Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):287-290
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500007
Purpose: to evaluate the knowledge and practice of breast self-examination among medical students and to determine possible factors associated with this practice. Method: the authors used a questionnaire to gather information about the students and their knowledge of this self-examination. This questionnaire also allowed the authors to verify the frequency with which the female students performed breast self-examination. The chi² test and Student's "t" test were used, when applicable, to check the association of certain factors. Results: of the 348 questionnaires which were answered, 16% (55) were submitted by 5th year medical students, who had already attended the Gynecology course; 43% were answered by females, 62% of the students had medical doctors among their relatives, and 17% had a family history of breast cancer. In terms of breast self-examination, 95% knew about the method. Of the 149 females who answered the questionnaire, only 64% checked their breasts regularly. The reasons given for not performing self-examination varied: 24% considered themselves to be too young, 4% thought they would not have cancer, 9% listed fear as the reason, 19% reported they were too lazy, and 44% of the female students had no clear reason for not performing breast self-examination. Neither the knowledge nor the practice of the breast self-examination were associated with the subjects the students had or had not yet taken in medical school, with a family history of breast cancer or with the fact that one or more relatives were medical doctors. Conclusion: breast self-examination is known by practically all the medical students; nevertheless, only one third of the female students performed it regularly. This fact highlights the importance of emphasizing breast self-examination among medical students, so that they can help to disseminate this practice among the general population, rather than delegating this responsibility to the midia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(6):323-326
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000600004
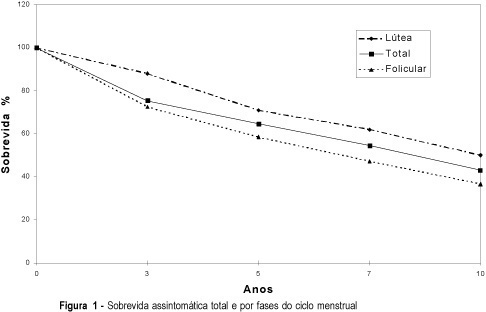
Purpose: to offer new data for the conflicting reports which present different prognosis for patients with breast carcinoma, according to the timing of surgery in relation to the menstrual cycle. Patients and Methods: in a retrospective study on 451 premenopausal women with breast cancer, aged between 26 and 52 years, 130 cases were selected and followed for 60 months, at least. Sixty-eight were operated during the follicular phase and 62 in the luteal period, whose findings regarding clinical stages, axillary involvement and estrogen and progesterone hormonal receptor concentrations of the neoplasms were also analyzed. Results: the follow-up of 130 patients showed that 64.4% had a disease-free survival after five years and 43% exceeded 10 years. Subdividing the cases into 2 subgroups, according to the timing of surgery, the survival rates were different, 58.8% at 5 and 36.7% at 10 years, when the operation occurred in the follicular phase, and 70.9% and 50%, at 5 and 10 years, respectively, during the luteal period. Conclusions: in this study, the patients operated in the luteal phase reached higher survival rates than the women operated during the follicular period. However, these values were lower than those displayed by the classic prognostic factors of axillary involvement and tumor size.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):79-87
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200004
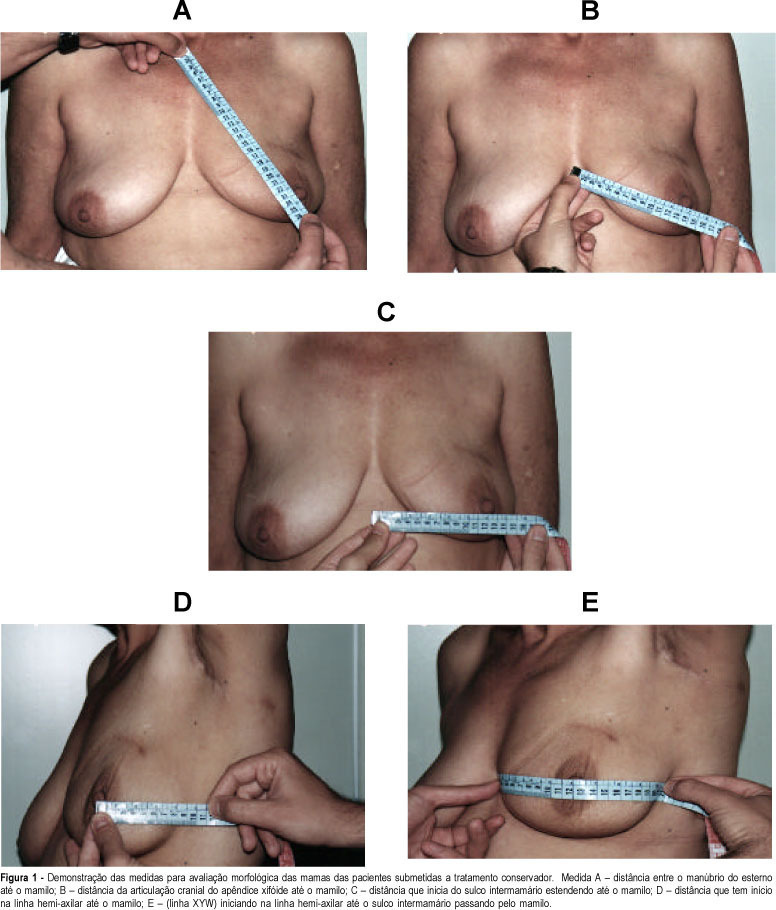
Purpose: to assess the esthetic results and personal satisfaction of patients submitted to conservative surgery for cancer of the breast. The study was conducted on 44 patients with breast cancer diagnosed at the mastology outpatient clinic of HCFMRP-USP from January 1990 to December 1994, who fulfilled inclusion criteria according to a previously established protocol. The study consisted of analysis of the esthetic results after conservative treatment of breast cancer and analysis of the degree of patient satisfaction, with a comparison of the morphometry of the treated breast to that of the normal breast. The results were obtained on the basis of five previously established parameters using the esthetic evaluation score proposed by Westreich¹. Methods: of the 44 patients studied, 10 had been submitted to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (CT) because they presented locally advanced tumors, and 2 because of an unfavorable tumor/breast ratio for conservative treatment. Mean follow-up time was 65 months. All 27 patients followed-up at the outpatient clinic received a convocation letter. An evaluation questionnaire was applied to the 20 patients who came to the clinic, followed by breast measurement. Fifteen of these patients had been submitted to surgery with separate incisions and 5 to surgery with a single incision. Results: according to morphometry, the results were classified as excellent in 17 cases (85%), as good in two (10%), and as poor in only one case (5%), an evaluation comparable to the subjective evaluation made by the patients themselves. Considered separately, both measurement "A" (distance from the manubrium of the sternum to the nipple) and measurement "B" (distance from the cranial articulation of the xyphoid appendix to the nipple) showed a greater discriminative power than the measurements as a whole, since with these measurements the cases classified as poor by the patients would have also been classified as poor according to these same criteria separately (A and/or B). Conclusion: there was a significant difference in esthetic results between surgical treatment with a single incision or separate incisions, with the separate incision providing better results. There was high agreement between the classification made by the patients and the morphometric results obtained by us.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):125-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200007
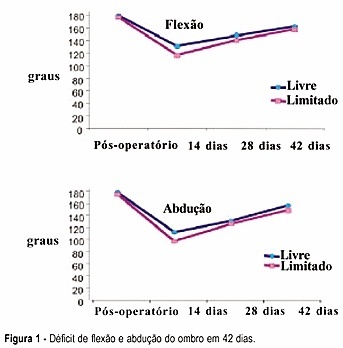
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficacy of a physical exercise protocol in the recovery of shoulder movement in women who underwent complete axillary lymph node dissection due to breast carcinoma, comparing free and restricted amplitude movements. METHODS: 59 women who underwent complete axillary lymph node dissection associated with modified mastectomy (46) or quadrantectomy (13) were included in this clinical, prospective and randomized study. On the first day after surgery 30 women were randomized to do the shoulder movement with free amplitude and 29 women had this amplitude restricted to 90º in the first 15 days. Nineteen exercises were done, three sessions per week, for six weeks. Mean (± standard error) deficits of shoulder flexion and abduction were compared, as well as gross and adjusted incidence rates of seroma and dehiscence. RESULTS: 42 days after surgery, flexion and abduction means were similar in the two groups. Both presented a mean flexion deficit (17.2º and 21.6º, respectively), and abduction deficit (19.7º and 26.6º, respectively). The incidence rates of seroma and dehiscence were neither related to exercise nor to the type of surgery, time of drain permanence, number of dissected or compromised lymph nodes, age or obesity. CONCLUSION: early physiotherapy with free movement of the women's shoulder was associated neither with functional capacity nor with postsurgical complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):37-42
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the accuracy of directional vacuum-assisted biopsy (mammotomy), guided by ultrasonography, in the diagnosis of nonpalpable breast lesion, as compared with excision biopsy, and to evaluate the therapeutic value of mammotomy in nonpalpable benign lesions. METHODS: 114 patients, who presented nonpalpable breast lesion, visible on ultrasonography, were included. The patients were referred to complementary ultrasonographic evaluation due to mastalgia or earlier found mammographic alteration. All were submitted to mammotomy guided by ultrasonography using Mammotome® (Biopsys, Irvine, Califórnia), with a 11 gauge needle. The excision biopsy was performed with previous puncture of those patients who presented residual lesion after the mammotomy, that is, 88 patients. To evaluate comparatively the mammotomy results with those of excision biopsy, the sensitivity and specificity rates, positive and negative predictive values, and the agreement proportion were calculated. Not only the sensibilities, but also the specificities and the agreement proportions of both examinations were compared through Wald statistics, using a model for classified data. RESULTS: of 114 patients, 88 were submitted to excision biopsy. The remaining 26 did not show post-mammotomy lesions visible on ultrasonography, and for one year they were without alterations on the bi-annual mammographic and ultrasonographic examinations. The diameter of those lesions was less than 1.5 cm. Among the 88 patients that underwent excision biopsy, 69 (78,4%) showed benign and 19 (21,6%), malignant lesions. Mammotomy diagnosed 16 of the malignant lesions, with three false-negative and no false-positive results. The false results occurred in the first cases, showing the existence of a learning curve of the method, or due to technical difficulty such as the blurring of ultrasonographic image by bleeding. The sensitivity and specificity were 84,2% and 100%, respectively, with 100% positive predictive and 95,8% predictive negative values. The mammotomy accuracy was 96,6%. Complications were rare: two cases of hematomas, none of them needing surgical drainage; a case of vasovagal reflex not allowing the conclusion of the examination. The cosmetic results were very favorable due to small incisions (3 mm) and to the smaller amount of excised tissue. CONCLUSION: mammotomy guided by ultrasonography showed to be a diagnostic method with high accuracy, and it may be used as therapy for benign, smaller than 1.5 cm lesions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):45-52
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the relationship between epidemiologic, anthropometric, reproductive and hormonal factors and mammographic density in postmenopausal women. METHODS: this is a retrospective, cross-sectional study, including 144 women aged 45 years or more, with at least 12 months of amenorrhea and who were non users of hormone replacement therapy during the last six months. Medical charts were reviewed to evaluate age, weight, body mass index (BMI), parity, age at menarche, age at menopause and levels of estradiol, follicle stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing hormones. Mammograms were analyzed by two blinded investigators. The films were taken in the craniocaudal and mediolateral views and mammography was classified as dense and nondense, according to the Wolfe criteria. For statistical analysis, the frequency, median, minimum and maximum values, the Wilcoxon test and the odds ratio were used. Multiple logistic regression was performed, using the stepwise selection, with a 5% significance level. RESULTS: the frequency of dense breasts was 45%. Women with dense breasts were of lower weight (60.5 vs. 71.9 kg - p<0.01), had a lower BMI (25.9 vs 31.0 kg/m² - p<0.01), a shorter time since onset of menopause (6.0 vs 10 years - p<0.01) and higher levels of FSH (75.2 vs 60.3 mU/mL - p<0.01). The probability of having dense breasts decreased in women whose weight was 67 kg or more (OR = 4.0, CI 95% = 1.50-10.66), BMI was higher than 30 kg/m² (OR = 6.69, CI 95% = 1.67-36.81), time since onset of menopause was superior or equal to seven years (OR = 2.05, CI 95% = 1.05-3.99) and FSH levels were lower than 134.8 mU/mL. CONCLUSION: weight, BMI, parity, time since menopause and FSH levels were significantly associated with mammographic density patterns.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(6):333-337
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000600003
Purpose: to evaluate the efficacy of conservative axillary dissection (levels I and II) in the surgical treatment of stage I breast cancer. Methods: the results of 142 mastectomies performed from January/93 to December/98 in patients with clinical stage I breast cancer (T1NO) were evaluated. Removing the axillary lymph nodes present at levels I and II, with the preservation of the pectoralis muscles, the axillary lymph nodes were dissected by the author (LAGB), and subsequently one section of each lymph node was histopathologically evaluated. Quadrantectomy was performed in 138 cases and modified mastectomy (Patey), in 4 cases. The predominance of the T1c (130 cases) was observed. Results: a total of 3,282 lymph nodes were removed (2,456 at level I and 826 at level II), with an average of 23.1 nodes per axilla. Only 68 were histologically involved (2%). "Skip" metastasis was present only in one case (0.7%). Thirty-five false negative cases were observed (24.6%), with involvement of level I in 34 cases (97.1%) and of level II in 2 cases (5.7%). We observed 107 cases with negative axillary lymph nodes (75.4%). Conclusion: the axillary dissection of levels I and II is sufficient to treat the axilla in clinical stage I breast cancer. In clinical stage II and III of the disease, the complete axillary dissection including levels I, II and III is indicated. The interpectoral Rotter group will be removed if surgically suspicious.