Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):190-195
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400006
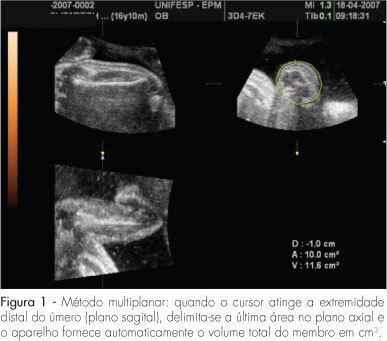
PURPOSE: to evaluate the accuracy of fetal upper arm volume, using three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS), in the prediction of birth weight. METHODS: this prospective cross-sectional study involved 25 pregnancies without structural or chromosomal anomalies. Bidimensional parameters (biparietal diameter, abdominal circumference and femur length) and the 3DUS fetal upper arm volume were obtained in the last 48 hours before delivery. The multiplanar method, using multiple sequential planes with 5.0-mm intervals, was used to calculate fetal upper arm volume. Polynomial regressions were used to determine the best equation in the prediction of fetal weight. The accuracy of this new formula was compared with Shepard's and Hadlock's formulas. RESULTS: fetal upper arm volume was strongly correlated to birth weight (r=0.83; p<0.005). Linear regression was the best equation [birth weight=681.59 + 43.23 x fetal upper arm volume]. The fetal upper arm volume mean error (0 g), mean absolute error (196.6 g) and mean percent absolute error (6.5%) were lower than using Shepard's formula; however, the difference did not reach significance (p>0.05). Birth weight predicted by fetal upper arm volume had a mean error lower than Hadlock's formula, but this difference was not statistically significant (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the accuracy of fetal upper arm volume obtained through 3DUS is similar to the accuracy of bidimensional ultrasound in the prediction of birth weight. These findings need to be confirmed by larger studies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(3):190-194
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000300009
PURPOSE: to verify the viability of early diagnosis of fetal gender in maternal plasma by the real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) starting at the 5th week of pregnancy. METHODS: peripheral blood was collected from pregnant women with single fetus starting at the 5th week of gestation. After centrifugation, 0.4 mL plasma was separated for fetal DNA extraction. The DNA was analyzed in duplicate by real-time PCR for two genomic regions, one of the Y chromosome and the other common to both sexes, through the TaqMan® method, which uses a pair of primers and a fluorescent probe. Patients who aborted were excluded. RESULTS: a total of 79 determinations of fetal DNA in maternal plasma were performed in 52 pregnant women. The results of the determinations were compared to fetal gender after delivery. Accuracy according to gestational age was 92.6% (25 of 27 cases) at 5 weeks with 87% sensitivity, and 95.6% (22 of 23 cases) at 6 weeks with 92% sensitivity. Starting at the 7th week of pregnancy, accuracy was 100% (29 of 29 cases). Specificity was 100% regardless of gestational age. CONCLUSION: real-time PCR for the detection of fetal gender in maternal plasma starting at the 5th week of gestation has good sensitivity and excellent specificity. There was agreement of the results in 100% of the cases in which male gender was diagnosed, regardless of gestational age, and from the 7th week of gestation for female gender diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):190-199
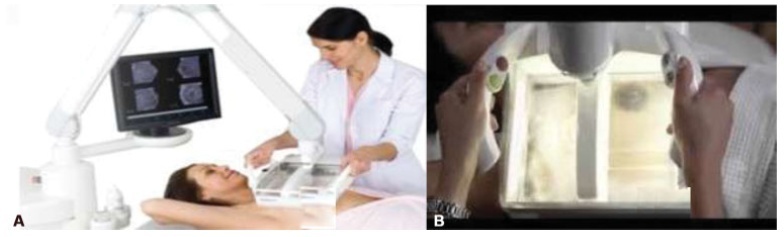
To compare hand-held breast ultrasound (HHBUS) and automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) as screening tool for cancer.
A cross-sectional study in patients with mammographically dense breasts was conducted, and both HHBUS and ABUS were performed. Hand-held breast ultrasound was acquired by radiologists and ABUS by mammography technicians and analyzed by breast radiologists. We evaluated the Breast Imaging Reporting and
(BI-RADS) classification of the exam and of the lesion, as well as the amount of time required to perform and read each exam. The statistical analysis employed was measures of central tendency and dispersion, frequencies, Student t test, and a univariate logistic regression, through the odds ratio and its respective 95% confidence interval, and with p<0.05 considered of statistical significance.
Atotal of 440 patientswere evaluated. Regarding lesions,HHBUS detected 15 (7.7%) BI-RADS 2, 175 (89.3%) BI-RADS 3, and 6 (3%) BI-RADS 4, with 3 being confirmed by biopsy as invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs), and 3 false-positives. Automated breast ultrasound identified 12 (12.9%) BI-RADS 2, 75 (80.7%) BI-RADS 3, and 6 (6.4%) BI-RADS 4, including 3 lesions detected by HHBUS and confirmed as IDCs, in addition to 1 invasive lobular carcinoma and 2 high-risk lesions not detected by HHBUS. The amount of time required for the radiologist to read the ABUS was statistically inferior compared with the time required to read the HHBUS (p<0.001). The overall concordance was 80.9%. A total of 219 lesions were detected, from those 70 lesions by both methods, 126 only by HHBUS (84.9% not suspicious by ABUS) and 23 only by ABUS.
Compared with HHBUS, ABUS allowed adequate sonographic study in supplemental screening for breast cancer in heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breasts.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):190-190
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):191-199
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400002
Purpose: to determine the frequency of prenatal diagnosis in newborns with gastroschisis operated at the Instituto Materno-Infantil de Pernambuco (IMIP) and to analyze its repercussions on neonatal prognosis. Patients and Methods: a cross-sectional study was carried out, including 31 cases of gastroschisis submitted to surgical correction in our service from 1995 to 1999. Prevalence risk (PR) of neonatal death and its 95% confidence interval were calculated for the presence of prenatal diagnosis and other perinatal and surgical variables. Multiple logistic regression analysis was carried out to determine the adjusted risk of neonatal death. Results: only 10 of 31 cases of gastroschisis (32.3%) had prenatal diagnosis and all were delivered at IMIP. No newborn with prenatal diagnosis was preterm but 43% of those without prenatal diagnosis were premature (p < 0,05). Birth-to-surgery interval was significantly greater in the absence of prenatal diagnosis (7.7 versus 3.8 hours). The type of surgery, need of mechanical ventilation and frequency of postoperative infection were not different between the groups. Neonatal death was more frequent in the group without prenatal diagnosis (67%) than in the group with prenatal diagnosis (20%). The main factors associated with increased risk of neonatal death were gestational age <37 weeks, absence of prenatal diagnosis, delivery in other hospitals, birth-to-surgery interval > 4 hours, staged silo surgery, need of mechanical ventilation and postoperative infection. Conclusions: prenatal diagnosis was infrequent among infants with gastroschisis and neonatal death was extremely high in its absence. It is necessary to achieve greater rates of prenatal diagnosis and to improve perinatal care in order to reduce this increased mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):191-191
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300010
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):191-191
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300011
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):191-197
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400007
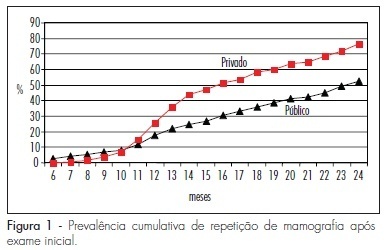
PURPOSE: to assess compliance with the recommendations for opportunistic breast cancer screening by mammography. METHODS: 460 women from the town of Taubaté, São Paulo, Brazil, were followed-up prospectively after the index mammography, 327 of them attended by the public health system and 133 by the private system. We evaluated the prevalence of mammography repetition, the adherence rates and predictive factors associated with the current recommendations of mammographic screening. The association of the outcomes with the independent variables was studied by obtaining the risk rates (RR) and the respective 95% confidence intervals (95%CI). The adjusted prevalence rates were calculated by the COX regression model. RESULTS: although more than 90% of the studied women repeated the mammography at least once, the rate of correct compliance with the recommendations of mammographic screening, with repetition of the procedure every 24 months, was low (about 30% of the study sample). The preditive factors associated with compliance with mammographic screening were related to the unequal access to public or private healthcare services (RR=1.77; 95%CI=1.26-2.48) and to previous screening (RR=3.07; 95%CI=1.86-5.08). CONCLUSION: we concluded that compliance with the recommendations of opportunistic mammographic screening for breast cancer was low in both studied population segments.