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):794-799
12-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticlesImpacts of Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) Genetic Polymorphism in Tamoxifen Therapy for Breast Cancer Impactos do polimorfismo genético do citocromo P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) na terapia com tamoxifeno para câncer de mama
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):794-799
12-01-2018Views139See moreAbstract
Tamoxifen (TMX) is the main drug used both in pre and postmenopausal women as adjuvant treatment for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. An important barrier to the use of TMXis the development ofdrug resistance causedby molecular processes related to genetic and epigenetic mechanisms, such as the actions of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) polymorphisms and of its metabolites. The present study aimed to review recent findings related to the impact of CYP2D6 polymorphisms and how they can affect the results of TMX in breast cancer treatment. The keywords CYP2D6, tamoxifen, and breast cancer were searched in the PubMed, Scopus, The Cochrane Library, Scielo, and Bireme databases. Studies related to other types of neoplasms or based on other isoenzymes from cytochrome P450, but not on CYP2D6, were excluded. The impact of CYP2D6 polymorphisms in the TMX resistance mechanism remains unclear. The CYP2D6 gene seems to contribute to decreasing the efficacy of TMX, while the main mechanism responsible for therapy failure, morbidity, and mortality is the progression of the disease.
-
Original Article
Does Knowing Someone with Breast Cancer Influence the Prevalence of Adherence to Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):203-208
04-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleDoes Knowing Someone with Breast Cancer Influence the Prevalence of Adherence to Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):203-208
04-01-2018Views96Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the prevalence of adherence to screening methods for breast and cervical cancer in patients attended at a university hospital and to investigate whether knowing someone with breast cancer, moreover belonging to the patient’s family, affects the adherence to the screening recommendations.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional and quantitative study. A structured interview was applied to a sample of 820 women, between 20 and 69 years old, who attended a university hospital in the city of Juiz de for a, MG, Brazil. For the analysis, the chi-square test was used to assess possible associations between the variables, and the significance level was set at p-value ≤ 0.05 for a confidence interval (CI) of 95%.
Results
More than 95.0% of the sample performed mammography and cervical cytology exam; 62.9% reported knowing someone who has or had breast cancer, and this group was more likely to perform breast self-examination (64.9%; odds ratio [OR] 1.5; 95% CI 1.12-2.00), clinical breast examination (91.5%; OR 2.11; 95% CI 1.37-3.36), breast ultrasound (32.9%; OR 1.81, 95% CI 1.30-2.51), and to have had an appointment with a breast specialist (28.5%; OR 1.98, 95% CI 1.38-2.82).Women with family history of breast cancer showed higher propensity to perform breast self-examination (71.0%; OR 1.53 95% CI 1.04-2.26).
Conclusion
There was high adherence to the recommended screening practices; knowing someone with breast cancer might make women more sensitive to this issue as they were more likely to undergo methods which are not recommended for the screening of the general population, such as breast ultrasound and specialist consultation; family history is possibly an additional cause of concern.
Key-words Breast neoplasmsbreast selfexaminationMass screeningPublic healthUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
Late-Stage Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Brazil: Analysis of Data from Hospital-Based Cancer Registries (2000-2012)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):127-136
03-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleLate-Stage Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Brazil: Analysis of Data from Hospital-Based Cancer Registries (2000-2012)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):127-136
03-01-2018Views117Abstract
Objective
To analyze the time trend and the factors regarding the diagnosis of latestage breast cancer in Brazil from 2000 to 2012.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from hospital-based cancer registries. Joinpoint regression was used to analyze the time trends of stage at diagnosis. The risk of late-stage presentation was estimated using multinomial logistic regression.
Results
A total of 170,757 cases were analyzed. The median time from diagnosis to treatment was of 43 days (range: 0-182 days). The percentage of cases with late-stage diagnosis decreased from2000 to 2002, with an annual percent change (APC) of -6.6%(95%confidence interval [95%CI]: -7.6--5.5%); it increased from 2002 until 2009, with an APC of 1.1% (95% CI: 0.9-1.3%), and remained stable up to 2012.Women with college education (compared with illiterate women) had less chance of having a late-stage diagnosis (odds ratio [OR]: 0.32; 95%CI: 0.29-0.35). The odds were greater among brown women (OR: 1.30; 95%CI: 1.21-1.41) and black women (OR: 1.63; 95%CI: 1.47-1.82), compared with white women. The odds were also higher for women treated in facilities located and in the Northern region of Brazil (OR: 1.23; 95%CI: 1.04-1.45) and in the Midwest (OR: 1.61;95%CI: 1.34-1.94), compared with those treated in the southern region of the country. Age, histological type, and marital status were some of the other factors that were positively related to staging at the diagnosis.
Conclusion
Access to diagnosis of breast cancer is uneven in Brazil, and women with lower socioeconomic status present a greater probability of having an advanced stage at diagnosis.
Key-words Breast neoplasmsdisease registriesHealth services accessibilityoncologywomen’s health serviceSee more -
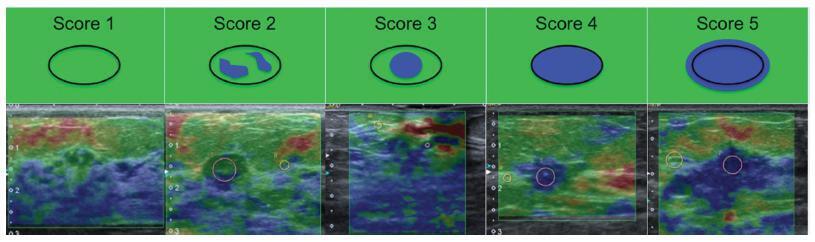
Original Article
Elastographic Evaluation of Indeterminate Breast Masses on Ultrasound
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):72-79
02-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleElastographic Evaluation of Indeterminate Breast Masses on Ultrasound
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):72-79
02-01-2017Views103See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of elastography for breast cancer identification in patients with indeterminate lesions on ultrasound.
Methods
This prospective, descriptive study included patients with indeterminate breast lesions in the ultrasound and with indication for percutaneous or surgical biopsy. The elastography was evaluated by qualitative analysis and by two methods for the semi quantitative analysis.
Results
We evaluated 125 female patients with 159 lesions, with a mean age of 47 years, and a range of 20-85 years. Ultrasound has shown to be a method with good sensitivity (98.1%), but with a lower specificity (40.6%). On the elastography qualitative analysis, the specificity and accuracy were of 80.2% and 81.8% respectively. The mean size of the lesions showed no difference in classification by elastography. For the semiquantitative elastography, the mean values of the malignant lesions were statistically higher when compared with the subcutaneous tissue or the adjacent fibroglandular tissue. The analysis of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for these two semiquantitativemethods showed that both are considered satisfactory, with an area under the curve above 0.75 and statistical significance (p < 0.0001). The best results were obtained when using the findings of combined conventional ultrasound and qualitative elastography, with 100% sensitivity and 63.2% specificity.
Conclusions
Elastography can be a useful complementary method, increasing the specificity and diagnostic accuracy of conventional ultrasound for the diagnosis of breast cancer in patients with indeterminate breast lesions.