Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):591-596
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001200005
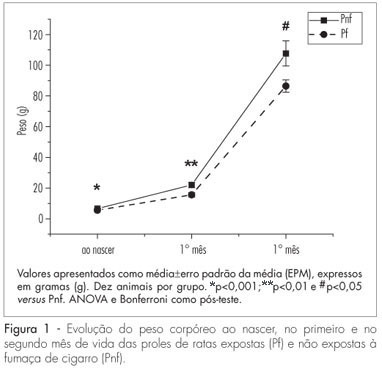
PURPOSE: to investigate the effect of cigarette smoke exposure on body and tissue weight gain, serum parameters and milk yield during pregnancy and lactation in rats, and the impact on offspring from birth toil young adulthood. METHODS: 40 Wistar pregnant rats were randomly divided into: CG - not exposed to cigarette smoke and sacrificed at the end of pregnancy; CL - not exposed to cigarette smoke and sacrificed at the end of lactation; FG - exposed to cigarette smoke and sacrificed at the end of pregnancy; FL - exposed to cigarette smoke and sacrificed at the end of lactation. The offspring were separated by gender and divided according to their mothers' groups. Tissue weight, body weight and serum parameters were evaluated in rats and offspring. Milk yield per pup was calculated. RESULTS: body weight was decreased in FL during lactation (CL=267.0±7.2; FL=235.5±7.2 g*,*p<0.05). Adipose tissue was not detected in the CL and FL groups, and was reduced in FG compared to CG (CG=3.3±0.3; FG=2.4±0.3 g*, *p<0.05). Rats exposed to cigarette smoke had higher blood glucose levels (CG=113±17, CL=86±16, FG=177±21*, FL=178±23 mg/dL*, *p<0.05 CG versus FG e CL versus FL), CL and FL groups presented lower HDL-cholesterol with no change in total cholesterol. Finally, rats exposed to cigarette smoke had lower milk yield compared to unexposed rats (CL=6.7±0.4, FL=5.4±0.3 g*, *p<0.05). In offspring from the FG and FL groups, there was a decrease of body weight from birth to young adulthood, with no changes in gastrocnemius, liver or heart weights in any group, and adipose tissue was no detected in female offspring. There was an increase in blood glucose in offspring of both sexes from rats exposed to cigarette smoke (males: Pcg=107±10.5, Pcl=115±8.6, Pfg=148±16.8*, Pfl=172±11.2**; females: Pcg=109±27.2, Pcl=104±9.7, Pfg=134±20.0*, Pfl=126±13.3**; p<0.05 *Pcg versus Pfg and **Pcl versus Pfl). CONCLUSIONS: exposure to cigarette smoke provokes impairment of morphometric and serum parameters during pregnancy and lactation both in mothers and offspring, which is maintained during young adulthood.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):591-593
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(12):592-597
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001200003
PURPOSE: The adaptation into Portuguese and evaluation of the Index of Scientific Quality (ISQ) questionnaire applicability's in texts presented by Brazilian magazines on woman's health. METHODS: A transversal cohort study. Texts published from August 2005 to July 2007, in the main weekly magazines Veja, Época and Isto é, were collected. The questionnaire used is composed of eight items, with five alternatives each, measuring the applicability, opinion degree, validity and implications of the finding, precision, coherence and relevance of the data, besides a global item summarizing all the other items. ISQ was translated, retro-translated and submitted to a pilot test till the final version, which was used by two medical doctors and two journalists. After the texts analysis', the internal consistency of the questionnaire items was checked through Cronbach's alpha coefficient, and the inter and intra-observer agreement, for each item, by Kappa's index. RESULTS: The sample was composed by 80 articles. The internal consistency of items has varied from 0.81 to 0.96. The inter-evaluators' agreement ranged from -0.03 to 0.48, and the intra-observer varied from 0.27 to 0.34 (CI 95%). CONCLUSION: The questionnaire items have adequately measured the scientific quality of the texts, but the low agreement inter and intra-observers points to the need for further studies to assess the Brazilian version of ISQ.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):593-601
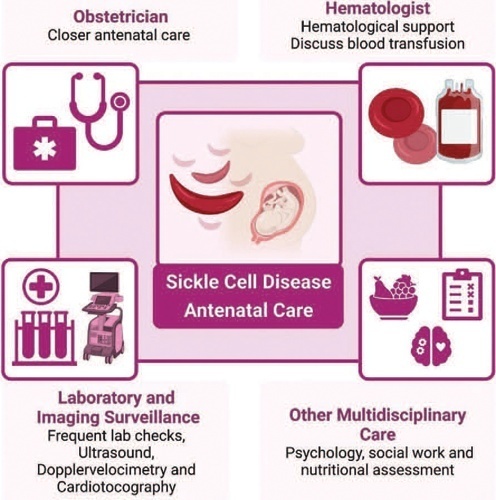
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is the most common monogenic disease worldwide, with a variable prevalence in each continent. A single nucleotide substitution leads to an amino-acid change in the β-globin chain, altering the normal structure of hemoglobin, which is then called hemoglobin S inherited in homozygosity (HbSS) or double heterozygosity (HbSC, HbSβ), and leads to chronic hemolysis, vaso-occlusion, inflammation, and endothelium activation. Pregnant women with SCD are at a higher risk of developing maternal and perinatal complications. We performed a narrative review of the literature considering SCD and pregnancy, the main clinical and obstetrical complications, the specific antenatal care, and the follow-up for maternal and fetal surveillance. Pregnant women with SCD are at a higher risk of developing clinical and obstetric complications such as pain episodes, pulmonary complications, infections, thromboembolic events, preeclampsia, and maternal death. Their newborns are also at an increased risk of developing neonatal complications: fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, stillbirth. Severe complications can occur in patients of any genotype. We concluded that SCD is a high-risk condition that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. A multidisciplinary approach during pregnancy and the postpartum period is key to adequately diagnose and treat complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):593-598
To analyze endocan-1, a biomarker of vascular endothelial related pathologies, and the placental growth factor (PlGF), an angiogenic factor and a placental dysfunction marker in patients with preeclampsia (PE).
Case-control study conducted at Hospital São Lucas, in the city of Porto Alegre, Brazil. Endocan-1 and PlGF levels were quantified in the maternal plasma using the MagPlexTH-C microsphere system (MAGPIX System, Luminex, Austin, Texas, US) and evaluated through analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) and adjusted by body mass index (BMI), gestational age and maternal age. To estimate the difference between the groups, the mean ratio (MR) and the 95% confidence interval (95%CI) were calculated. The Pearson correlation test was used to establish any association between endocan-1 and PlGF levels. The null hypothesis was rejected when p < 0.05.
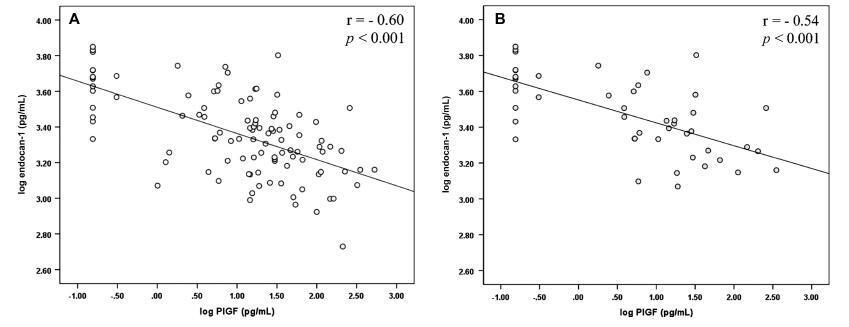
The group of patients was composed by normotensive (n = 67) patients and patients with PE (n = 50). A negative correlation between endocan-1 and the PlGF was noted in the entire normotensive group (linear correlation coefficient [r] = -0.605; p < 0.001), as well as in the PE group (r = -0.545; p < 0.001).
Endocan-1 levels are increased in patients with PE, and are inversely correlated with PlGF levels. We suggest that it is important to analyze angiogenic and proinflammatory molecules concomitantly in women with PE to better understand the pathophysiology of the disease. Both molecules are strong candidates for PE biomarkers, and future studies will examine any mechanisms connecting these factors in PE.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(12):593-599
To evaluate the antifungal susceptibility profile of the aqueous extract of the bark of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi against the strains of the genus Candida.
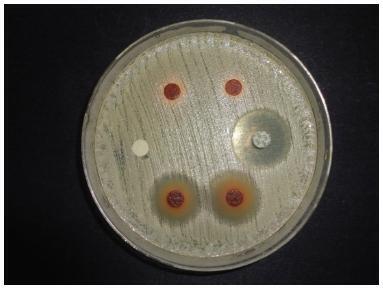
By using the disk diffusion method, 50 samples of the genus Candida (Candida albicans; Candida krusei; Candida glabrata; and Candida tropicalis), isolated from patients receiving treatment at Hospital Santa Casa de Misericórdia de São Paulo, and 1 American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) sample of each species were tested against: the isolated aqueous extract of the bark of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi, isolated nystatin, and the association of nystatin and the aqueous extract of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi.
There were no significant differences regarding the different strains of Candida tested. In the presence of the aqueous extract of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi, no inhibition halo was visible. Isolated nystatin formed an inhibition halo measuring respectively 18.50 mm and 19.50 mm for the Candida albicans species and the others referred to as non-Candida albicans (Candida krusei; Candida glabrata; and Candida tropicalis). The association of nystatin and the aqueous extract of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi resulted in inhibition halos measuring 14.25 mm and 16.50 mm respectively. The comparisons of these results are statistically significant (p < 0,001).
The aqueous extract of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi showed no antifun-gal activity in vitro against the strains tested, whereas the association of nystatin and the aqueous extract of Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi caused a decrease in the inhibition halo when compared with isolated nystatin.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):593-601
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100008
There is evidence that estrogen, progesterone and testosterone have modulatory effects over both cellular and humoral immune responses. These effects occur via immune-neuroendocrine interactions, involving the pituitary, gonadal steroids, thymic hormones, and the presence of specific receptors and messengers. These immune responses may be altered during pregnancy, gonadectomy, menopause and hormone therapy. Estrogen depresses the cellular immunity, suppresses the natural killer cell activity and increases the production of antibodies. Progesterone/progestogen suppresses the cellular immune system. Androgens, after metabolization in estrogens, might stimulate the humoral immune response. Hormone therapy is still broadly used in post-menopause women with the purpose of decreasing climacteric symptoms, as well as preventing genital atrophy and bone loss. Its use to attenuate the risk of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases remains in debate. A few studies have been carried out to examine the effect of post-menopause hormone therapy on the immune system. There is evidence that the hypoestrogenic state, following menopause, could result in less resistance to infections. The present review examines the interaction between sexual steroids and the immune system and, based on epidemiological and clinical studies, evaluates the effects of hormone therapy on the immune responses. It was concluded that the hormone therapy normalizes the cellular immune response in post-menopausal women.