Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(1):68-68
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000100012
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):680-685
Our aim is to demonstrate the importance of methotrexate (MTX) therapy for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy (EP).
This retrospective study consisted of 99 patients (72 tubal EPs, 20 pregnancies of unknown location (PUL), 4 cesarean section (CS) scar EPs and 3 cervical EPs) treated with MTX.
Methotrexate therapy was successful in 68.5% of EPs. There were statistically significant differences between the MTX success and failure groups based on ultrasonographic findings, patient complaints, gestational week and serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) values. The MTX success rates in PUL and tubal pregnancies were 95% and 61.1%, respectively. The MTX success rates in single-dose, two-dose and multi-dose protocol groups were 86.9%, 28.6% and 40%, respectively. All cervical and CS scar ectopic pregnancies were treated successfully with MTX therapy.
Methotrexate might be the first-line treatment option for EPs under certain conditions. Physicians must be more cautious in cases with higher hCG values, the presence of abdominal-pelvic pain, the presence of fetal cardiac activity, larger gestational sac (GS) diameters, and more advanced gestational weeks according to the last menstrual period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(10):681-684
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000008
PURPOSE: to assess ovarian function in patients with cervical cancer following radical hysterectomy with ovarian preservation. METHODS: we retrospectively analyzed patients with cervical carcinoma, submitted to radical hysterectomy with ovarian preservation at the Gynecologic Clinic of the São Marcos Hospital-SPCC, from April 1998 to October 2001, with evaluation of symptoms of estrogenic deprivation (flushing, dry vagina) and the measurement of FSH levels after surgery. All data were analyzed using the Pearson test. RESULTS: FSH levels were measured in 42 patients; of these, 33 (78.5%) patients had normal FSH levels (below 30 mU/mL). The median level was 21.05 mU/mL (range 1.2-132.44 mU/mL). Five (55.6%) of the nine patients with high FSH levels had received postoperative radiotherapy (p<0.0001). There was no correlation between postoperative FSH levels and age over 40 years (p=0.33). Benign ovarian cysts occurred in four patients (7.7%). One patient presented recurrence of the lesion in the vaginal dome and metastasis to the scalp, and died. CONCLUSION: in 78.5% of the patients, ovarian function was preserved. Ovarian transposition was inadequate to preserve ovarian function in patients who underwent postoperative radiotherapy. There was no correlation between age and postoperative FSH levels.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(12):682-687
The present study aims to understand to what extent obesity is related to adversematernal, obstetrical, and neonatal outcomes in a Portuguese obstetrical population.
A retrospective case-control study was conducted at the Department of Obstetrics of a differentiated perinatal care facility. The study compared 1,183 obese pregnant womenwith 5,399 normal or underweight pregnantwomen for the occurrence of gestational diabetes, hypertensive pregnancy disorders, and preterm birth. Mode of delivery, birthweight, and neonatal intensive care unit (ICU) admissionswere also evaluated. Mean blood glucose values were evaluated and compared between groups, in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. Only singleton pregnancies were considered.
The prevalence of obesity was 13.6%. Obese pregnant women were significantly more likely to have cesarean sections (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.0, p< 0.001), gestational diabetes (aOR 2.14, p< 0.001), hypertensive pregnancy disorders (aOR 3.43, p< 0.001), and large-for-gestational age ormacrosomic infants (aOR 2.13, p< 0.001), and less likely to have small-for-gestational age newborns (aOR 0.51, p< 0.009). No significant differences were found in terms of pretermbirths, fetal/neonatal deaths, low birthweight newborns, and neonatal ICU admissions among cases and controls. Maternal obesity was significantly associated with higher mean blood glucose levels, in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy.
Obesity is associated with increased risks of adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes. These risks seem to increase progressively with increasing body mass index (BMI) class. Female obesity should be considered a major public health issue and has consequences on maternal-fetal health.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(9):682-689
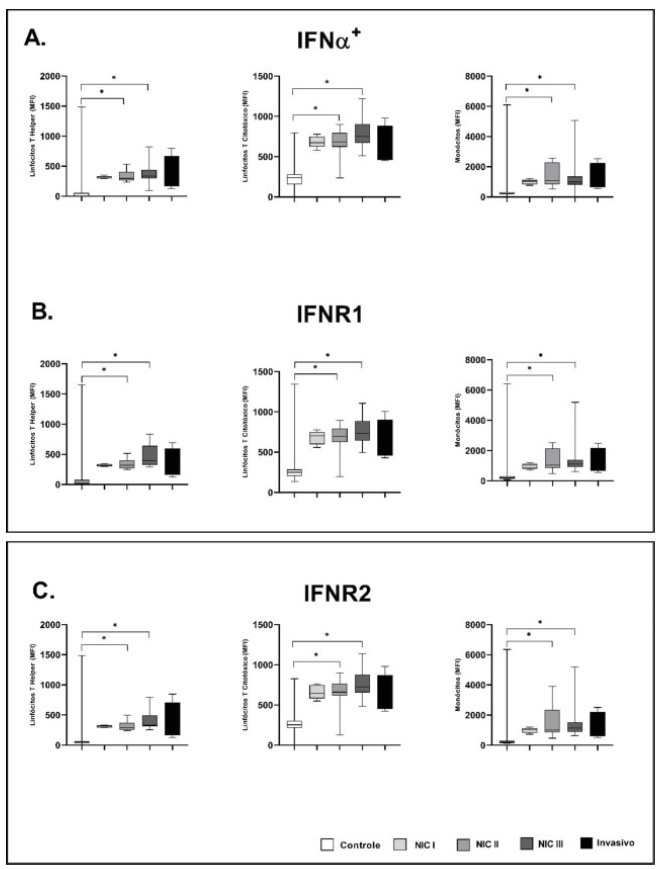
The aim of the present study was to compare the local and systemic expression of the factors linked to the interferon alpha (IFN-α) activation pathway in different degrees of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer.
A total of 128 patients with CIN I, CIN II, CIN III and cervical cancer was evaluated. The real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique was used to evaluate the gene expression of IFNR1, IFNR2, IFN-α, oligoadenylate synthase (2’5′OAS), cytokine signal suppressor 1 (SOCS) 1, SOCS3, signal transducer and transcription activator 1 (STAT1), and IRF9 from 128 biopsies. A total of 46 out of 128 samples were evaluated by flow cytometry for IFNAR1, IFNAR2, STAT1, IRF7 and IFN-α in peripheral blood cells.
Patients with CIN II and III (63 samples) had a low local expression of IFNR1, but not IFNR2. Patients with some degree of injury showed high expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3. Systemically, patients with CIN II and III (20 samples) had a significant increase in IFNR1, IFNR2, STAT1, IRF7, and IFN-α in helper, cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and in monocytes.
Patients with high-grade lesions have increased systemic expression of IFN-α and its activation pathways in helper and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, as well as in monocytes due to an exacerbation of the immune response in these patients. This phenomenon is not accompanied by resolution of the lesion due to a defect in the IFN-α activation pathway that revealed by low local IFNAR1 expression and high local expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):683-690
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100009
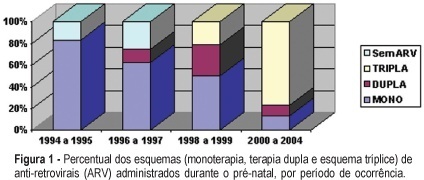
PURPOSE: to evaluate human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vertical transmission and risk factors related to perinatal infection. METHODS: descriptive study of 170 HIV-infected pregnant women and their 188 neonates, admitted from June 1994 to September 2004 at the "Maternidade do Hospital das Clínicas da UFMG". Demographic characteristics, mother's serologic state, mode of delivery and perinatal results were analyzed. Children were followed for 18 months after birth. Data were stored and analyzed by Epi-Info, version 6.0. Confidence interval was established at 95% (p<0.05). RESULTS: HIV infection was confirmed in 84 (45.4%) patients during gestation. Viral load was below 1,000 copies/mL in 60.4% patients. Highly active antiretroviral therapy was the predominant antiretroviral regimen (65.5%). C-section rate was high: 79.5%. Prematurity rate was 18.2%. There were 184 (97.8%) live births and four (2.2%) perinatal deaths among 188 neonates. Among live neonates 97.8% received zidovudine after birth. Global mother-to-child transmission rate was 3.8%. Virus vertical transmission rates for each period were: 60%, until 1996; 28% between 1996 and 1998; 0.68%, between 1999 and 2004. Significant risk factors were not found related to perinatal HIV-infection because there was a small number of infected neonates (n=6). CONCLUSION: there was a great reduction of HIV vertical transmission during the analyzed period. Current transmission rate is zero. This confirms that by adopting adequate measures perinatal virus transmission can be prevented.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(9):683-683