You searched for:"Jose Guilherme Cecatti"
We found (51) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1999;21(9):519-525
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900004
Purpose: to present the perinatal outcomes resulting from the use of a protocol for assistance to diabetic pregnant women used at the Center for Integral Assistance to Women's Health (CAISM), of the University of Campinas. Methods: ninety diabetic pregnant women, who were assisted at the institution with this protocol, were compared with two control grups: the first consisted of 180 pregnant women with equal number of gestations and same age (control A) and the second consisted of 180 randomly selected pregnant women (control B). The study variables were route of delivery, indication for cesarean section, gestational age, Apgar score at first and fifth minute, weight, adequacy of weight for gestational age and perinatal morbidity and mortality. For the statistical analysis Student's t-test and the chi2 test were used. Results: there was a higher incidence of cesarean sections, prematures and large to gestational age (LGA) babies among diabetic women, as well as higher occurrence of neonatal morbidity such as hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress and neonatal depression. The incidence of low Apgar score and perinatal mortality was significantly higher than in the randomly selected group, but the same as in the group matched regarding age and number of pregnancies. Conclusions: although this protocol intends to obtain a perfect metabolic control among diabetic pregnant women, the perinatal outcomes are still unfavorable in comparison to nondiabetic pregnant women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(9):554-562
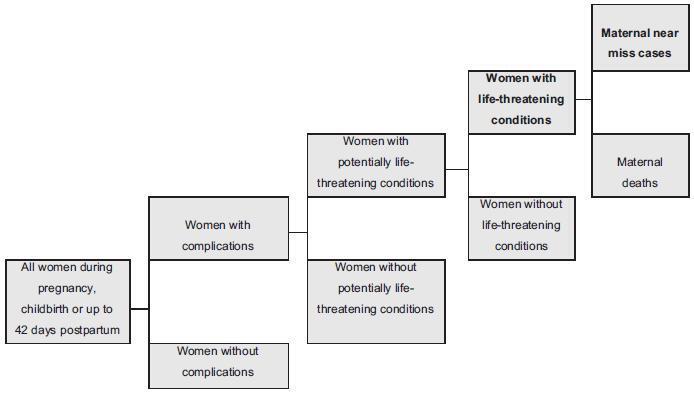
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):555-556
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(9):579-584
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000900007
Purpose: to evaluate the avoidable mortality among women in reproductive age, living in Campinas, SP, comparing two five-year periods: 1985-89 and 1990-94. Methods: death certificates of 3.086 women aged 10 to 49 years were studied, representing the total number of deaths during the period from January 1985 through December 1994. The criteria for avoidance were applied to these deaths using preventive, sanitary, early diagnosis and treatment, and mixed measures. The deaths were also classified as: with hardly avoidable causes, not well-defined causes and other causes. The specific mortality coefficient for each period of five years and the ratio between these coefficients were calculated. Results: there was a 20% increase in the avoidable mortality rate from the first to the second period. The main failure was observed among the group of avoidable causes by preventive and sanitary measures. The main increase in death causes by preventive measures resulted from AIDS. Among the causes of death avoidable by mixed measures, the increase of 50% in maternal mortality caused by abortion, as well as causes due to violence specially homicides, are emphasized. Conclusion: there was an increase in the proportion of avoidable death causes. Measures to prevent AIDS, abortion and to reduce violent deaths, specially homicides, should be political and social priorities in our Country.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):639-646
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900004
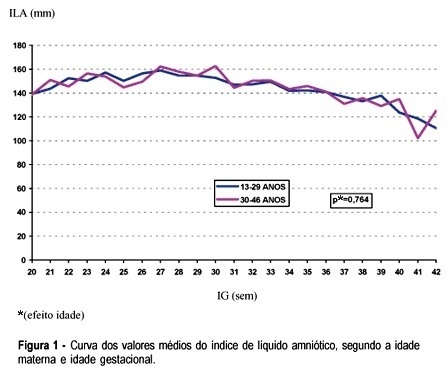
PURPOSE: to evaluate the association between the variability of amniotic fluid index (AFI) values with gestational age and some sociodemographic and obstetric variables among low-risk pregnant women. METHOD: a comparative study was carried out including 2868 low-risk pregnant women who had routine obstetric ultrasound examination, including fetal biometry and the measurement of AFI, from 20 to 42 weeks of gestation. The data were analyzed using Student's t test, analysis of variance of mean AFI values along gestational ages, according to other control variables, and also by multiple linear regression analysis. RESULTS: there was no significant variation of mean AFI values during the time of pregnancy neither when separately evaluating its association with maternal age, color, education, smoking habit, parity, and the presence of previous cesarean section scars, nor when the evaluation was performed through multivariate analysis. In this situation only the increase in gestational age showed to be associated with the decrease of AFI. Generally speaking, the mean AFI values fluctuated between 140 and 180 mm between the 20th and the 36th week, then showing values below 140 mm in a progressive decrease after this limit of gestational age. CONCLUSIONS: AFI values do not show a significant variation during pregnancy regarding the studied sociodemographic and obstetric variables.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(10):641-646
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000002
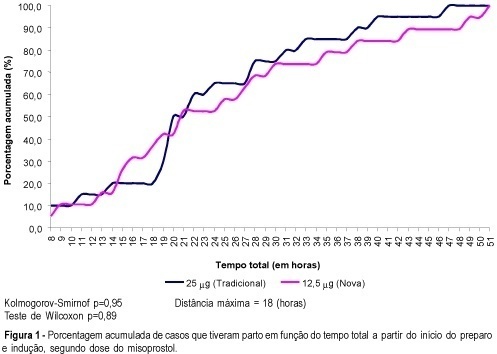
PURPOSE: to compare the effectiveness and safety of two different doses of misoprostol (12.5 mug and 25 mug) administered vaginally for cervical ripening and labor induction in term pregnancies with an indication for interruption. METHODS: this was a pilot randomized controlled single blinded trial, including 40 pregnant women treated with one of the two different doses of misoprostol. The independent variable was the dose of misoprostol and the main dependent variables were the mode of delivery, time between induction and delivery, perinatal complications and maternal side effects. The main control variables were maternal age, gestational age, literacy, parity, skin color and conditions of the cervix at the beginning of induction. For data analysis Student's t test, chi2, exact Fisher, Wilcoxon and Kolmogorov-Smirnof tests were used, besides survival analysis. RESULTS: the groups using 12.5 and 25 mug were similar and did not present any significant difference regarding time for onset of uterine contractions (20.9±20.4 and 16.6±9.8 h, respectively), time between onset of uterine contractions and delivery (7.8±3.4 and 6.9±5.0 h), vaginal delivery (65 and 80%) and maternal and perinatal side effects (similar Apgar scores and hyperstimulation syndrome in both groups). CONCLUSION: the higher percentage of vaginal births and the shorter time for delivery using 25 mug, although not significant, does not allow to recommend the dose of 12.5 mug as more advantageous for cervical ripening and labor induction in term pregnancies.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1998;20(1):7-11
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100002
With the purpose of identifying the causes of maternal deaths, this study evaluated all cases of deaths of 10 to 49-years-old women which occurred in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, during 1992 and 1993. The data were obtained from 1013 death certificates and were complemented by medical and anesthetia records forms, nursing reports, necropsies and also interviews with physicians who took care of the women, or with their relatives. The main basic causes of maternal deaths identified were arterial hypertension (23.8%), infections (19.0%), abortion (11.9%), hemorrhage (9.5%), pulmonary embolism (4.8%) and anaesthetic accident (2.4%). About 70% of maternal deaths in Recife in the studied period were due to directo obstetrical causes.