You searched for:"Jose Guilherme Cecatti"
We found (51) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2013;35(2):49-54
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000200002
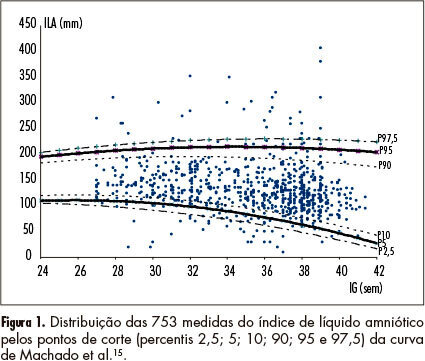
PURPOSE: To evaluate the performance of a Brazilian reference curve of fundal height (FH) regarding its capacity of screening the deviations of volume of amniotic fluid using a Brazilian reference curve of amniotic fluid index (AFI) as gold standard. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study evaluating 753 pregnant women receiving prenatal care at the public health services of João Pessoa (PB), from March to October 2006, who had a routine ultrasound exam scheduled for after 26 weeks of gestational age. Cases with diagnoses of twin pregnancy, intrauterine fetal death and major fetal malformations were excluded. Besides socio-demographic information, data regarding fundal height measured in a standard way, estimated fetal weight, AFI and gestational age at the time of the ultrasound exam were also collected. The capacity of the FH curve to predict deviations of the amniotic fluid volume was assessed using the Brazilian curve of AFI according to gestational age as the gold standard. For this purpose, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were estimated for different cut-off points. RESULTS: The measurement of FH identified 10.5% of women as having low FH possibly associated with oligohydramnios and 25.2% as having high FH possibly associated with polyhydramnios. Using a Brazilian reference curve of AFI, the FH was able to poorly predict the occurrence of oligohydramnios (sensitivity ranging from 37 to 28%) and to reasonably predict the occurrence of polyhydramnios (sensitivity ranging from 88 to 69%). CONCLUSIONS: The measurement of fundal height showed a poor performance for predicting oligohydramnios and a reasonable performance for predicting polyhydramnios. Its use for this purpose is then only supported in settings where the ultrasound exam is not easily or routinely available in order to help define priorities for cases that should have this exam performed.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(8):493-500
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800010
The interest of modern obstetrics in labor induction can be demonstrated by the huge amount of scientific articles published during the last few years. The advances of medicine in general and particularly of obstetrics allowed that more risky pregnancies reach term or near term, with a maternal or fetal indication for pregnancy interruption before the spontaneous onset of labor and delivery. This leads the obstetrician to the situation of choosing between cesarean section and labor induction. With the aim of helping the obstetrician to make the choice for labor induction and thus collaborate with the reduction in cesarean section rates, it is necessary that an accessible, cheap, safe, effective, easy to be used method with good acceptability is available. Although several methods of labor induction reported in medical literature do exist, it is known that there is no ideal method. However, among them, two are highlighted. The first is oxytocin, which has the advantages of promoting physiologic uterine contractions of labor and reverting uterine hypercontractility when suspended. The other method is misoprostol, nowadays the most used, which ripens the uterine cervix and induces uterine contractions of labor. However, there are still some controversies regarding its ideal dose, route and safety.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1998;20(9):495-501
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900002
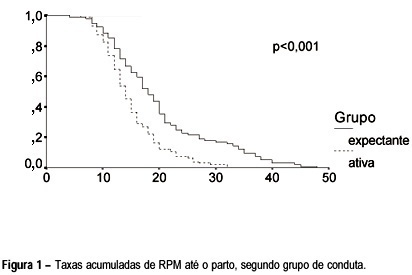
Objective: to compare the expectant versus active management with oxytocin in a Brazilian population of pregnant women with premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at term. Methods: a prospective, randomized and multicenter clinical trial was performed, evaluating variables concerning the time from PROM until the onset of labor and delivery, and maternal and neonatal hospitalization periods. Two hundred pregnant women with PROM at term were selected from four public hospitals in São Paulo state, from November 1995 to February 1997. They were randomly divided into two groups: active management, with oxytocin induction of labor until 6 h of PROM; and expectant management, waiting for the spontaneous onset of labor up to 24 h. The data were analyzed with the Epi-Info and SPSS-PC+ packages, using the statistical c², Student's t and log-rank tests. Results: the results indicate that the differences between the two managements concern to the longer time needed for the expectant management group until onset of labor and delivery, besides the higher number of women and neonates who remained in hospital for more than three days. Conclusions: the time between admission and onset of labor and delivery, and also the latent period were longer in the expectant management group.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1999;21(9):499-504
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900002
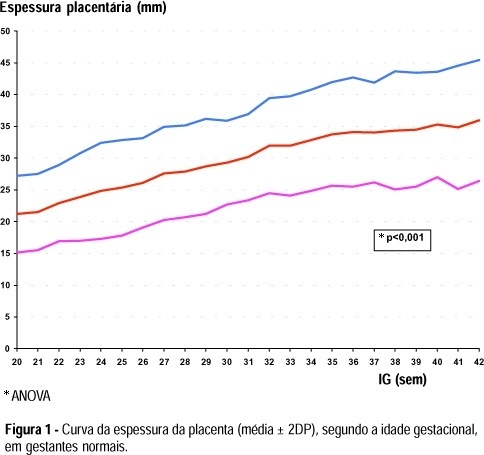
Purpose: to evaluate the ultrasound characteristics of normal pregnancies, according to the placental maturity, local of insertion and thickness, fetal presentation and position during the second half of pregnancy. Methods: a descriptive study was perfomed, including at least 120 measures in each gestational age, in 2,868 normal pregnant women from Campinas, Brazil, studied through routine obstetric ultrasound examinations, with fetal biometry and placental evaluation, applying Grannum, Berkowitz, Hobbins (1979) criteria for placental maturity. Placental thickness was measured at the cord insertion site. Results: grade 0 placentas were more frequent up to 31 weeks and grade I after 32 weeks. Grade II did not appear until 32 weeks and grade III was more frequent after 36 weeks. The placental thickness significantly increased with gestational age and the most frequent placental locations were anterior and posterior. The cephalic presentation was the most frequent all gestational ages, with only 1% of breech presentation at term. The most frequent fetal position was fetal spine left side, followed by right side. Conclusions: the studied factors showed a similar distribution to that expected for normal populations and could be used as a standard for the Brazilian population.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(7):517-525
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the experience of implementation of the Brazilian Prenatal and Birth Humanization Program (PHPN) in 2001 and 2002, through a population descriptive study. METHODS: the study was performed through documental analysis and using data generated by SISPRENATAL, comparatively evaluating the indicators concerning criteria for prenatal follow-up in different states, regions and period. RESULTS: until the end of 2002, 3983 municipalities joined the Program (72% adhesion) and, among them, 71% reported results, constituting a data base of 720,871 women. In 2002 only 28% of the pregnant women were already registered, 25% before 120 days of pregnancy. Nearly 22% of the women had six prenatal visits, 6% had the post-partum visit and the compulsory tests performed, only 4% had also the HIV test and were vaccinated against tetanus, and 12% had two examinations performed for syphilis. There were important regional variations, generally showing better indicators for the Southeast and South regions. CONCLUSIONS: although the indicators of quality of care showed an improvement from 2001 to 2002, the recorded low percentages attest the need for permanent evaluations and new interventions with the aim of improving the quality of this care, especially in the North and Northeast regions.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(9):518-526
To assess the relationship between the use of psychoactive substances during pregnancy and the occurrence of severe maternal morbidity (SMM), perinatal outcomes and repercussions on the neuropsychomotor development of exposed children.
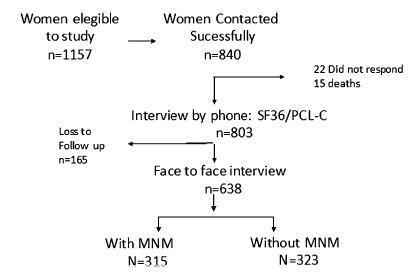
A case-control study nested within a cohort of severe maternal morbidity (COMMAG) was performed. Women with SMM were considered cases. Controls were thosewith low-risk pregnancy,without SMMand admitted during the same time period as the cases. Cohort data were collected retrospectively in hospital records for childbirth. A face-to-face interview was also performed with 638 women (323 without SMM and 315 with SMM) and their children of the index pregnancy between 6 months and 5 years after childbirth. During the interview, substance abuse during pregnancy was assessed by a modified question from the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test 2.0 (ASSIST) and the neuropsychomotor development in the children was assessed by the Denver Developmental Screening Test, 2nd edition.
The prevalence of licit or illicit drug use during pregnancy was ~ 17%. Among drug users, 63.9% used alcohol, 58.3% used tobacco, 9.2% used cocaine/crack and 4.6% used marijuana. There was no association between drug use during pregnancy and SMM, although tobacco use during pregnancy was associated with bleeding, presence of near-miss clinical criteria (NMCC) and alteration in infant development; alcohol use was associated with neonatal asphyxia; and cocaine/crack use was associated with the occurrence of some clinical complications during pregnancy.
The use of psychoactive substances during pregnancy is frequent and associated with worse maternal, perinatal and child development outcomes.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(8):519-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800008
Purpose: to evaluate the results of assistance to breech deliveries. Methods: this was a descriptive study where 160 pregnant women with breech presentation and live newborns were analyzed. They were divided into two groups according to the route of delivery. Clinical data concerning labor, delivery and newborns were studied. For statistical analysis vaginal deliveries were compared with cesarean sections using mean and standard deviation estimates, Student's t, Mann-Whitney and chi² tests. Results: the global cesarean section rate was 81.2%. The gestational age and the weight of the newborns were significantly lower in the vaginal delivery group. Prematurity and low birth weight were significantly associated with vaginal delivery. Only 14 newborns had an Apgar score below 7 at the fifth minute, almost 60% of them in the vaginal delivery group. Conclusions: this population presented a high cesarean section rate and also high perinatal morbidity, prematurity and low birth weight in the vaginal delivery group. These findings do not allow conclusions regarding the real relationships among breech presentation, route of delivery and perinatal outcomes. The control regarding gestational age and parity, besides a random decision on the route of delivery, is necessary for future conclusions.