Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):113-113
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):113-115
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200010
The authors report a rare case of dermatomyositis diagnosed at the Mastology Sector of the Division of Gynecology of the Federal University of São Paulo - Escola Paulista de Medicina, which caused breast deformity due to formation of bilateral dystrophic calcifications.
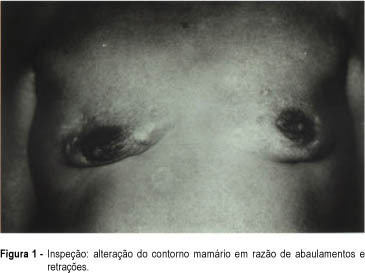
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(3):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000300004
PURPOSE: To determine the association between maternal complications and type of delivery in women with heart disease and to identify the possible clinical and obstetrical factors implicated in the determination of the route of delivery. METHODS: This was a retrospective and descriptive study of the medical records of pregnant women with heart disease admitted to a tertiary reference hospital in the municipality of Fortaleza, Ceará, from 2006 to 2007. The study population included all pregnant women with an antepartum diagnosis of heart disease admitted for delivery, while women who received a diagnosis of heart disease after delivery were excluded, regardless of age and gestational week. A semi-structured questionnaire regarding sociodemographic, clinical and obstetrical variables was used. A descriptive analysis was first performed based on simple frequencies and proportions of the sociodemographic variables. Next, possible associations between clinical and obstetrical aspects and type of delivery were analyzed, with the verification of association between maternal complications and type of delivery. The Fisher exact test was applied for this analysis, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. The collected data were processed and analyzed using the Epi-InfoTM software version 6.04 (Atlanta, USA). RESULTS: Seventy-three pregnant women with heart disease were included in the study. Interatrial communication was the condition most frequently observed among congenital diseases (11.0%) and mitral calcification among the acquired ones (24.6%). The proportion of cesarean deliveries was higher than the proportion of vaginal deliveries, except for women with acquired heart disease. An association was detected between type of heart disease and type of delivery (p=0.01). There were 13 cases of maternal complications (17.8%). Among them, ten (76.9%) occurred during cesarean section and three during vaginal delivery. No association mas detected between maternal complications and type of delivery in pregnant women with heart disease (p=0.74). CONCLUSIONS: There was no association between the occurrence of maternal complications and route of delivery among pregnant women with heart disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1134-1140
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)is an entity with evolving conceptual nuances that deserve full consideration. Gestational diabetes leads to complications and adverse effects on the mother's and infants' health during and after pregnancy. Women also have a higher prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) related to the hyperglycemic status during pregnancy. However, the exact pathophysiological mechanism is still uncertain. We conducted a narrative review discussing the impact of GDM on the women's pelvic floor and performed image assessment using three-dimensional ultrasonography to evaluate and predict future UI.
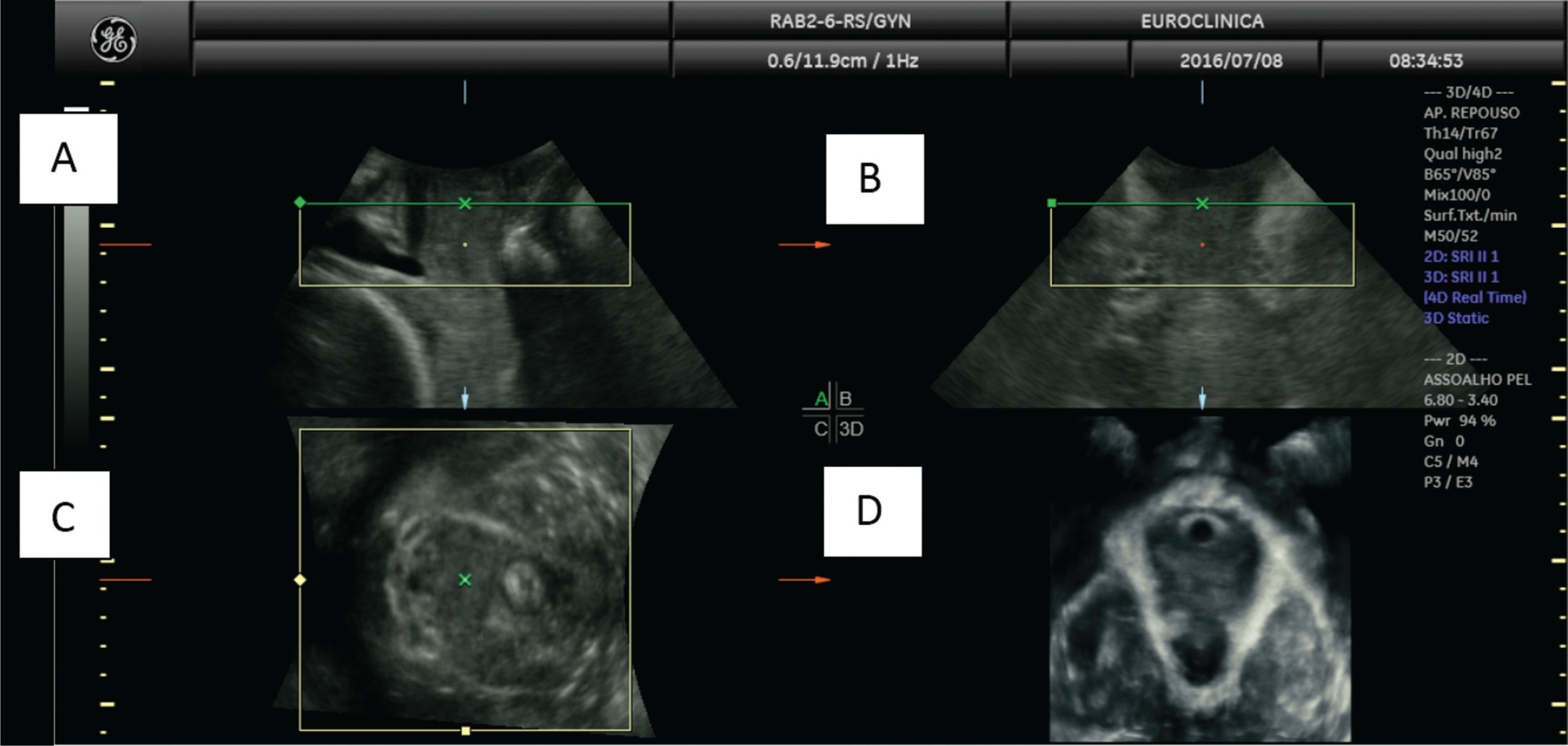
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):114-119
Several factors trigger the development of genetic mutations that are responsible for causing a neoplasm. Medulloblastoma is a malignant and invasive cerebellar neoplasm, that affects children and young adults. Mucinous carcinoma is a special type of breast cancer. Being a special atypical subtype of invasive carcinoma, it most frequently affects women of advanced age and represents 1 to 7% of all breast cancers. The reported case aims to show the rarity of the occurrence of desmoplastic medulloblastoma and mammary mucinous carcinoma in a young patient in a short period of time, in different sites, without direct anatomical attachment and without occurrence of metastasis. Initially, this patient had a desmoplastic medulloblastoma and was treated with lumpectomy and radiotherapy. After 13 months, the patient was diagnosed with a mucinous breast carcinoma, underwent mastectomy, adjuvant chemotherapy and is currently undergoing endocrinotherapy. We conclude, based on the metachronous characteristic of the neoplasia and clinical characteristics, that the patient is likely to have Li-Fraumeni syndrome, an autosomal dominant disease with mutation of the TP53 gene, which is the the main involved. Because the patient does not present all the characteristics of the phenotype of the syndrome, she can thus be classified as having Li-Fraumeni variant or Li-Fraumeni-like syndrome.
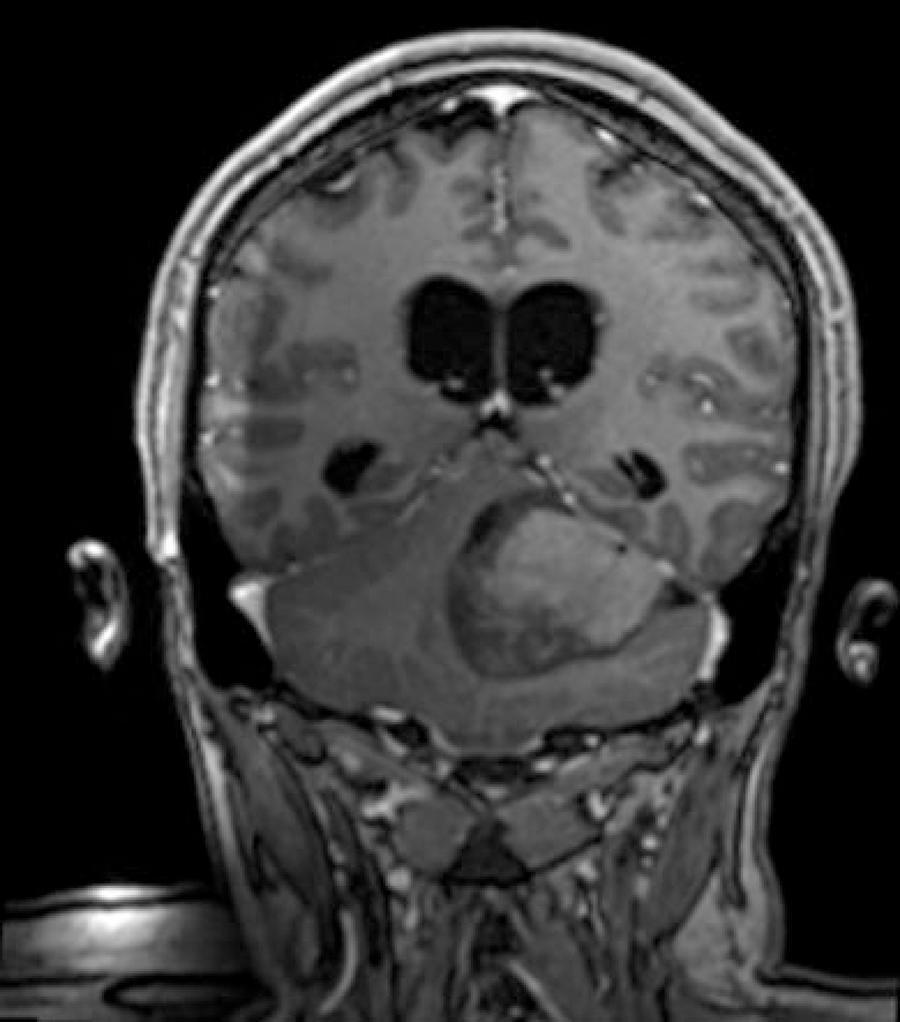
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Surrogacy is the process in which a woman carries and delivers a baby to other person or couple, known as intended parents. When carriers are paid for surrogacy, this is known as commercial surrogacy. The objective of the present work is to review the legal, ethical, social, and cultural aspects of commercial surrogacy, as well as the current panorama worldwide.
This is a review of the literature published in the 21st century on commercial surrogacy.
A total of 248 articles were included as the core of the present review. The demand for surrogate treatments by women without uterus or with important uterine disorders, single men and same-sex male couples is constantly increasing worldwide. This reproductive treatment has important ethical dilemmas. In addition, legislation defers widely worldwide and is in constant change. Therefore, patients look more and more for treatments abroad, which can lead to important legal problems between countries with different laws. Commercial surrogacy is practiced in several countries, in most of which there is no specific legislation. Some countries have taken restrictive measures against this technique because of reports of exploitation of carriers.
Commercial surrogacy is a common practice, despite important ethical and legal dilemmas. As a consequence of diverse national legislations, patients frequently resort to international commercial surrogacy programs. As of today, there is no standard international legal context, and this practice remains largely unregulated.
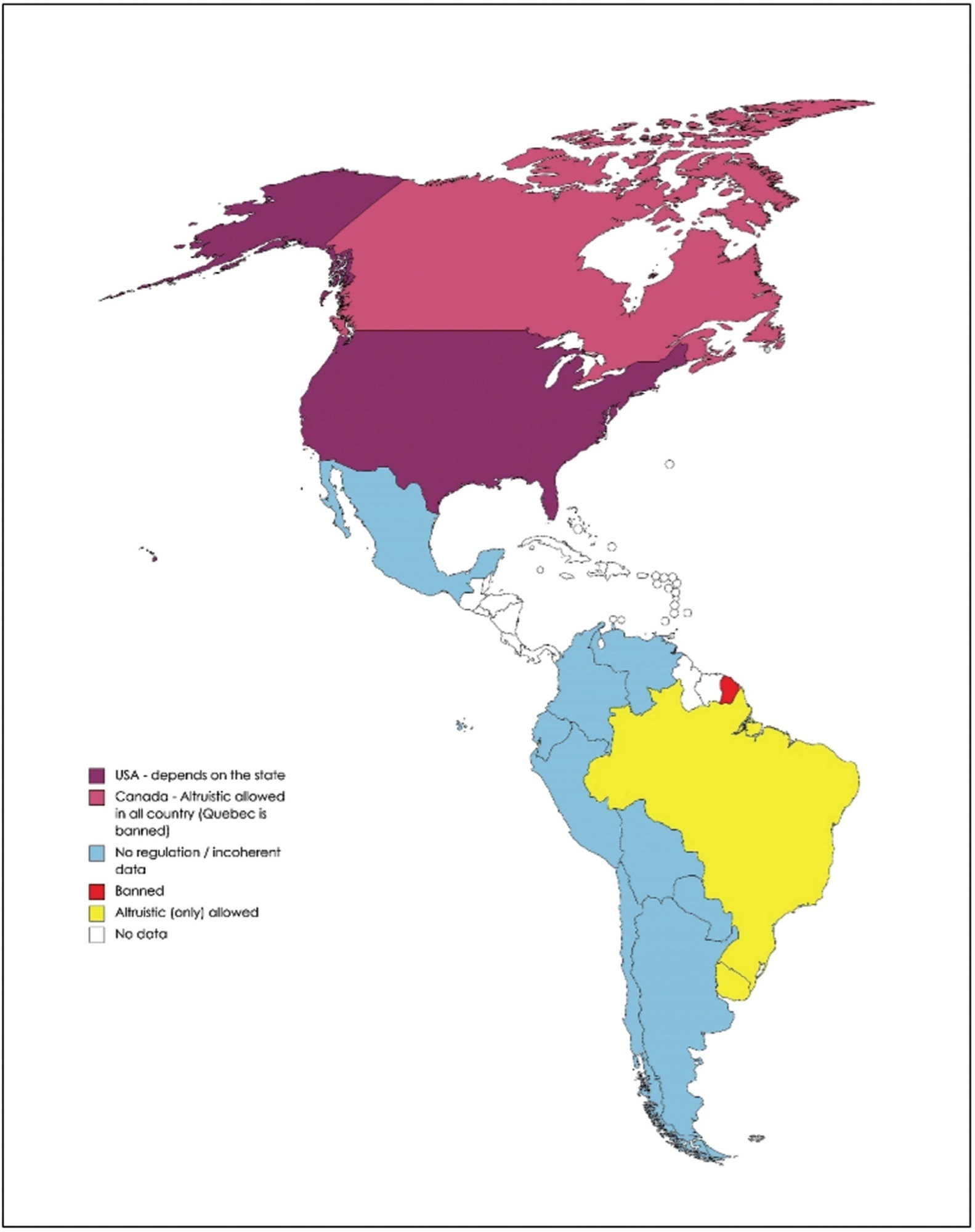
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):115-118
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005257
To evaluate the treatment outcome of tubo-ovarian abscesses managed by transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration.
Descriptive analysis of all patients with tubo-ovarian abscesses treated with a minimally invasive procedure, ultrasound-guided drainage, at the Department of Gynecology, Centro Hospitalar Vila Nova de Gaia/Espinho, during a period of 5 years (from June 2009 to June 2014).
Twenty-six cases were included in the study. The mean age of the study group was 42.8 years. All patients were submitted to transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration and sclerosis with iodated solution, as well as received broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics. The mean time from admission to drainage was 2.5 days. Cultures for aerobic and anaerobic pathogens were positive in 14 of the 26 cases. A complete response was noted in 23 of the 26 cases. No complications or morbidity were noted as a consequence of the drainage procedures.
Minimally invasive treatment of tubo-ovarian abscesses by transvaginal ultrasound-guided drainage is an effective and safe approach.