Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):578-584
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005445
To estimate the future pregnancy success rate in women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
A retrospective cohort study including 103 women seen at a clinic for recurrent pregnancy loss (loss group) between January 2006 and December 2010 and a control group including 204 pregnant women seen at a low-risk prenatal care unit between May 2007 and April 2008. Both groups were seen in the university teaching hospital the Maternidade Climério de Oliveira, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Reproductive success rate was defined as an alive-birth, independent of gestational age at birth and survival after the neonatal period. Continuous variables Means and standard deviations (SD) were compared using Student's t-test and nominal variables proportions by Pearson χ2test.
Out of 90 who conceived, 83 (91.2%) had reproductive success rate. There were more full-term pregnancies in the control than in the loss group (174/187; 92.1 versus 51/90; 56.7%; p<0.01). The prenatal visits number was satisfactory for 76 (85.4%) women in the loss group and 125 (61.3%) in the control (p<0.01). In this, the beginning of prenatal care was earlier (13.3; 4.2 versus 19.6; 6.9 weeks). During pregnancy, the loss group women increased the weight more than those in the control group (58.1 versus 46.6%; p=0.04). Although cervix cerclage was performed in 32/90 women in the loss group, the pregnancy duration mean was smaller (34.8 weeks; SD=5.6 versus 39.3 weeks; SD=1.6; p<0.01) than in the control group. Due to gestational complications, cesarean delivery predominated in the loss group (55/83; 64.7 versus 73/183; 39.5%; p<0.01).
A very good reproductive success rate can be attributed to greater availability of healthcare services to receive pregnant women, through prenatal visits (scheduled or not), cervical cerclage performed on time, and available hospital care for the mother and newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):110-114
DOI 10.1590/SO-720320150005258
To assess the reproductive outcomes after hysteroscopic septoplasty.
A retrospective observational study was performed with analysis of the medical records of 28 women with infertility or recurrent abortions undergoing hysteroscopic septoplasty. To evaluate reproductive outcomes we consulted the medical records of our hospital and of primary health care units between septoplasty and the present or first pregnancy. Primary outcomes were pregnancy rate, newborns, and abortions after septoplasty. Uterine septum was diagnosed by 2D or 3D ultrasound and classified according to the American Fertility Society. All procedures were performed in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle using monopolar or bipolar energy and/or microscissors. To compare the reproductive outcomes before and after septoplasty we used Microsoft Excel and SPSS version 17. Fisher's exact test was considered statistically significant if p<0.05.
Hysteroscopic septoplasty was performed in 20 patients (72%) with secondary infertility and in 8 patients (28%) with primary infertility. The septum was incompletely removed during the first hysteroscopy in 5 cases (18%), which required a second surgery. One case was complicated with minor uterine perforation. After hysteroscopic septoplasty, 64% of women became pregnant and 48% live neonates were delivered; 4% of the patients had a tubal pregnancy; and 19% had miscarriages.
The results of this study are consistent with those described in the literature. Patients obtained a significant improvement of reproductive outcomes with a fivefold reduction in miscarriage rate after hysteroscopic septoplasty.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):71-76
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005223
To investigate the association between polymorphisms in genes that encode enzymes involved in folate- and vitamin B12-dependent homocysteine metabolism and recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA).
We investigated the C677T and A1298C polymorphisms of the methylenetetrahydrofalate reductase gene (MTHFR), the A2756G polymorphism of the methionine synthase gene (MS) and the 844ins68 insertion of the cystathionine beta synthetase gene (CBS). The PCR technique followed by RFLP was used to assess the polymorphisms; the serum levels of homocysteine, vitamin B12 and folate were investigated by chemiluminescence. The EPI Info Software version 6.04 was used for statistical analysis. Parametric variables were compared by Student's t-test and nonparametric variables by the Wilcoxon rank sum test.
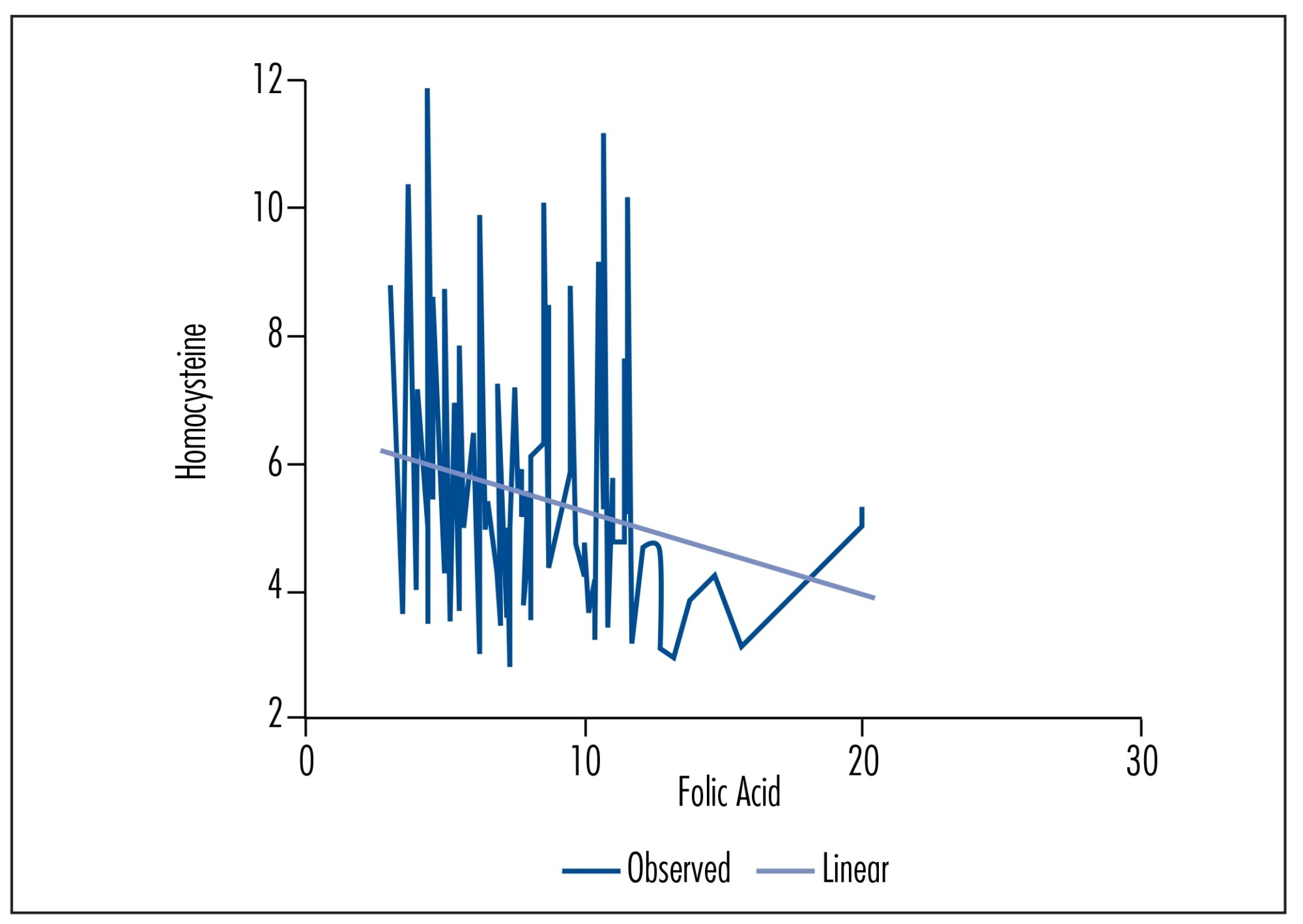
The frequencies of gene polymorphisms in 89 women with a history of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage and 150 controls were 19.1 and 19.6% for the C677T, insertion, 20.8 and 26% for the A1298C insertion, 14.2 and 21.9% for the A2756G insertion, and 16.4 and 18% for the 844ins68 insertion, respectively. There were no significant differences between case and control groups in any of the gene polymorphisms investigated. However, the frequency of the 844ins68 insertion in the CBS gene was higher among women with a history of loss during the third trimester of pregnancy (p=0.003). Serum homocysteine, vitamin B12 and folate levels id not differ between the polymorphisms studied in the case and control groups. However, linear regression analysis showed a dependence of serum folate levels on the maintenance of tHcy levels.
The investigated gene polymorphisms and serum homocysteine, vitamin B12 and folate levels were not associated with idiopathic recurrent miscarriage in the present study. Further investigations are needed in order to confirm the role of the CBS 844ins68 insertion in recurrent miscarriage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(5):229-233
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500005
PURPOSE: to assess a possible association between polymorphism of the progesterone receptor gene (PROGINS) and recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA). METHODS: in this case-control study, 85 women with at least three previous spontaneous abortions without an identifiable cause (RSA Group) and 157 women with at least two previous term pregnancies without pathologies and no previous miscarriage (Control Group) were selected. An amount of 10 mL of peripheral blood was collected by venipuncture and genomic DNA was extracted by the DTAB/CTAB method, followed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) under specific conditions for this polymorphism and by amplification by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The bands were visualized with an ultraviolet light transilluminator and the gels were photographed. Differences in the PROGINS genotype and allele frequencies between groups were analyzed by the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. The Odds Ratio (OR) was also used, with 95% confidence intervals 95%CI. RESULTS: PROGINS genotypic frequencies were 72.3% T1T1 and 27.7% T1T2 for the RSA group and 764% T1T1, 22.3% T1T2 and 1.3% T2T2 for the control group. There were no differecnes between groups when the genotype and allele frequencies were analyzed: respectively p=0.48 (OR: 0.8) and p=0.65 (OR: 0.9). CONCLUSIONS: our results suggest that PROGINS polymorphism is not associated with RSA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(2):68-74
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200004
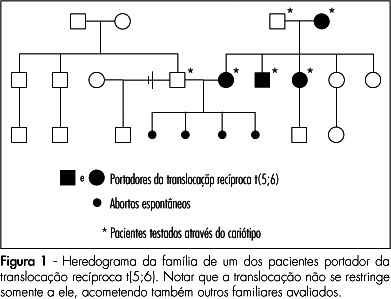
PURPOSE: to asses the prevalence and clinical characteristics of couples with history of recurrent spontaneous abortion and chromosome abnormality, attended at the present service. METHODS: all the couples referred to our service due to history of recurrent spontaneous abortion, from January 1975 to June 2008, were evaluated. Only the ones whose chromosome karyotype analysis by GTG bands has been successfully made were included in the study. Clinical data on their age, as well as on the number of abortions, stillbirth, multiple malformations, livebirth per couple, and the result of the karyotype exam were collected. Fisher's exact test (p<0.05) has been used to compare the incidence of chromosome alterations found in our study, with data in the literature. RESULTS: there were 108 couples in the sample. Their ages varied from 21 to 58 years old among the men (average of 31.4 years old), and from 19 to 43 among the women (average of 29.9 years old). In ten couples, one of the mates (9.3%) presented chromosome alterations, which corresponded respectively to three cases (30%) of reciprocal translocation [two of t(5;6) and one of t(2;13)], two (20%) of Robertsonian translocation [two of der(13;14) and one of der(13;15)], five(50%) of mosaicism (mos) [two cases of mos 45,X/46,XX, one of mos 46,XX/47,XXX, one of mos 46,XY/47,XXY and one of mos 46,XY/47,XYY] and one (10%) of chromosome inversion [inv(10)]. In one of the couples, the female presented two concomitant alterations: t(2;13) and der(13;14). Chromosome abnormalities were found in 5% of the couples with a history of two abortions, in 10.3% with three abortions, and in 14.3% with four or more abortions. CONCLUSIONS: the incidence of chromosome abnormalities seen in our study (9.3%) was similar to most of the studies carried out in the last 20 years, varying from 4.8 to 10.8%. Nevertheless the high percentage of patients with mosaicism in our sample, has called our attention. It is believed that this fact may be associated to the high number of metaphases ordinarily analyzed in the present service.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):561-567
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100003
PURPOSE: to verify the association of abortion, recurrent fetal loss, miscarriage and severe pre-eclampsia with the presence of hereditary thrombophilias and antiphospholipid antibodies in pregnant women. METHODS: observational and transverse study of 48 pregnant women with past medical record of miscarriage, repeated abortion and fetal loss story (AB Group) and severe pre-eclampsia (PE Group), attended to in the High Risk Pregnancy Ambulatory of the Faculdade de Medicina (Famed) from the Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso do Sul (UFMS) from November 2006 to July 2007. The pregnant women of both groups were screened for the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, lupic anticoagulant and anti-beta2-glycoprotein I) and hereditary thrombophilias (protein C and S deficiency, antithrombin deficiency, hyperhomocysteinemia and factor V Leiden mutation). The laboratorial screening was performed during the pregnancy. The parametric data (maternal age and parity) were analyzed with Student’s tau test. The non-parametric data (presence/absence of hereditary thrombophilias and antiphospholipid antibodies, presence/absence of pre-eclampsia, fetal loss, miscarriage and repeated abortion) were analyzed with Fisher’s exact test in contingency tables. It was considered significant the association with p value <0.05. RESULTS: out of the 48 pregnant women, 31 (65%) were included in AB Group and 17 (35%) in PE Group. There was no significant difference between maternal age and parity within the groups. There was significant statistical association between recurrent fetal loss, recurrent abortions and previous miscarriages and maternal hereditary thrombophilias (p<0.05). There was no statistical association between the AB Group and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies. Neither there were associations of the PE Group with maternal hereditary thrombophilias and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies. CONCLUSIONS: the data obtained suggest routine laboratorial investigation for hereditary thrombophilias in pregnant women with previous obstetrical story of recurrent fetal loss, repeated abortion and miscarriage.