Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(2):94-101
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200008
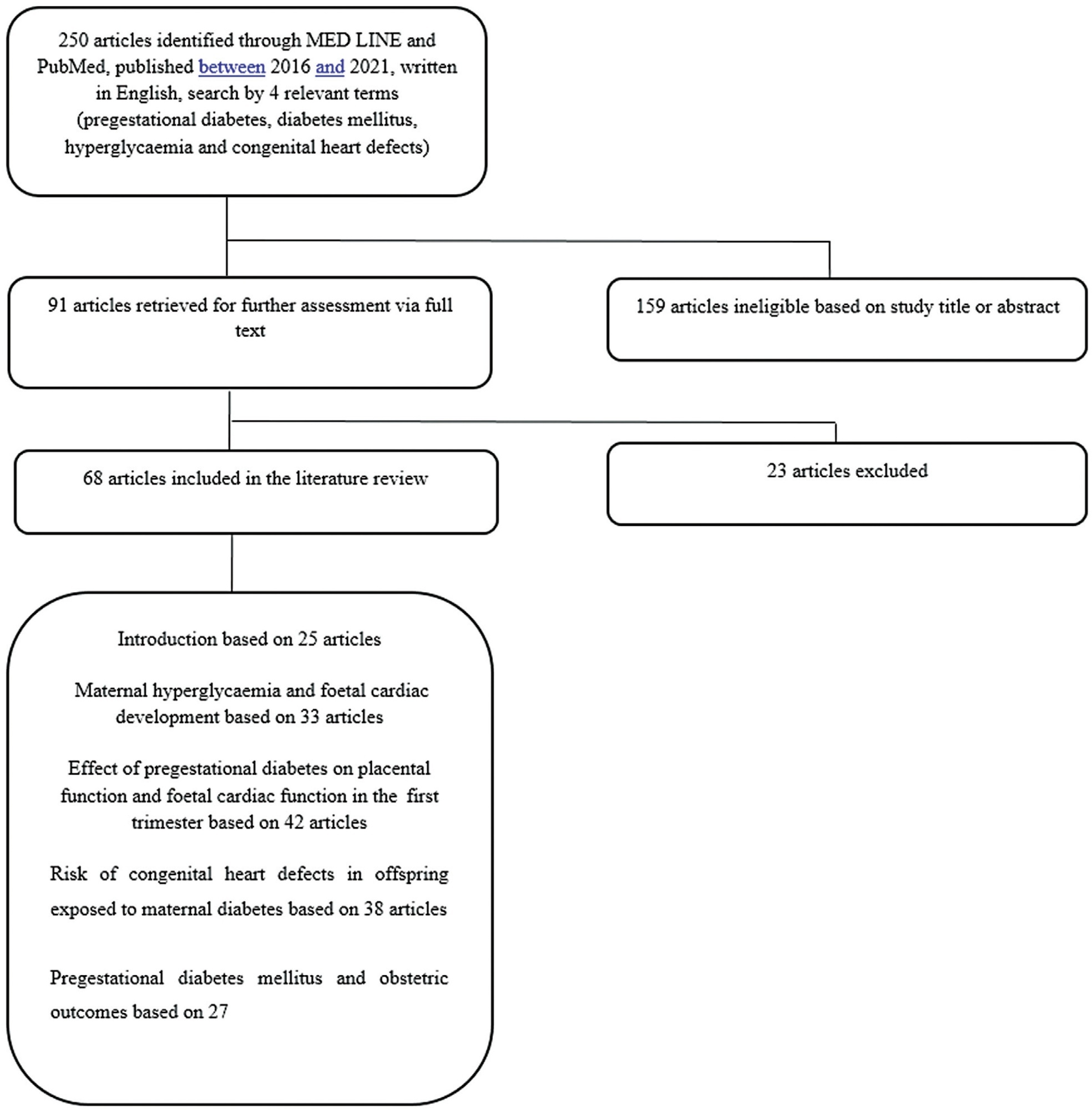
The hydatiform mole is a relatively rare pregnancy complication, but with potential to evolve to forms which need systemic treatment and can be a threat to life. There are two histopathological and clinical entities under the name of hydatiform mole: the partial and the complete mole. The differences between the two forms are important due to risk of evolution to persistent forms, which is higher for the complete moles. The diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of hydatiform mole have been under important changes in the last years. The number of asymptomatic patients has increased, due to the use of ultrasonography at the onset of pregnancy. The use of medication that induces uterine contractions must be avoided, and vacuum aspiration should be used. Soon after emptying the mole, a hormonal contraceptive method should be prescribed. Follow-up should be based on weekly serial dosages of chorionic gonadotropin. It is important that the method employed detects all the forms of chorionic gonadotropins (intact molecule, with hyper glycol, free β subunit, and central fragment β subunit).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):94-101
Anemia is a very frequent event among pregnant women. There are evidences of differences in the incidence of dental caries between pregnant and nonpregnant women, but the relationship between salivary iron (Fe) and serummarkers of anemia and caries development has not been investigated.
To evaluate the correlation between salivary (Fe) and serum iron (Fe, ferritin and hemoglobin) parameters in pregnant women with the development of dental caries.
A prospective cohort was conducted with 59 women. The outcome of interest was represented by new dental caries lesions during pregnancy, using the Nyvad criteria. Pregnant women were evaluated at three clinical times: up to the 16th week of gestational age (GA) (T1), in the last trimester of pregnancy (T2), and postpartum (T3), at the Mother and Child Unit ofUniversityHospital of the Universidade Federal doMaranhão.A stimulated saliva sample was collected for biochemical analysis of salivary Fe, and a blood sample was collected early in the morning. The correlation between salivary and serum Fe was evaluated through the Pearson correlation test. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Kruskal-Wallis were used to compare the means of anemia parameters at different times. The Student's t and Mann-Whitney tests were used to compare the anemia parameters between the groups of pregnant women (with and without new caries lesions).
SerumFe concentrationswere higher in the first trimester of pregnancy and lower after delivery (p = 0.036). It was also observed that the ferritin concentrations were higher in the first trimester and lower at the end of gestation (p = 0.011). Therewas no association between the expositions of salivary iron and anemia, and the development of dental caries. There was a positive correlation between serum Fe in T1 and salivary Fe in T2 (p < 0.05).
The serummarkers of anemiaweremore prevalent in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):940-948
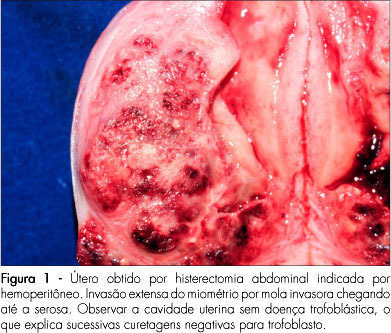
Women have metabolic, immunological, and genetic variables that ensure more protection from coronavirus infection. However, the indication of treatment for several pathologies and contraception is determined by hormones that have adverse effects and raise doubts about their use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, the present study searches women specificities and the relation between female sexual hormones and COVID-19, and reports the main recommendations in this background. To this end, a review of the literature was conducted in the main databases, auxiliary data sources, and official websites. Therefore, considering the hypercoagulability status of COVID-19, the debate about the use of contraceptives due to the relative risk of thromboembolic effects that they impose arises. However, the current available evidence, as well as the recommendations of main health organs around the world, demonstrate that the use of hormonal contraceptives must be maintained during the pandemic.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):945-952
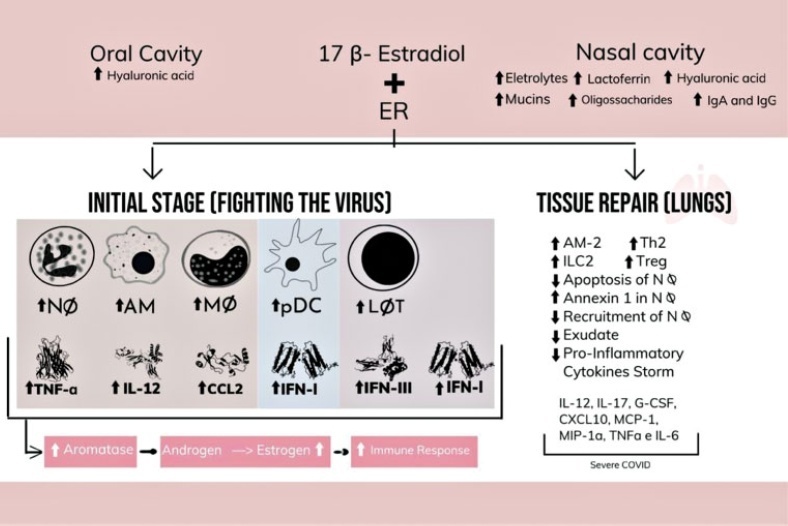
To analyze the cases of all women who attend to a service of legal termination of pregnancy in cases of sexual violence in a public reference hospital and to identify the factors related to its execution.
Cross-sectional observational study with information from medical records from January 2014 to December 2020. A total of 178 cases were included, with an evaluation of the data referring to the women who attended due to sexual violence, characteristics of sexual violence, hospital care, techniques used, and complications. The analysis was presented in relative and absolute frequencies, medians, means, and standard deviation. Factors related to the completion of the procedure were assessed using binary logistic regression.
Termination of pregnancy was performed in 83.2% of the cases; in 75.7% of the cases, the technique used was the association of transvaginal misoprostol and intrauterine manual aspiration. There were no deaths, and the rate of complications was 1.4%. Gestational age at the time the patient's sought assistance was the determining factor for the protocol not being completed. Pregnancies up to 12 weeks were associated with a lower chance of the interruption not occurring (odds ratio [OR]: 0.41; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.12–0.88), while cases with gestational age > 20 weeks were associated with a greater chance of the interruption not happening (OR: 29.93; 95%CI: 3.91–271.50).
The service studied was effective, with gestational age being the significant factor for resolution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):949-960
To analyze the clinical and obstetric aspects of pregnant women with COVID-19.
A systematic literature review in the MEDLINE/PubMed, LILACS, SCIELO, and CNKI databases was performed from March to May 2020, with the descriptors: Pregnancy; 2019-nCov; Coronavirus; SARS-Cov-2, Covid-19. Of those chosen were original titles, without language and period restriction and that addressed pregnant women with a clinical and/or laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19. Revisions, editorials, and duplicate titles were excluded. The Newcastle-Ottawa (NOS) and Murad et al. scales were used to assess the quality of the studies.
We included 34 articles with 412 pregnant women infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-Cov-2), with an average age of 27.5 years of age and 36.0 gestational weeks. The most common symptom was fever (205 [49.7%]), and 89 (21.6%) pregnant women progressed to severe viral pneumonia. Laboratory tests showed an increase in C-reactive protein (154 [37.8%]), and radiological tests showed pneumonia with peripheral ground-glass pattern (172 [51.4%]). Emergency cesarean delivery was indicated for most pregnant women, and the most common gestational complication was premature rupture of ovarian membranes (14 [3.4%;]). We detected 2 (0.5%) neonatal deaths, 2 (0.5%) stillbirths, and 1 (0.2%) maternal death.
Pregnant women with COVID-19 presented a clinical picture similar to that of non-infected pregnant women, with few obstetric or neonatal repercussions. There was a greater indication of cesarean deliveries before the disease aggravated, and there was no evidence of vertical transmission of the infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(2):95-102
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000200004
PURPOSE: to test the efficacy of and tolerance to Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi gel in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. METHODS: forty-eight women with symptomatic bacterial vaginosis (according to Amsel's criteria) were enrolled in a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial comparing Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi gel (25 cases) with placebo (23 cases). The main outcome parameters were: rate of cure, presence of lactobacilli in Pap smear after treatment and side effects. Statistical analysis was performed using the chi2 and the Fisher exact test at 5% level of significance. RESULTS: using Amsel's clinical parameters of bacterial vaginosis, the cure rate was 84% in the Schinus group and 47.8% in the placebo group (p=0.008). A significant increase in the frequency of lactobacilli was observed in the Pap smear of the group treated with Schinus (43.5%) compared to the patient group (4.3%) (p=0.002). Treatment-related adverse events were not frequent in either group. CONCLUSIOS: the present study indicates that Schinus vaginal gel is effective and safe in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. In addition, potential beneficial effects on the vaginal flora are suggested.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):95-100
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200006
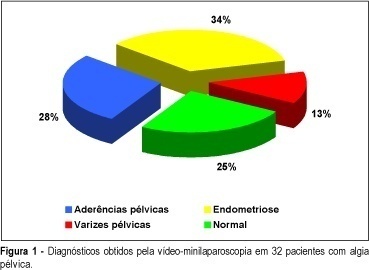
SUMMARY Purpose: to study the usefulness of minilaparoscopy in diagnosing the cause of pelvic pain. Methods: women with pelvic pain were prospectively analyzed and underwent an office video-microlaparoscopy. We analyzed the data regarding procedure time, stay in the recovery room, acceptance of anesthesia, and morbidity. Results: the average procedure time of the office video-microlaparoscopy was 19 min, the average stay for recovery was 43 min, and the technical quality of the image was excellent or good in 100% of the selected patients. The following laparoscopic findings were reported: 34.4% endometriosis, 28.1% pelvic adhesion, 12.5% pelvic varices, and 25% normal. Based on Bordhal et al.'s¹ criteria, a low frequency of pain manifestation during local anesthesia (12.5%) and discomfort on pneumoperitoneum (46.9%) were noticed. It could also be observed that, according to Milki and Tazuke's² criteria, the tolerance to the method was excellent and good (96.9%). Twenty-four hours after the procedure the morbidity rate was in accordance with Chung et al.'s³ criteria, showing a high frequency of pain at the incision area (59.4%) and sleepiness (43.8%). Only 3.1% reported they felt pain during the procedure, which shows the acceptance of the method by the patients. Conclusions: the acceptance of anesthesia and of the surgical procedure and the low morbidity allow the use of minilaparoscopy as a very important method in investigating patients with pelvic pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):953-961
Studies have consistently shown a significant increase in the risk of congenital heart defects in the offspring of diabetic mothers compared with those of nondiabetic pregnancies. Evidence points that all types of pregestational diabetes have the capacity of generating cardiac malformations in a more accentuated manner than in gestational diabetes, and there seems to be an increased risk for all congenital heart defects phenotypes in the presence of maternal diabetes. Currently, the application of some therapies is under study in an attempt to reduce the risks inherent to diabetic pregnancies; however, it has not yet been possible to fully prove their effectiveness. The present review aims to better understand the mechanisms that govern the association between pregestational diabetes and congenital heart defects and how maternal diabetes interferes with fetal cardiac development, as there is still a long way to go in the investigation of this complex process.