Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo59
To assess the association between sociodemographic and perinatal factors and hospital practices to encourage exclusive breastfeeding in near miss neonates in maternity hospitals.
This is a prospective cohort of live births from the survey “To be born in Brazil” conducted between 2011 and 2012. The weighted number of newborns who met the neonatal near miss criteria was 832. Exclusive breastfeeding at hospital discharge and 45 days after delivery were dependent variables of the study. The sociodemographic and perinatal factors of the puerperal women and hospital practices to encourage breastfeeding were independent variables. The data were analyzed with Poisson regression and set with p value<0.05. Is exclusive breastfeeding in neonatal near misses associated with factors related to sociodemographic conditions, maternal characteristics and the organization of health services?
Data from 498 women and their children were analyzed. Mothers with incomplete primary education were more likely (36%) to have exclusive breastfeeding (RR: 1.36; 95% CI: 1.06-1.74) at discharge. Women who did not offer the breast to the newborn in the joint accommodation (65%) were less likely to be breastfeeding exclusively (RR: 0.65; 95% CI: 0.56-0.75) at discharge. Variables that increased the probability of exclusive breastfeeding after 45 days of delivery were primiparity (RR: 1.36; 95% CI: 1.08-1.69) and having the newborn in the delivery room (RR: 1.90; 95% CI: 1.12-3.24).
Exclusive breastfeeding in neonatal near misses was associated with maternal characteristics and important hospital practices, such as being breastfed in the joint accommodation and the newborn being in the mother’s lap in the delivery room.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo58
To assess a panel of cytokines and placental insufficiency with the risk of preterm delivery (PTD).
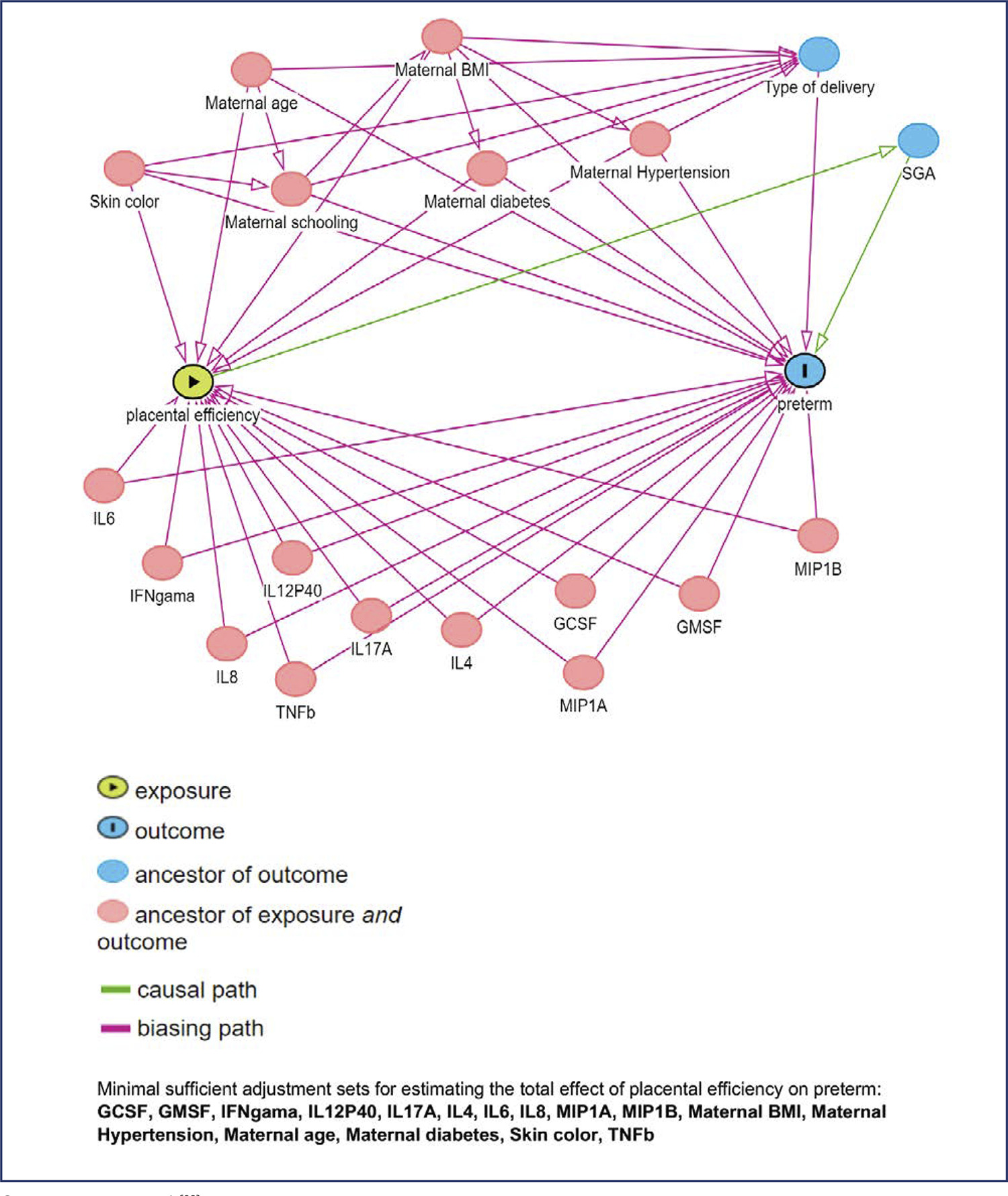
Nested case-control study into the BRISA birth cohort. Eighty-two mother-infant-placenta pairs were selected at 20+0 to 25+6 weeks. Circulating biomarker levels were performed using Luminex flowmetric xMAP technology. Cytokines classified as Th1, Th2 or Th17 and other biomarkers were selected. The ratio between birth weight and placental weight (BW/PW) was used as a proxy for placental efficiency. Spearman correlation, univariate analyses and logistic regression models were calculated. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios were calculated using the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve.
Mean gestational age was 250 days, 14,6% were small for gestational age, 4,8% large for gestational age and 13,4% stunted. Placental efficiency was higher for term newborns (p<0,001), and 18/22 (81%) preterm biomarker values were higher than the control group. Th1 cytokines were highly correlated, while the weakest correlation was observed in other biomarkers. Less education was associated with a higher risk of PTD (p = 0.046), while there was no appreciable difference in the risk of PTD for placental insufficiency. Biomarkers showed negligible adjusted OR of PTD (0.90 to 1.02). IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, TNFβ, IL-4, IL-13, GCSF, MIP1A, VEGF, EGF, and FGF2 presented a higher sensitivity ranging from 75.56% to 91.11%.
IL-8, IL-12p40, IL-4, IL-13, GCSF, MIP1B, and GMSF in asymptomatic pregnant women were associated with PTD. This finding suggests an activation of maternal inflammatory response.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo57
High-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is associated with cervical cancer while low-risk HPV strains mostly cause benign lesions. Multiple studies have also associated HPV with coronary artery (CAD) disease in women. Furthermore, the climacteric period in women, triggers chronic inflammation and has major implications for CAD and associated lipid disorders. The association of HPV with coronary artery disease in climacteric women has few studies, and the objective of this review is to gather and analyse scientific data on the subject. This is an integrative review performed on PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “HPV”, “coronary heart disease” and “climacteric”, among these keywords the boolean operator AND and the publication date filter. (2018 onwards). Five articles were found, whose main results show presence of high-risk vaginal HPV in climacteric women. Climacterium and HPV were associated with a three-fold increased risk of CAD, as well as with factors related to menopause that promote atheroma formation, lipid disorders and chronic inflammation. Thus, these results support the association between HPV infection and CAD in climacteric women, possibly via chronic inflammation, hormonal factors related to menopause and dyslipidemia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo73
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo42
To evaluate the effects of surgical treatment of deep endometriosis on the metabolic profile, quality of life and psychological aspects.
Prospective observational study, carried out with women of reproductive age diagnosed with deep endometriosis, treated in a specialized outpatient clinic, from October/2020 to September/2022, at a University Hospital in Fortaleza - Brazil. Standardized questionnaires were applied to collect data on quality of life and mental health, in addition to laboratory tests to evaluate dyslipidemia and dysglycemia, at two moments, preoperatively and six months after surgery. The results were presented using tables, averages and percentages.
Thirty women with an average age of 38.5 years were evaluated. Seven quality of life domains showed improved scores: pain, control and impotence, well-being, social support, self-image, work life and sexual relations after surgery (ES ≥ 0.80). There was an improvement in mental health status with a significant reduction in anxiety and depression postoperatively. With the metabolic profile, all average levels were lower after surgery: total cholesterol 8.2% lower, LDL 12.8% lower, triglycerides 10.9% lower, and fasting blood glucose 7.3% lower (p < 0.001).
Surgical treatment of deep endometriosis improved the quality of life and psychological aspects of patients. The lipid profile of patients after laparoscopy was favorable when compared to the preoperative lipid profile.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo47
In Brazil, postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is a major cause of maternal morbidity and mortality. Data on the profile of women and risk factors associated with PPH are sparse. This study aimed to describe the profile and management of patients with PPH, and the association of risk factors for PPH with severe maternal outcomes (SMO).
A cross-sectional study was conducted in Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira (IMIP) obstetric intensive care unit (ICU) between January 2012 and March 2020, including patients who gave birth at the hospital and that were admitted with PPH to the ICU.
The study included 358 patients, of whom 245 (68.4%) delivered in the IMIP maternity, and 113 (31.6%) in other maternity. The mean age of the patients was 26.7 years, with up to eight years of education (46.1%) and a mean of six prenatal care. Uterine atony (72.9%) was the most common cause, 1.6% estimated blood loss, 2% calculated shock index (SI), 63.9% of patients received hemotransfusion, and 27% underwent hysterectomy. 136 cases of SMO were identified, 35.5% were classified as maternal near miss and 3.0% maternal deaths. Multiparity was associated with SMO as an antepartum risk factor (RR=1.83, 95% CI1.42-2.36). Regarding intrapartum risk factors, abruptio placentae abruption was associated with SMO (RR=2.2 95% CI1.75-2.81). Among those who had hypertension (49.6%) there was a lower risk of developing SMO.
The principal factors associated with poor maternal outcome were being multiparous and placental abruption.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo48
Evaluate the prevalence of macrosomic newborns (birth weight above 4000 grams) in a high-risk maternity from 2014 to 2019, as well as the maternal characteristics involved, risk factors, mode of delivery and associated outcomes, comparing newborns weighing 4000-4500 grams and those weighing above 4500 grams.
This is an observational study, case-control type, carried out by searching for data in hospital’s own system and clinical records. The criteria for inclusion in the study were all patients monitored at the service who had newborns with birth weight equal than or greater than 4000 grams in the period from January 2014 to December 2019, being subsequently divided into two subgroups (newborns with 4000 to 4500 grams and newborns above 4500 grams). After being collected, the variables were transcribed into a database, arranged in frequency tables. For treatment and statistical analysis of the data, Excel and R software were used. This tool was used to create graphs and tables that helped in the interpretation of the results. The statistical analysis of the variables collected included both simple descriptive analyzes as well as inferential statistics, with univariate, bivariate and multivariate analysis.
From 2014 to 2019, 3.3% of deliveries were macrosomic newborns. The average gestational age in the birth was 39.4 weeks. The most common mode of delivery (65%) was cesarean section. Diabetes mellitus was present in 30% of the deliveries studied and glycemic control was absent in most patients. Among the vaginal deliveries, only 6% were instrumented and there was shoulder dystocia in 21% of the cases. The majority (62%) of newborns had some complication, with jaundice (35%) being the most common.
Birth weight above 4000 grams had a statistically significant impact on the occurrence of neonatal complications, such as hypoglycemia, respiratory distress and 5th minute APGAR less than 7, especially if birth weight was above 4500 grams. Gestational age was also shown to be statistically significant associated with neonatal complications, the lower, the greater the risk. Thus, macrosomia is strongly linked to complications, especially neonatal complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo54
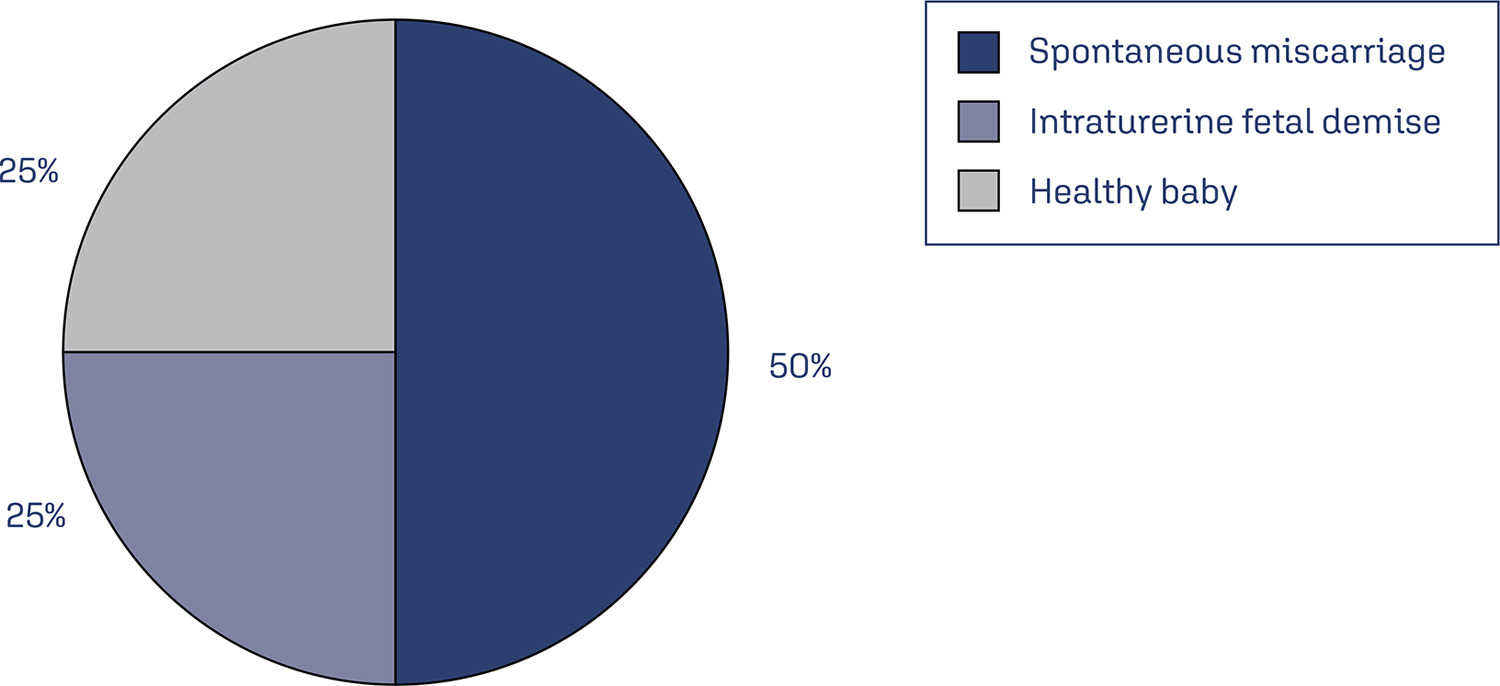
Monkeypox (MPX), an orthopoxviral disease endemic in Africa, is now a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) as declared by the World Health Organization in July 2023. Although it is generally mild, the overall case fatality rate was reported to be 3%, and the basic reproduction number (R0) is > 1 in men who have sex with men (MSM, i.e., Portugal (1.4), the United Kingdom (1.6), and Spain (1.8)). However, R0 is < 1 in other settings. In concordance with the smallpox virus, it is also expected to increase the risk of adverse outcomes for both the mother and the fetus. The outcomes of the disease in an immunocompromised state of pregnancy are scary, showing high mortality and morbidity of both mother and fetus, with up to a 75% risk of fetal side effects and a 25% risk of severe maternal diseases. Therefore, it warrants timely diagnosis and intervention. The reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT PCR) test is the standard approach to diagnosis. We summarized the recent findings of MPX on pregnancy, and the associated risk factors. We also give recommendations for active fetal surveillance, perinatal care, and good reporting to improve outcomes. The available vaccines have shown promise for primary disease prevention.