Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 07-01-2017;39(7):322-329
Considering the physical, mental and behavioral problems related to fetal alcohol exposure, prenatal clinical guides suggest a brief evaluation of alcohol consumption during pregnancy to detect alcohol intake and to adjust interventions, if required. Even if any alcohol use should be considered risky during pregnancy, identifying women with alcohol use disorders is important because they could need a more specific intervention than simple advice to abstain. Most screening tests have been developed and validated in male populations and focused on the long-term consequences of heavy alcohol use, so they might be inappropriate to assess consumption in pregnant women.
To analyze the internal reliability and validity of the alcohol screening instruments Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), Alcohol Use Disorders IdentificationTest- Consumption (AUDIT-C), Tolerance, Worried, Eye-Opener, Amnesia and Cut-Down (TWEAK), Rapid Alcohol Problems Screen - Quantity Frequency (RAPSQF) and Tolerance, Annoyed, Cut-Down and Eye-Opener (T-ACE) to identify alcohol use disorders in pregnant women.
A total of 641 puerperal women were personally interviewed during the 48 hours after delivery. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves and the sensitivity and specificity of each instrument using different cut-off points were analyzed.
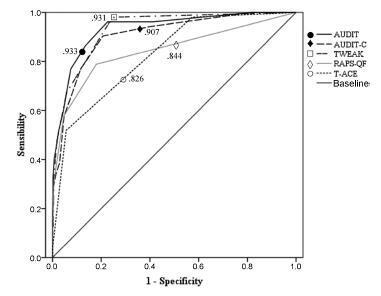
All instruments showed areas under the ROC curves above 0.80. Larger areas were found for the TWEAK and the AUDIT. The TWEAK, the T-ACE and the AUDIT-C showed higher sensitivity, while the AUDIT and the RAPS-QF showed higher specificity. Reliability (internal consistency) was low for all instruments, improving when optimal cut-off points were used, especially for the AUDIT, the AUDIT-C and the RAPS-QF.
In other cultural contexts, studies have concluded that T-ACE and TWEAK are the best instruments to assess pregnant women. In contrast, our results evidenced the low reliability of those instruments and a better performance of the AUDIT in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 08-28-2012;34(7):296-303
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700002
PURPOSE: To determine the pattern of alcohol use before and during pregnancy and associated risk factors in puerperal women hospitalized in a public university hospital in Southeastern Brazil. METHODS: Between June and September 2009, 493 puerperae were consecutively evaluated. Those with cognitive impairment were excluded from the study. The AUDIT and CAGE questionnaires were used to diagnose alcohol use/abuse before pregnancy, in addition to the T-ACE during pregnancy. Another questionnaire was applied to collect sociodemographic data, such as age, educational level, marital status, and household income. The χ² test was used in the statistical analysis and the Odds Ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95%CI) were calculated. A p-value <0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: Before pregnancy, the CAGE was positive in 50/405 (12.3%) women and the AUDIT identified alcohol use in 331 (67.1%), which was of low risk in 233 (47.3%), risky in 73 (14.8%), and harmful or indicating possible alcohol dependence in 25 (5%). During pregnancy, the CAGE was positive in 53/405 (13.1%) women and the T-ACE in 84 (17%); the AUDIT identified alcohol use in 114 women, which was of low risk in 73 (14.8%), risky in 27 (5.5%), and harmful or indicating possible alcohol dependence in 14 (2.8%). During pregnancy, alcohol use was more frequent (OR=2.8; 95%CI 1.2 - 6.2) among women with a lower educational level (8.8 versus 3.3%) and more frequent (OR=3.8; 95%CI 1.3 - 11.1) among those who did not cohabit with a partner (6 versus 1.7%). Among pregnant women who drank alcohol, 49/114 (43%) were advised to stop drinking. CONCLUSIONS: Alarming alcohol use was observed during pregnancy, especially among pregnant women with a lower educational level and those who did not cohabit with a partner. There was a low frequency of counseling aimed at abstinence and the AUDIT was the instrument that most frequently diagnosed alcohol consumption.