Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):239-245
to evaluate the agreement between the clinical and pathological stagings of breast cancer based on clinical and molecular features.
this was a cross-sectional study, in which clinical, epidemiological and pathological data were collected from 226 patients who underwent surgery at the Prof. Dr. José Aristodemo Pinotti Women's Hospital (CAISM/Unicamp) from January 2008 to September 2010. Patients were staged clinically and pathologically, and were classified as: understaged, when the clinical staging was lower than the pathological staging; correctly staged, when the clinical staging was the same as the pathological one; and overstaged, when the clinical staging was greater than the pathological staging.
understaged patients were younger (52.2 years; p < 0.01) and more symptomatic at diagnosis (p = 0.04) when compared with correctly or overstaged patients. Clinicopathological surrogate subtype, menopausal status, parity, hormone replace therapy and histology were not associated with differences in staging. Women under 57 years of age were clinically understaged mainly due to underestimation of T ( tumor staging) (p < 0.001), as were the premenopausal women (p < 0.01). Patients whose diagnosis was made due to clinical complaints, and not by screening, were clinically understaged due to underestimation of N (lymph nodes staging) (p < 0.001).
the study shows that the clinicopathological surrogate subtype is not associated with differences in staging, while younger women diagnosed because of clinical complaints tend to have their breast tumors understaged during clinical evaluation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):170-176
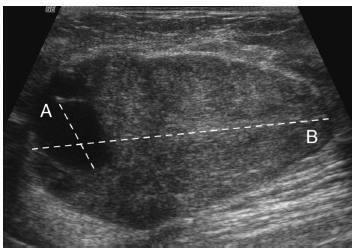
The objective of this study is to assess whether the largest cyst diameter is useful for BI-RADS ultrasonography classification of predominantly solid breast masses with an oval shape, circumscribed margins, and largest axis parallel to the skin, which, except for the cystic component, would be likely classified as benign.
This study received approval from the local institutional review board. From March 2009 to August 2014, we prospectively biopsied 170 breast masses from 164 women. We grouped the largest cyst and mass diameters according to histopathological diagnoses. We used Student's t-test, linear regression, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for statistical assessment.
Histopathological examination revealed 143 (84%) benign and 27 (16%) malignant masses. The mean largest mass diameter was larger among malignant (mean standard deviation, 34.1 16.6 mm) than benign masses (24.7 16.7 mm) (P < 0.008). The mean largest cyst diameter was also larger among malignant (9.9 7.1 mm) than benign masses (4.6 3.6 mm) (P < 0.001). Agreement between measurements of the largest mass and cyst diameters was low (R2 = 0.26). AUC for the largest cyst diameter (0.78) was similar to the AUC for the largest mass diameter (0.69) ( p = 0.2). A largest cyst diameter < 3, 3 to < 11, and 11 mm had a positive predictive value of 0, 15, and 52%, respectively.
A largest cystic component < 3 mm identified within breast masses that show favorable characteristics may be considered clinically inconsequential in ultrasonography characterization. Conversely, masses with a largest cystic component 3 mm should be classified as BI-RADS-US category 4.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):244-250
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005004
This study investigated short-term changes in body composition, handgrip strength, and presence of lymphedema in women who underwent breast cancer surgery.
Ninety-five women participated in a cross-sectional study, divided into two groups: Control (n=46), with healthy women, and Experimental (n=49), with women six months after breast cancer surgery . The Experimental Group was subdivided into right total mastectomy (RTM, n=15), left total mastectomy (LTM, n=11), right quadrant (RQ, n=13), and left quadrant (LQ, n=10). It was also redistributed among women with presence (n=10) or absence (n=39) of lymphedema. Presence of lymphedema, handgrip strength, and body composition were assessed.
Trunk lean mass and handgrip strength were decreased in the Experimental Group. Total lean mass was increased in the LTM compared to RTM or LQ. Left handgrip strength in LTM was decreased compared to RTM and RQ and in LQ compared to RTM and RQ. Finally, total lean mass, trunk fat mass, trunk lean mass, right and left arm lean mass were increased in women with lymphedema.
Breast cancer survivors have changes in their body composition and in handgrip strength six months after surgery; however, the interaction between the type of surgery and its impact is unclear. Furthermore, women who developed lymphedema in this period showed more significant changes in the body composition, but they were not enough to cause impairment in handgrip strength.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):209-213
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400006
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple method and free from complications, among great value in mastology. Its accuracy can suffer the influence of several factors, among which we can highlight the experience of the physician who performs it. With the objective of verifying the effectiveness of FNAC performed by general gynecologists, 341 patients were studied concerning the relationship between the results of FNAC and the histology of the breast lesion. We obtained sensitivity of 70.87%, specificity of 70.58%, predictive positive value of 92.40%, predictive negative value of 89.36% and accuracy of 70.67%. We concluded that FNAC is of great value in handling breast lesions and can be appropriately performed by general gynecologists. The method, however, may lead to errors of diagnosis. We do not recommend, therefore, the use of the result of FNAC as a definitive diagnosis; instead this result must be interpreted in the context of the clinical diagnosis and mammography.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):463-467
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800006
Purpose: to evaluate, in a prospective way, the performance of the fine needle aspiration biopsy in the differential diagnosis of palpable breast masses. Method: the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values for this test were evaluated in 102 women with age above 30 years and a palpable breast mass, who were attended at the University of Campinas. All punctures were performed by the same examiner. Results: the procedure had a sensitivity of 97%, specificity of 87%, positive predictive value of 94% and negative predictive value of 93%. The insufficient or unsatisfactory sample rate was 16% for the first aspiration, decreasing to 2% with a new procedure. Conclusions: this test showed to be highly sensitive and specific for the differential diagnosis of palpable breast masses, reassuring its great importance for the clinical approach of palpable masses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):187-192
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400002
Purpose: analysis of histopathologic alterations caused by neoadjuvant chemotherapy (fluorouracil, epirubicine, cyclophosphamide; FEC - 4 cycles) at the tumor site, adjacent mammary tissue and homolateral lymph nodes, as observed in sections of patients with primary breast carcinomas. Method: histological studies performed on 30 surgical sections obtained from radical mastectomy (Patey) of patients with primary breast carcinomas, who underwent prior neoadjuvant systemic therapy. Results: all sections showed tumor regression with variable intensity. This regression occurred irregularly, several refractory tumor cells remaining at the primary tumor site. Resistant tumor cells, independent of the primary tumor, were found in mammary tissue. Other histopathological findings, resulting from chemotherapy in tumoral and mammary tissues, such as calcifications and fibrosis, and in axillary homolateral lymph nodes were obtained. Conclusion: the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is not uniform, refratory tumor cells remaining not only at primary tumor site, but also in distant regions. Furthermore, we found no correlation between the regression of the tumor and the axillary metastatic lymph nodes. Thus, a conservative surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (FEC) should be avoided.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):133-137
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000300003
Purpose: to evaluate how knowledgeable medical students at the Universidade Federal de Goiás were concerning the basic diagnostic principles breast cancer. The study also aimed at promoting a debate among the students and at assessing the understanding of the students in the fifth year of medical school, who had already attended the Gynecology course. Methods: Through questionnaires given to 348 individuals, from the first to the fifth year, out of a total population of 550 students, the authors searched for information with regard to basic knowledge on the diagnosis of breast cancer. Of the 348 questionnaires, 55 (16%) were given to fifth-year students, who had already attended the Gynecology course. Furthermore, 43% of the students were women, 62% had medical doctors in their immediate family, and 17% had a family history of breast cancer. Results: in regard to the knowledge of diagnostic methods, 84% of the students were aware of the most frequent sign of breast cancer, 34% knew which was the best screening method, 49% knew when to refer asymptomatic women to mammography, 37% knew the recommended interval between mammography for women above the age of 50, and 24% knew when to associate ultrasound to mammography for the detection of breast cancer. The fifth-year students provided correct answers at a significantly higher rate, when compared to the others. Concerning gender, the only difference regarded the fact that women showed a better knowledge as to the best time for self-examination and when to recommend ultrasound associated with mammography. The presence of medical doctors in the family and a history of family members with breast cancer did not have any influence on the answers. Conclusion: The lack of information in regard to the diagnosis of breast cancer is very high, even among medical students. Nevertheless, the rate of information increases significantly after students are taught Gynecology, which is only offered during the fifth year of the medical school.