You searched for:"Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge"
We found (33) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):647-654
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900005
PURPOSE: to study the effects of physiotherapeutic techniques applied by the Multidisciplinary Program of Preparation for the Childbirth and Maternity on musculoskeletal discomforts during pregnancy. METHODS: prospective cohort study, with 71 low-risk nulliparous women, distributed according to participation (study: n=38) or not (control; n=33). The Multidisciplinary Program of Preparation for Childbirh and Maternity had 10 meetings (18th to 38th week), with educational, physiotherapeutic, and interaction activities. Occurrence, characteristics, and evolution of musculoskeletal discomforts were compared by means of a specific questionnaire, both at the beginning and at the end of the program. The average of results of the initial assessment was compared through analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the F test. For the study between proportions in the beginning and at the end of the program the c² was used. The statistical significance was determined at 5% of limit (p<0.05). RESULTS: at the beginning of the program, 63.6% of the pregnant women of the control group and 84.2% of the study group reported musculoskeletal symptoms (p=0.05), characterized by back and posterior pelvic pain. In the control group, light intensity (18.2%) and serious intensity pain (18.4) were predominant, while in the study group, the serious was 36.8%, and the isolated or associated was 31.6%. At the end, the control group showed symptoms of serious intensity (60.6%), with daily frequency (42.4%) and length of more than 3 h (69.7%; p<0.05). The study group reported light intensity (57.9%) and bimonthly frequency (50.0%) with a maximum length of one hour (55.3%) (p<0.05). Symptom evolution was also differentiated and there were worsening in 63.6% of pregnant women of the control group and improvement in 65.8% of participants of the program (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the physiotherapeutic techniques of the Multidisciplinary Program of Preparation for Childbirth and Maternity were related to a decrease in intensity, frequency and length and to a better evolution of musculoskeletal discomforts during pregnancy.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):677-682
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100008
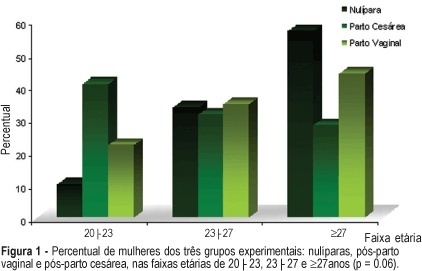
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of the delivery route on pelvic floor (PF) muscle strength. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate PF muscle strength by the pelvic floor strength evaluation (PFSE) test and perineometer in primiparous patients aged 20 to 30 years 4 to 6 months after delivery. The categorization was: zero lack of muscle contraction; one - weak contraction; two - moderate contraction not sustained for 6 s and three - normal contraction sustained for 6 s. A total of 94 patients were divided into there groups based on prior delivery route. They were: 32 patients with vaginal delivery with singleton cephalic presentation; 32 patients with cesarean delivery, and 30 nulliparous patients as a control group. The independent variable was delivery route and the dependent one was the muscle strength of the PF. Comparison between contraction levels was performed by Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn multiple comparison tests and the influence of delivery method was tested by chi2. Confidence interval of 95% was obtained for relative risk (RR) of Pf muscle strength changes and kappa statistics. RESULTS: the 1st and 3rd quartiles of delivery route regarding PF muscle strength were lower (p=0.01) for vaginal delivery (2.0;1-2) and intermediate for cesarean section (2.0;2-3) compared to the nulliparous (3.0;2-3) by the PFSE test and perineometer. RR of the altered examination was increased after vaginal delivery (RR=2.58; CI 95%: 1.32-5.04, p=0.002); (RR=2.31; CI 95%: 1.24-4.32, p=0.005), and after cesarean section (RR=1.56; CI 95%: 0.94-2.57, p= 0.12); (RR=1.38; CI 95%: 0.85-2.23, p=0.29) by AFA and perineometer, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: vaginal delivery decreased PF muscle strength when compared with cesarean delivery and control groups.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):691-697
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100010
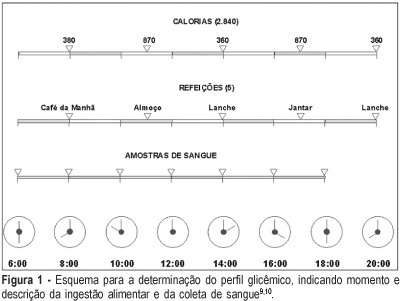
This is both a synthesis and a review of the major research findings, with the aim of validating Rudge's group IB. In this group of pregnants, screening for gestational diabetes was positive while the diagnosis was negative (normal 100 g-oral glucose tolerance test 100 g-OGTT). Nonetheless, the variations in glucose levels observed throughout the day, and confirmed by the glycemic profile (GP), characterized diurnal hyperglycemia, which accounts for maternal risk and adverse perinatal outcome. The description of this group is unique for both the establishment of the diagnosis during gestation and the follow-up of both the mother and the infant. These pregnancies have been erroneously classified as "low risk" and have not been diagnosed or treated. The IB group corresponds to 13.8% of the pregnant women screened in our service. This rate, added to the 7% of pregnancies complicated by diabetes, increase the occurrence of hyperglycemic disorders during gestation to up to 20.0%. In Rudge's group IB: a) perinatal mortality rate is 41‰, which is similar to that observed among diabetic pregnant women and 10 times higher than that found among non-diabetics; b) the observed placental abnormalities (both morphological and functional) differed from those seen in non-diabetic and diabetic pregnant women, indicating an adjustment to maintain functional activities that facilitated the passage of glucose to the fetus and explained fetal macrosomia (53.8% in non-treated pregnancies); c) maternal risk for hypertension, obesity and hyperglycemia was high and seemed to reproduce a model of metabolic syndrome, favoring the potential risk for future diabetes; d) 10 years after the index-pregnancy, type 2 diabetes was confirmed in 16.7% of the women in group IB. The authors suggest the development of multicentric studies in order to identify biomarkers specific for Rudge's group IB and establish protocols for the diagnosis of gestational hyperglycemic disorders using the combination GP + 100g-GTT as a standard. This procedure may cause an impact on the morbidity/mortality rate among pregnancies complicated by diurnal hyperglycemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(12):709-711
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(10):725-730
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003001000005
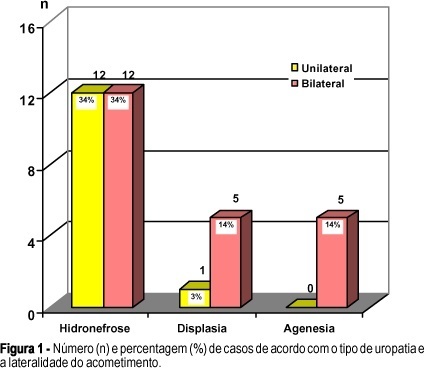
PURPOSE: to evaluate the perinatal outcome of fetuses with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. METHODS: we reviewed the perinatal outcome of 35 fetuses with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. The following characteristics related to the uropathy were analyzed: type (hydronephrosis, dysplasia and renal agenesis), side of lesion (bilateral or unilateral), and level of the obstruction (high or low, in hydronephrosis). The perinatal outcome was evaluated according to these characteristics. The data were analyzed by the c² test and by the exact Fisher test. The level of significance was 0.05. RESULTS: the incidence of hydronephrosis was 68.6%. Half of the fetuses had unilateral hydronephrosis. Renal dysplasia occurred in 17.1% of the cases; 83.3% of these were bilateral and 16.7%, unilateral. The incidence of renal agenesis was 14.3%, all bilateral. The fetuses with dysplasia/agenesis had a 91% incidence of oligohydramnios, preterm birth, low birth weight, and death. In the group with bilateral disease the presence of oligohydramnios, preterm birth, low birth weight, death, urinary tract infections, and the need of hospitalization for a period greater than 7 days was significant when compared to the group with unilateral disease. The need of hospitalization for a period greater than 7 days in patients with low obstruction was significantly higher when compared to the patients with high obstruction. CONCLUSIONS: hydronephrosis, bilateral disease, and lower obstruction were the most frequent uropathies. The dysplasia/agenesis group had a worse prognosis when compared with the hydronephrosis group. Bilateral disease had a worse prognosis when compared with the unilateral disease group. In the low obstruction group, the need for a period of hospitalization greater than seven days was higher than in the high obstruction group.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(2):87-91
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000200005
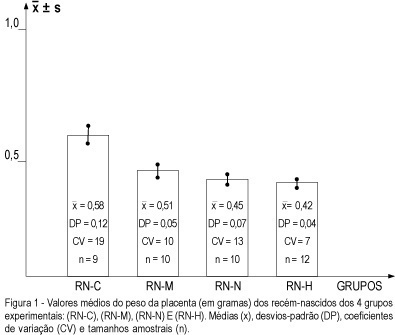
Purpose: to study the repercussion regarding placental weight and placental index determined by induced experimental hypertension in rats. Methods: a total of 82 rats in reproductive age were used. They were randomly assigned to 4 different groups (control, handled, nephrectomy and hypertension) and renal hypertension was produced by a controlled constriction of the main left renal artery, according to the technique described by Goldblatt, and contralateral nephrectomy (Goldblatt I one kidney--one clip model). Furthermore, they were distributed into non-pregnant groups and pregnant (P) groups. From the pregnant groups, the following newborn groups were obtained: RN-C (control -- newborn group from the pregnant rats without surgical treatment), RN-M (manipulation -- newborn group from the pregnant rats with surgical manipulation), RN-N (nephrectomy -- newborn group from the pregnant rats with nephrectomy) and RN-H (hypertension -- newborn group from pregnant rats with hypertension). Results: the RN-C newborn group ( = 0.58 ± 0,12) showed placental weight higher than the other three groups (RN-M:
= 0.58 ± 0,12) showed placental weight higher than the other three groups (RN-M:  or = 0.51 ± 0.05; RN-N:
or = 0.51 ± 0.05; RN-N:  or = 0.45 ± 0.07 and RN-H:
or = 0.45 ± 0.07 and RN-H:  or = 0.42 ± 0.04). On the other hand, it was possible to observe that the placental weight of the RN-M was higher than that of RN-N and RN-H, respectively, but no difference was observed between the RN-N and RN-H groups. The placental index showed no difference between P-C (Md = 0.1085) and P-M (Md = 0.1110), and also between P-N (0.1175) and P-H (0.1211), but it was observed that the placental indexes of P-C and P-M were smaller that those of P-N and P-H. Conclusion: unilateral nephrectomy and hypertension determined a reduction in placental weight and an increase in the placental index, showing a repercussion regarding placental and fetal development.
or = 0.42 ± 0.04). On the other hand, it was possible to observe that the placental weight of the RN-M was higher than that of RN-N and RN-H, respectively, but no difference was observed between the RN-N and RN-H groups. The placental index showed no difference between P-C (Md = 0.1085) and P-M (Md = 0.1110), and also between P-N (0.1175) and P-H (0.1211), but it was observed that the placental indexes of P-C and P-M were smaller that those of P-N and P-H. Conclusion: unilateral nephrectomy and hypertension determined a reduction in placental weight and an increase in the placental index, showing a repercussion regarding placental and fetal development.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(1):9-14
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000100002
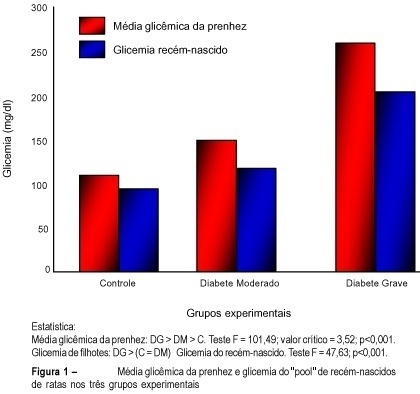
Purpose: to evaluate the effects of maternal diabetes on the fetal lung phospholipid profiles of rats with moderate and severe diabetes measuring lecithin (L), sphingomyelin (S), phosphatidyl-glycerol (PG), phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), and the relationships between L/S and PG/PI. Methods: fifty-four mature Wistar rats were submitted to experimental diabetes and pregnancy¹. Diabetes was induced by alloxan (42 mg/kg of weight, iv) and three groups were formed: control; moderate diabetes (MD), with glycemia levels between 120 and 200 mg/dl, and severe diabetes (SD), with glycemia levels higher than 200 mg/dl. On the 21st day, cesarian section was performed, and the fetal lungs were macerated and pooled. The phospholipids were measured by unidirectional thin-layer chromatography. Results: 1) the fetal lungs of the rats with moderate diabetes showed higher weight (0.159 g) and lower concentration of PG (3.0 µg/ml) and PI (3.4 µg/ml) than the controls, and the same relationship between L/S (2.2) and PG/PI (2.0). The fetal lungs of the rats with severe diabetes showed lower weight (0.145 g), the same values of L/S (1.9) and PG/PI (2.1), and lower PI (5.1 µg/ml) value than the controls. Conclusions: 1) the pulmonary maturity retardation in the pups of rats with moderate diabetes is explained by the higher pulmonary weight associated with lower concentration of PG and PI; 2) the pulmonary maturity acceleration in the pups of rats with severe diabetes is explained by the lower pulmonary weight associated with the same concentration of PG and PI.