Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):142-147
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300007
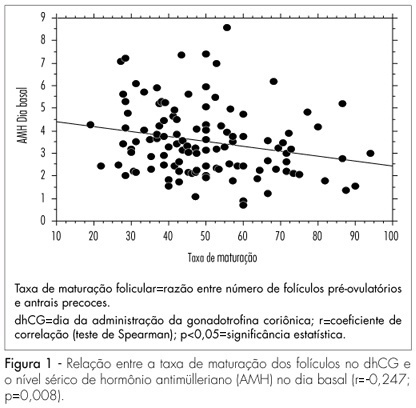
PURPOSE: to test the hypothesis that the anti-müllerian hormone (AMH) serum level reflects the antral follicles' response to the administration of FSH. METHODS: prospective study, including 116 normo-ovulatory infertile patients submitted to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with GnRH and FSH agonists. The AMH serum level was measured after reaching the pituitary suppression and before the FSH administration (basal day). The number of antral follicles was determined by ultrasonography at the basal day (precocious antral follicles; 2 to 8 mm) and at the day of hCG administration (dhCG; pre-ovulatory follicles; >16 mm). The follicle response to FSH was determined by the percentage of precocious antral follicles which reached pre-ovulatory stage in response to FSH (maturation rate). The correlation of AMH with the patients' age, the total number of precocious antral and pre-ovulatory follicles, collected oocytes, total dose of FHS in the controlled ovarian stimulation and the rate of follicular maturation was studied. For the statistical analysis, it simple regression analysis and the Spearman's test were used, at a 5% significance level. RESULTS: The serum level of AMH was positively correlated with the number of precocious antral follicles at the basal day (r=0.64; p<0.0001) and pre-ovulatory follicles in dhCG (r=0.23; p=0.01). Exceptionally, the serum level of AMH was negatively correlated with the maturation ratio (r=-0.24; p<0.008). CONCLUSIONS: AMH attenuates the follicular development caused by FSH administration.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):142-148
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000004
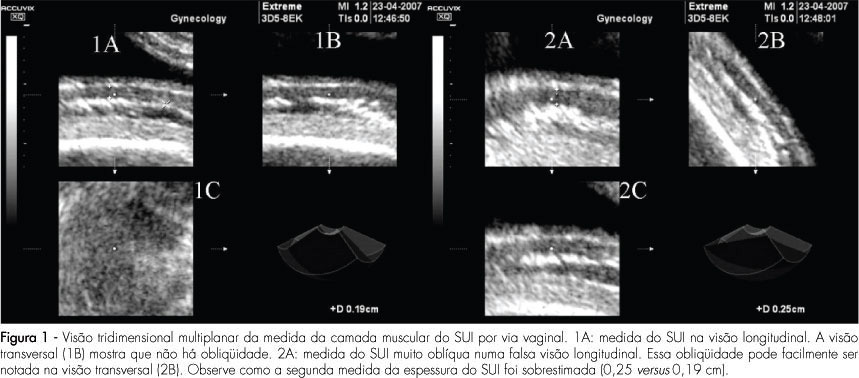
PURPOSE: to compare the intra and interobserver reproducibility of the total thickness measurement of the inferior uterine segment (IUS), through the abdominal route, and of the muscle layer measurement, through the vaginal route, using bi and tridimensional ultrasonography. METHODS: the IUS thickness measurement of 30 women, between the 36th and 39th weeks of gestation with previous caesarean section, done by two observers, was studied. Abdominal ultrasonography with the patient in both supine and lithotomy position was performed. In the sagittal section, the IUS was identified and four bidimensional images and two tridimensional blocks of the total thickness were collected through the abdominal route, and the same for the muscle layer, through the vaginal route. Tridimensional acquisitions were manipulated in the multiplanar mode. The time was measured with a chronometer. Reproducibility was evaluated by the computation of the absolute difference between measurements, the ratio of differences smaller than 1 mm, the intraclass coefficient (ICC), and the Bland and Altman's concordance limits. RESULTS: the average bidimensional measurement of IUS thickness was 7.4 mm through the abdominal and 2.7 mm through the vaginal route, and the tridimensional measurement was 6.9 mm through the abdominal and 5.1 mm through the vaginal route. Intra- and interobserver reproducibility of vaginal versus abdominal route: smaller absolute difference (0.2-0.4 mm versus 0.8-1.5 mm), greater ratio of differences (85.8-97.8% versus 48.7-72,8%), with p<0,0001, higher ICC (0.8-0.9 versus 0.6-0.8) and lower concordance limits (-0.9 to 1.5 versus -3.8 to 4 mm) for the vaginal route. Tri versus bidimensional ultrasonography: lower absolute difference (0.2-1.4 versus 0.4-1.5 mm), higher ratio of differences (57.7-97.8% versus 48.7-91.7%) with p>0.05[A1] and similar lower concordance limits (-38 to 3.4 versus -3.6 to 4 mm) for tridimensional ultrasonography and ICC (0.6-0.9 versus 0.7-0.9). CONCLUSIONS: from the above, we came to the conclusion that the measurement of the IUS muscle layer, through the vaginal route using tridimensional ultrasonography is more reproducible. Nevertheless, our results do not indicate that this measurement shows any clinical evidence to predict uterine tear, as that was not the aim of this study. The only work that has correlated the UIS thickness with risk of uterine tear, without interfering in the obstetrician behavior or anticipating delivery, was done by bidimensional abdominal measurements of the total thickness.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):142-148
To understand the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on in vitro fertilization (IVF) clinical pregnancy rates and analyze factors that may have influenced their outcome.
This was a retrospective observational study conducted at a tertiary-care Brazilian fertility center. All fresh IVF and embryo warming cycles performed from March 11 to December 31, 2018–2021 were analyzed, and their data were used to calculate fertilization, embryo cleavage, cycle cancellation, embryo transfer (ET), and clinical pregnancy rates. Statistical tests were used to evaluate the alterations found. Logistic regression models were used to explore the association of the categorical variables with the observed clinical pregnancy rates. Data from 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and 2020 and 2021 (pandemic) were grouped.
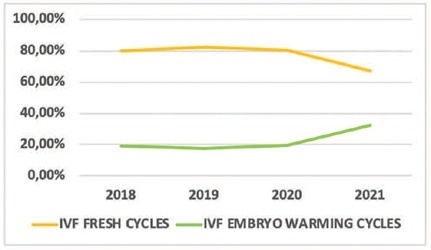
A total of 756 cycles were analyzed (n = 360 prepandemic and n = 396 pandemic). The age group of the patients, fertilization rates, and cleavage rates did not have significant differences (p > 0.05). There was a reduction in the percentage of fresh IVF and an increase in embryo warming cycles (p = 0.005) during the pandemic. There was also an increase in fresh cycle cancellations (p < 0.001) and a reduction in ET rates (p < 0.001). The pandemic had a negative impact on clinical pregnancy rates (p < 0.001) especially due to the increase in fresh cycle cancellations (p < 0.001).
Embryo warming cycles with subsequent frozen-thawed ET were presented as a viable alternative to continue assisted reproductive treatments against pandemic restrictions on fresh cycles, ensuring clinical pregnancy, albeit at a lower rate than that of the prepandemic period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):142-146
Frozen section examination is a rapid method for identifying products of conception in endometrial curetting, yet its accuracy is inconclusive. The purposes of this study is to determine the accuracy of frozen section analysis of endometrial curetting in pregnancies of unknown location, and to verify the relation of β-human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) level and endometrial thickness to the assessed accuracy.
We reviewed data from January 2009 to December 2014 of diagnostic curettages from women with suspected ectopic pregnancies sent for frozen section examination at a medical center. A frozen section diagnosis was considered accurate if it concurred with the final pathologic diagnosis.
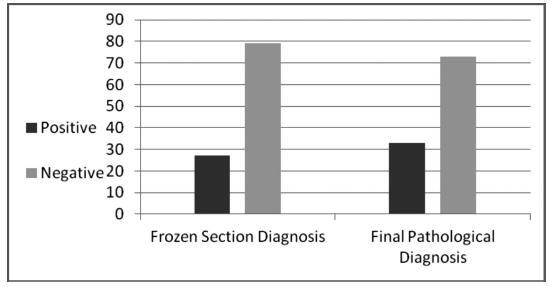
Of 106 frozen section studies, the diagnosis was accurate in 94 (88.7%). Of 79 specimens interpreted as negative on frozen sections (no products of conception noted), 9 (11.4%) were positive on final pathologic review. Three of the 27 (11.1%) specimens interpreted as positive by a frozen section failed to demonstrate products of conception on a final pathologic section. The sensitivity of frozen sections in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy was 72.7%, specificity 95.9%, positive predictive value 88.9%, negative predictive value 88.6%, and accuracy 88.6%. A statically significant correlation was found between β-hCG level and high accuracy of the frozen section technique (p< 0.001). No correlation was found between endometrial thickness and the accuracy of the frozen section technique.
The accuracy of frozen section examination was high and was found to correlate with β-hCG level, but not with endometrial thickness.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):142-146
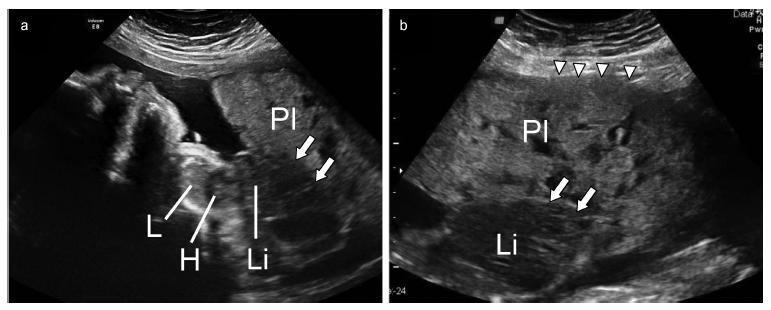
A case was reported of a fetus with the anomaly of limb body wall complex associated with placenta accreta. To date, only one account of this condition has been published in the world literature. Due to the low frequency of both complications, the hypothesis has been raised that this association may have happened not by mere coincidence, but rather by a possible common etiopathogenic mechanism. For the first time, a study proposes the existence of a possible etiopathogenic connection between the anomaly of limb body wall complex and hypoxic disorders caused by inadequate placentation in previous uterine scarring.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):143-145
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400040001
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):143-145