Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):683-688
It is well known that female infertility is multifactorial. Therefore, we aimed to compare the effects of thyroid dysfunction, vitamin deficiency, and microelement deficiency in fertile and infertile patients.
Between May 1st, 2017, and April 1st, 2019, we conducted a retrospective case-control study with of 380 infertile and 346 pregnant patients (who normally fertile and able to conceive spontaneously). The fertile patients were selected among those who got pregnant spontaneously without treatment, had a term birth, and did not have systemic or obstetric diseases. The levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO), vitamin D, vitamin B12, folic acid, ferritin, and zinc of both groups were compared.
There was no difference between patients in the infertile and pregnant groups in terms of low normal and high serum T3 and T4 levels (p = 0.938; p > 0.05) respectively, nor in terms of normal and high anti-TPO levels (p = 0.182; p > 0.05) respectively. There was no significant difference regarding patients with low, insufficient, and sufficient vitamin D levels in the infertile and pregnant groups (p = 0.160; p >0.05) respectively. The levels of folic acid, ferritin, and zinc of the infertile group were significantly lower than those of the pregnant group.
The serum levels of folic acid, ferritin, and zinc in infertile patients presenting to our outpatient clinic were lower than those o the fertile patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(9):685-690
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900002
PURPOSE: to identify the responses of heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP), and hydrostatic weight (HW) in pregnant women immersed up to different anatomic points as far as the xiphoid process. METHODS: eleven pregnant women underwent the following experimental procedure: 10 minutes in recumbent position for evaluation of HR and BP at rest; 2 minutes in standing position for evaluation of initial measures of HR, BP and mass, and one minute for each immersion depth. HR, BP and HW were measured after immersion up to the level of the ankle, knee, hip, navel, and xiphoid process, respectively. Descriptive statistics, test of normality (Shapiro-Wilks), homogeneity of variance test (Levene), one-way ANOVA and the Bonferroni test (SPSS version 8.0) were used, with significance at p<0.05. RESULTS: significant differences were found for HR, diastolic BP and mean BP starting from the xiphoid process (79.1±5.1 bpm; 53.3±6.7 mmHg and 63.9±6.2 mmHg, respectively) and for the systolic BP starting from the navel (92.7±11.1 mmHg). Significant differences were seen in all measurements of percent HW reduction, as in previous studies carried out with non-pregnant women. CONCLUSION: the obtained results showed a decrease in HR and BP on water immersion when compared non-immersion, as well as decreases in HW, which were proportional to the depth of immersion. The decrease in HW was found to influence the decrease in mechanical load imposed on the lower limb joints, since the mechanical load depends on both the vertical force (hydrostatic weight) and on the acceleration with which the body touches the ground. As a result, it is concluded that water is a healthy environment for the population under study, and may be adequate for the practice of physical activities.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):685-685
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):685-685
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(10):685-685
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(10):685-685
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000009
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):686-691
To review literature and estimate the occurrence of preeclampsia and its complications in Brazil.
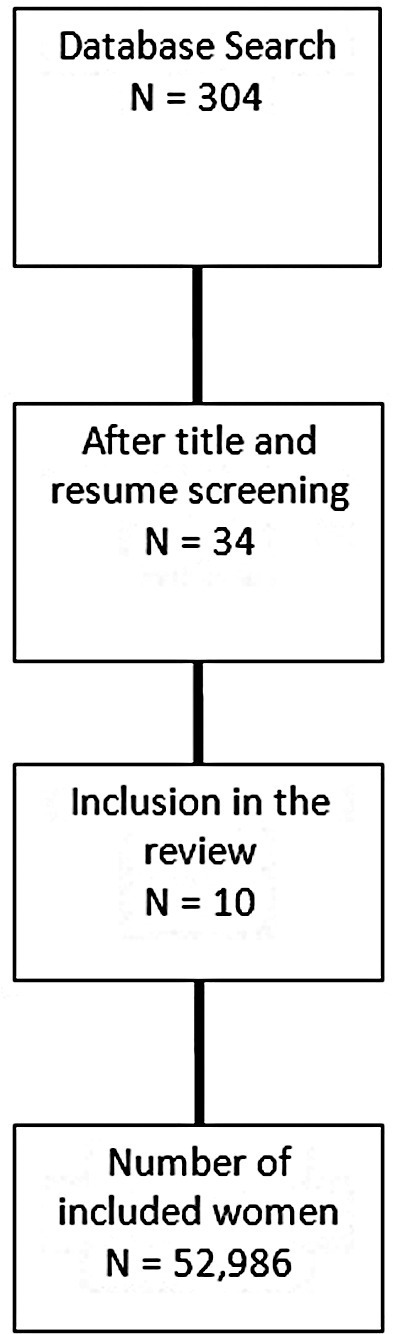
We performed an integrative review of the literature, and included observational studies published until August 2021 on the SciELO and PubMed databases that evaluated preeclampsia among pregnant women in Brazil. Other variables of interests were maternal death, neonatal death, hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count (HELLP) syndrome, and eclampsia. Three independent reviewers evaluated all retrieved studies and selected those that met inclusion criteria. A metanalysis of the prevalence of preeclampsia and eclampsia was also performed, to estimate a pooled frequency of those conditions among the studies included.
We retrieved 304 studies after the initial search; of those, 10 were included in the final analysis, with a total of 52,986 women considered. The pooled prevalence of preeclampsia was of 6.7%, with a total of 2,988 cases reported. The frequency of eclampsia ranged from 1.7% to 6.2%, while the occurrence of HELLP syndrome was underreported. Prematurity associated to hypertensive disorders ranged from 0.5% to 1.72%.
The frequency of preeclampsia was similar to that reported in other international studies, and it is increasing in Brazil, probably due to the adoption of new diagnostic criteria. The development of a national surveillance network would be essential to understand the problem of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):686-691
To verify if pethidine is safe for the conceptus when used during labor.
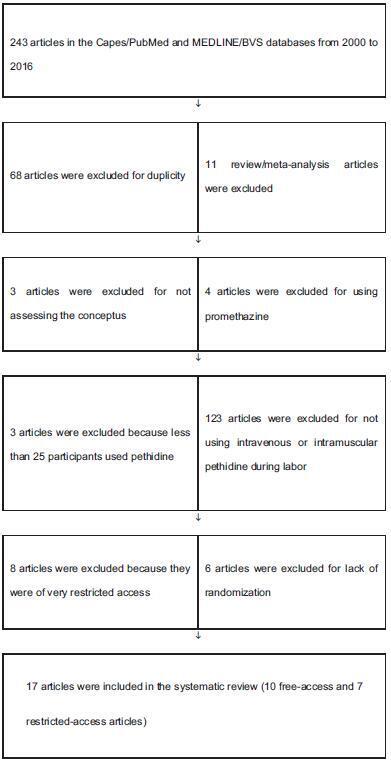
Systematic review in the Capes Periodicals/PubMed and MEDLINE/Virtual Health Library (BVS, in the Portuguese acronym) databases.
A total of 17 studies published from January 1st, 2000, to September 2nd, 2016, with a total of 1,688 participants involved were included in the present review. There was no record of conceptus vitality decrease associated with low doses of pethidine being administered to mothers during labor.
Intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) pethidine at low doses, of up to 50 mg, is safe to administer during labor.