Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) has been evolving since 1978, with the number of techniques performed increasing over the years. Despite continued advances, some couples continue to have difficulties getting pregnant, and it has recently been considered that the microbiome of the female genital tract (FGT) may influence embryo implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. This review aims to evaluate the role of probiotics on reproductive outcomes in infertile women on ART. A search throughout medical databases was performed, and six articles met the criteria. Five studies showed improvements in pregnancy rates, with only one demonstrating statistical significance. One article showed no improvement but reported a statistically significant reduction in the miscarriage rate in the probiotic group. Further research is needed to evaluate the true potential of probiotics, namely to assess whether they effectively modulate the FGT microbiome and if these changes are maintained over time.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(8):347-352
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005209
To investigate the association of the HLA-A, -B and -DRB1 alleles with the occurrence of Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion.
A case-control study of 200 women aged 18 to 35 years, consisting of a convenience sample of 100 women who had idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion and 100 women without abortion and with two or more children. Peripheral blood genomic DNA was extracted from 500l of Buffy Coat stored at -20°C. HLA typing was performed by the PCR-SSOP method (Polymerase Chain Reaction - Specific Sequence of Oligonucleotides Probes, One Lambda(r), CA, USA). The regions of the amplified DNA were exon 2 and 3 for the A and B loci and only exon 3 for the DRB1 locus. The HLA FUSIONTM program (One Lambda, Canoga Park, CA, USA, version 3.0) was used for HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-DRB1 genotyping. Absolute frequencies and percentages and calculation of mean and standard deviation were used for standard statistical analysis. The qualitative variables were compared by the χ2 test with Yates correction or by Fisher's exact test. The odds ratio with the 95%CI was used for the comparisons, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
The frequency of the A*34 allele was significantly higher in the case group compared to control (4.0 versus 0.5%; p<0.05). Alleles A*24 (6.0 versus 12.5%; p<0.05) and B*35 (8.0 versus 20.5%; p<0.05) were significantly less frequent in the case group. Among the class II alleles, DRB1*03 showed a slightly higher frequency in the case group (11.0 versus 5.5%, p = 0.056).
It was shown that the HLA-A*34 allele is a risk factor for recurrent spontaneous abortion, while the HLA-A*24 and HLA-B*35 alleles are associated with protection, and no allele of the DRB1 locus was associated with RSA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):152-156
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0004
It was to compare pregnant women who experienced recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) and those who did not in terms of the prevalence of depressive symptoms and sexual behavior.
A prospective case-control study was carried out. The first group consisted of women with RSA and the second, of primigravidae. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) and one more questionnaire, developed by the authors themselves, about emotional aspects resulting from sexual intercourse during pregnancy were applied. The Student t-test was used to compare quantitative variables with normal distribution, and categorical variables were compared by the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test. The level of significance was set at p<0.05.
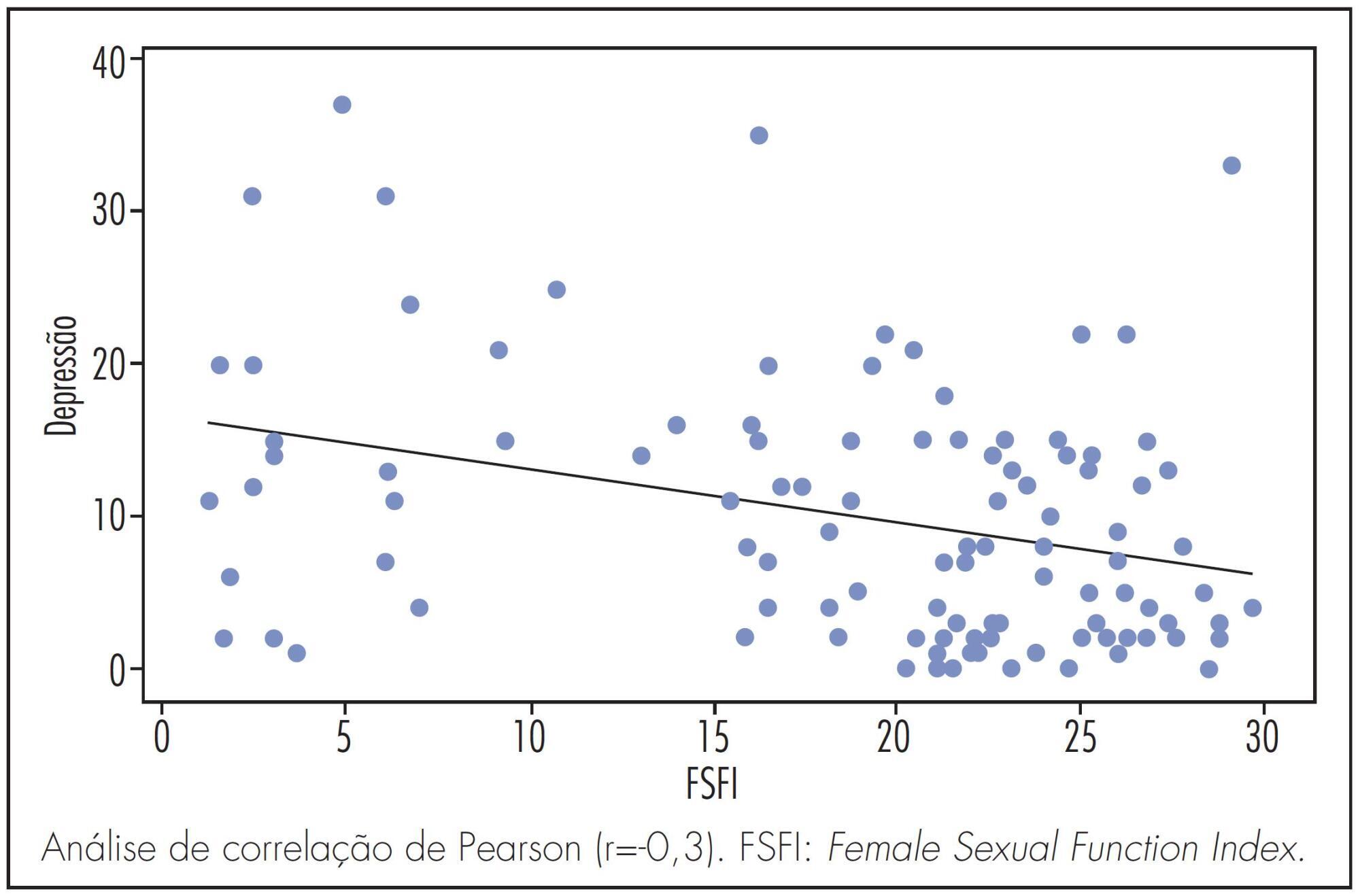
The BDI showed (19.9 versus 10.0%) approximately twice the incidence of depression in the RSA group. Regarding sexual function, the average scores of the FSFI were 21.1 and 16.4 (p<0.05) for the study and control groups, respectively, although no significant difference was observed only in the desire domain (average 3.4±1.3 for the RSA group and 3.7±1.1 for control group) (p=0.1). We observed that, regardless the presence or absence of an RSA history among the pregnant women, the higher the depression score, the lower the sexuality score (r=-0,3).
The RSA pregnant group often experiences twice higher depression and more impaired sexual function. There is an inverse association between depression and sexual function.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(3):105-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000300002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion reported by a sample of Brazilian women interviewed in the National Demographic Health Survey of 1996. METHODS: this was a secondary analysis of the Brazilian DHS-96 database, with information from interviews with a representative sample of 12,612 women about their reproductive life, focusing on the prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion in the last five years and the associated factors for the various regions of the country and for Brazil as a whole. The sampling method was implemented with a strategy selection in two stages, one for the households and the other for women. The prevalence of spontaneous and induced abortion was estimated for Brazil and regions, and the socio-demographic characteristics of the women were analyzed as a function of the abortion's experience. A multinomial regression model analysis was used for the identification of factors independently associated with both types of abortion; their OR and respective 95% CI are reported. RESULTS: the prevalence of reported spontaneous abortion was 14% and the prevalence of induced abortion was 2.4% for the country as a whole. The state with the highest prevalence of induced abortion was Rio de Janeiro with 6.5%, followed by the Northeast region with 3.1%. The places with the lowest prevalence were the state of São Paulo and the South region. Both spontaneous and induced abortion showed higher prevalences with increasing age of the women studied. Being from the urban area (OR=1.5; 95%CI=1.0-2.3), having had more than one live child (OR=2.2; 95%CI=1.5-3.2) and being non-white (OR=1.4; 95%CI=1.0-1.8) were the main risk factors for induced abortion. CONCLUSIONS: the non-modifiable risk factors for induced abortion identified in this study indicate the need for improvement of educational and contraceptive actions, with priority for these specific demographic groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):554-560
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900009
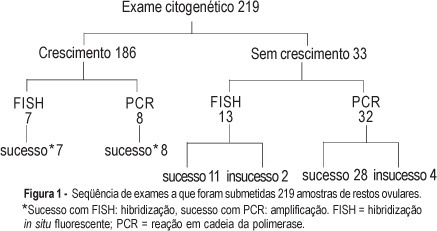
PURPOSE: to evaluate the performance of cytogenetic analysis, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the study of numerical chromosomal anomalies and in fetal sex determination of spontaneous abortion material. METHODS: cytogenetic analysis was performed on 219 spontaneous abortion specimens. Forty of these cases were also submitted to fetal sex determination using nested-PCR. Thirty-two of these cases were selected due to failed cytogenetic culture and the other eight were selected randomly. Twenty samples were submitted to the FISH technique, using probes for chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y. Thirteen of these samples were selected due to failed cytogenetic culture and the other seven were randomly selected. The success rates of each technique were compared using the chi2 test and an established p<0.05 level of significance. The results of samples submitted to more than one test were evaluated for accuracy, using the cytogenetic result as the gold standard. RESULTS: cytogenetic analysis was successful in 84.9% of the samples and in 51.1% of them the results were abnormal: 65.2% trisomy, 17.9% triploidy, 9.4% tetraploidy, 4.2% chromosome X monosomy, and 1.1% each for double trisomy, tetrasomy and structural abnormality. The most frequent trisomy was that of chromosome 16 (39%). The success rate of FISH and PCR techniques (90%) did nod differ significantly from the cytogenetic analysis. In all cases submitted to more than one test, the results were identical to those obtained through cytogenetic analysis. Samples that failed to grow on cytogenetic test and that were submitted to other techniques of molecular biology had a success rate of 87.5 and 84.6% for PCR and FISH, respectively. CONCLUSION: cytogenetic analysis of spontaneous abortions had a high success rate and chromosomal anomalies were identified in over half of the cases. Molecular biology techniques (PCR and FISH) complemented the cytogenetic study and proved to be reliable in the detection of numerical chromosomal anomalies and in fetal sex determination.