You searched for:"Edmund Chada Baracat"
We found (71) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(8):595-602
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800002
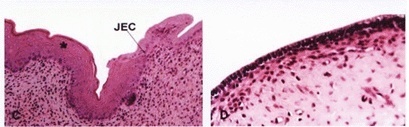
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of estradiol benzoate associated with dexamethasone on the squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) of rats in permanent estrus (PE) and then ovariectomized (Ovx). METHODS: thirty female rats were divided into six groups of five animals each: PhEG rats in physiological estrus (PhE) treated with propylene glycol (vehicle); OVXG rats in PhE, Ovx and treated with vehicle; PEG - rats in PE treated with vehicle; PEOVXG rats in PE, Ovx and treated with vehicle; ESTRG rats in PE, Ovx and treated with 10 mg per day benzoate of estradiol, and DEXAG in PE, Ovx and treated with 10 mg per day estradiol benzoate associated with 0.8 mg dexamethasone. PE induction was performed with 1.25 mg testosterone propionate per animal per day after birth. After 90 days, rats in the OVXG, EPOVXG, ESTRG, and DEXAG groups were ovariectomized. After 21 days of castration, all animals received the corresponding treatment for five days. At the end of the experiment, all animals were sacrificed and the uteri removed for histological routine. RESULTS: the borders of the SCJ in the PEG were irregular and not clearly delineated, with many buds towards the direction of the lamina propria as well as a reduction in the leukocyte number compared to the PhEG. The SCJ of the OVXG and PEOVXG was not very visible, with cubical epithelium on the endometrial side and with reduction in the layers of squamous epithelium due to stromal atrophy. The SCJ in the ESTRG was more developed than in the OVXG and PEOVXG, but it was similar to that of the PEG, having unclear borders. In contrast, the SCJ of the DEXAG was well-delineated and similar to the PhEG. CONCLUSION: our data suggest that estrogen associated with dexamethasone may be important for remodeling SCJ morphology in female rats with previously induced permanent estrus and subsequent ovariectomy.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(10):596-600
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000005
PURPOSE: To analyze gestation evolution and deliveries after myoma treatment by embolization of the uterine arteries. METHODS: In the initial evaluation, 112 patients submitted to embolization of uterine arteries were included for treatment of myoma. From those, only nine wanted to be submitted to conservative treatment in order to keep their reproductive capacity. This procedure was indicated to the nine patients, since they were not susceptible to a conservative surgical treatment. They were submitted to embolization of the uterine arteries with particles of polyvinyl alcohol or embospheres with diameters ranging from 500 to 700 µm, and they have evolved without intercurrence. RESULTS: During the follow-up of these patients, there was a good clinical response with significant reduction in the uterus and myoma volumes. Four of them got pregnant, two had an early abortion and two evolved normally till the end of gestation with a term delivery. One of these had twins. CONCLUSION: Embolization of the uterine arteries is an option for the treatment of uterine myoma, and presents good clinical and anatomical results, allowing patients to preserve their reproductive capacity.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(12):608-613
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200002
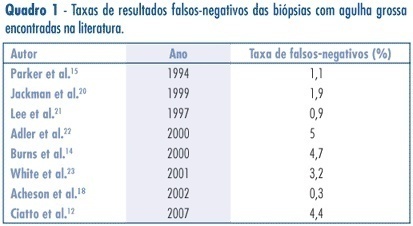
PURPOSE: to assess the accuracy (rate of correct predictions) of stereotactic core needle biopsy (CNB) of risk category BI-RADS® 4 breast lesions. METHODS: a retrospective analysis of category BI-RADS® 4 breast lesions that had been submitted to a stereotactic core-needle biopsy from June 1998 to June 2003. Patients with histological benign results consistent with the radiographic image were referred to mammographic follow-up. Patients with malign diagnosis and papillary lesions were submitted to standard specific treatment. Excisional biopsies were performed when results were benign, but in disagreement with the mammographic image. It was considered as a gold-standard attendance: (1) the mammographic follow-up of low suspicion lesions with benign results at CNB, which stayed unchanged for, at least, three years, and (2) surgical resection when specimen results were malign or benign, but with a high suspicion on mammography. Sensitivity (S) specificity (E) and overall accuracy of stereotactic CNB were statistically analyzed. RESULTS: among the 118 non-palpable lesions of category BI-RADS® 4 submitted to CNB, the results obtained were: 27 malign cases, 81 benign, and ten lesions with atypical or papillary lesions. The statistical analysis comprised 108 patients (atypical and papillary lesions were excluded). CNB sensitivity was 87.1% and specificity 100%. The positive predictive value was 100% and the negative, 95.1%. False negatives occurred in 3.7% (4/108) of cases. The prevalence of malign diagnostics in the BI-RADS® 4 lesions of this sample was 29.7 (31/118).The accuracy of this method in this casuistic was 96.3%. CONCLUSIONS: these results support stereotactic CNB as an extremely reliable alternative to open biopsy, in the diagnosis and definition of breast lesions. In positive results, it is possible to indicate the appropriate therapy, and, in negative (when mammography shows low suspicion), it allows a follow up.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(10):609-613
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000001000002
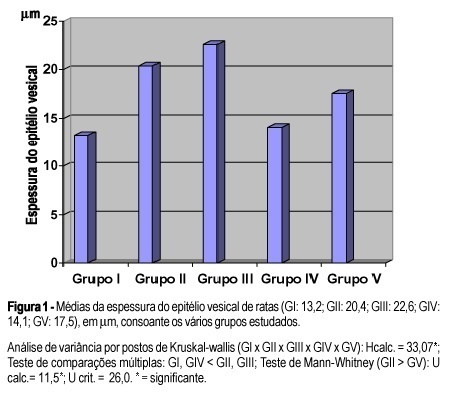
Purpose: the effects of corticosteroids on the female urinary tract are not well understood, specially in climacteric women with or without estrogen replacement therapy. We studied the effects of corticosteroids on the blood vessels and epithelium of the bladder and urethra of female rats. Method: fifty-four female rats were used, divided into five groups. Group I - ten castrated female rats; Group II - eleven castrated female rats which receivedintraperitoneally 15 mg/kg weight prednisolone, for 26 days; Group III - twelve castrated female rats which received the same amount of corticosteroid, during the same time, and subcutaneously 10 mg/kg 17 beta-estradiol, in the last five days before they were sacrificed; Group IV - eleven castrated rats which received placebo for 26 days; and Group V - no castrated female rats which received the same dose of corticosteroid during the same time as in Group II. Results: we observed an average of 1.8 vessels in the bladder of the castrated group which received corticosteroid, a similar number to that of those which received corticosteroid and estrogen, compared with 0.8 vessel in the placebo group. Regarding the urethra, 0.7 vessel was observed in the group which received corticosteroid, as compared with 0.9 vessel in the group treated with corticosteroid associated with estrogen and 0.4 in the placebo group. Regarding the mucous membrane, the vesical epithelium thickness of 14.1 mm in the placebo group increased to 20.6 mm in that with corticosteroid and to 22.6 mm in that with corticosteroid plus estrogen. The urethral epithelium thickness of 12.4 mm in the placebo group increased to 15.1 mm in the group with corticosteroid and to 16.7 mm in that with corticosteroid plus estrogen. Conclusion: corticosteroids significantly increased the vascularization and the thickness of the vesical and urethral epithelia of castrated female rats.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(11):658-663
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100005
PURPOSE: to analyze breast tissue of postmenopausal women before and after six months of continuous combined estrogen-progestin replacement therapy (0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogens associated with 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate). METHODS: all patients were evaluated before treatment and considered eligible to receive the drug. The material was obtained from the upper outer left quadrant, through a percutaneous large-core breast biopsy. Epithelial density and nuclear volume on hematoxylin-eosin-stained plates were evaluated for the morphological study. Morphometry was graphically analyzed by optical microscopy (400X) after acquisition of image by a digital image-capturing system (Vidcap 32) and image analysis system (Imagelab 2000 Software®). RESULTS: after six months of estrogen-progestin replacement therapy, there was a significant increase in nuclear volume in late postmenopausal women (103.6 to 138.1 µm³). There was no difference in epithelial density with the treatment (before 0.08 and later 0.10). CONCLUSIONS: estrogen-progestin combined replacement therapy for six months induced an enhacement in nuclear volume of breast epithelial cells, suggesting an increase in their metabolic activity. However, it is important to emphasize that this finding was observed only in late postmenopausal women. The increased nuclear volume could precede other events that confirm the stimulation of cellular proliferation by these hormones.
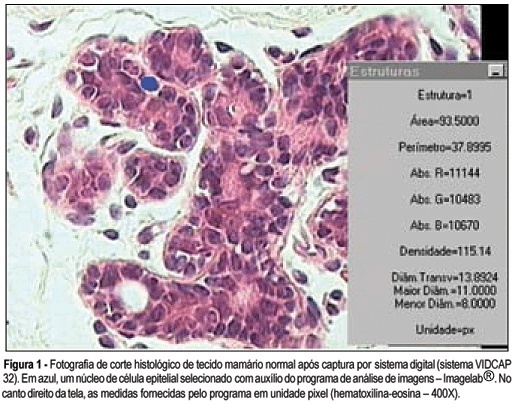
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(11):661-663
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):667-672
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900008
PURPOSE: to compare the results of hysterosonography with those of hysteroscopy and the histopathologic study in postmenopausal women. METHODS: hysterosonography, hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy were performed in 59 women who had an endometrial echo over 4 mm, age above 40 years and amenorrhea over one year, and whose follicle-stimulating hormone levels were over 35 mIU/mL. Patients using hormones were excluded, as well those in whom it was impossible to perform histerosonography, histeroscopy or endometrial biopsy. The statistical analysis was performed using the nonparametric "G"-Cochran and McNemar tests. In addition, sensitivity and specificity, as well as positive and negative predictive values were determined. The value of 0.05 or 5% for rejection level of the null hypothesis was applied. RESULTS: the agreement rates of hysterosonographic results compared to hysteroscopy and histopatology were 94.8 ande 77.6%, respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of hysterosonographic evaluation of the abnormal endometrial cavity were 98 and 75%, respectively, when compared to hysteroscopy. In addittion, positive and negative predictive values of hysterosonography were 96 and 86%, respectively. When the histopathologic study was used as the gold standard, sensitivity and specificity were 98 and 33%, with positive predictive value of 76% and negative predictive value of 86%, for the detection of the endometrial cavitary changes. One great concern were the histopathologic results of two patients with uterine synechia who showed endometrial hyperplasia. Also, one patient was diagnosed as normal using histerosonography and the histopatological result showed simple hyperplasia. CONCLUSIONS: our data suggest that hysterosonography presented good sensitivity as compared with hysteroscopy. However, uterine synechia is the great limitation of this method as compared with histopathology.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(1):67-73
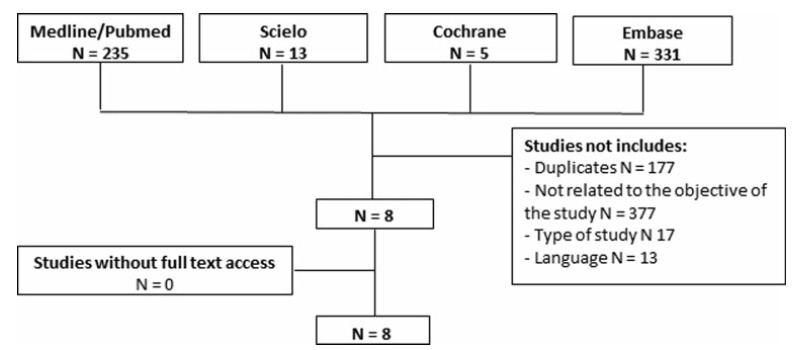
To evaluate the underestimation rate in breast surgical biopsy after the diagnosis of radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion through percutaneous biopsy.
A systematic review was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations. The PubMed, SciELO, Cochrane, and Embase databases were consulted, with searches conducted through November 2020, using specific keywords (radial scar OR complex sclerosing lesion, breast cancer, anatomopathological percutaneous biopsy AND/OR surgical biopsy).
Study selection was conducted by two researchers experienced in preparing systematic reviews. The eight selected articles were fully read, and a comparative analysis was performed.
A total of 584 studies was extracted, 8 of which were selected. One of them included women who had undergone a percutaneous biopsy with a histological diagnosis of radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion and subsequently underwent surgical excision; the results were used to assess the underestimation rate of atypical and malignant lesions.
The overall underestimation rate in the 8 studies ranged from 1.3 to 40% and the invasive lesion underestimation rate varied from 0 to 10.5%.
The histopathological diagnosis of a radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion on the breast is not definitive, and it may underestimate atypical andmalignant lesions, which require a different treatment, making surgical excision an important step in diagnostic evaluation.