Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):111-116
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300002
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether the presence of insulin resistance (IR) alters cardiovascular risk factors in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (POS). METHODS: transversal study where 60 POS women with ages from 18 to 35 years old, with no hormone intake, were evaluated. IR was assessed through the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI) and defined as QUICKI <0.33. The following variables have been compared between the groups with or without IR: anthropometric (weight, height, waist circumference, arterial blood pressure, cardiac frequency), laboratorial (homocysteine, interleucines-6, factor of tumoral-α necrosis, testosterone, fraction of free androgen, total cholesterol and fractions, triglycerides, C reactive protein, insulin, glucose), and ultrasonographical (distensibility and carotid intima-media thickness, dilation mediated by the brachial artery flux). RESULTS: Eighteen women (30%) presented IR and showed significant differences in the following anthropometric markers, as compared to the women without IR (POS with and without IR respectively): body mass index (35.56±5.69 kg/m² versus 23.90±4.88 kg/m², p<0.01), waist (108.17±11.53 versus 79.54±11.12 cm, p<0.01), systolic blood pressure (128.00±10.80 mmHg versus 114.07±8.97 mmHg, p<0.01), diastolic blood pressure (83.67±9.63 mmHg versus 77.07±7.59 mmHg, p=0.01). It has also been observed significant differences in the following laboratorial markers: triglycerides (120.00±56.53 mg/dL versus 77.79±53.46 mg/dL, p=0.01), HDL (43.06±6.30 mg/dL versus 40.45±10.82 mg/dL, p=0.01), reactive C protein (7.98±10.54 mg/L versus 2.61±3.21 mg/L, p<0.01), insulin (28.01±18.18 µU/mL versus 5.38±2.48 µU/mL, p<0.01), glucose (93.56±10.00 mg/dL versus 87.52±8.75 mg/dL, p=0.02). Additionally, two out of the three ultrasonographical markers of cardiovascular risk were also different between the groups: carotid distensibility (0.24±0.05 mmHg-1 versus 0.30±0.08 mmHg-1, p<0.01) and carotid intima-media thickness (0.52±0.08 mm versus 0.43±0.09, p<0.01). Besides, the metabolic syndrome ratio was higher in women with IR (nine cases=50% versus three cases=7.1%, p<0.01). CONCLUSIONS: POS and IR women present significant differences in several ultrasonographical, seric and anthropometric markers, which point out to higher cardiovascular risk, as compared to women without POS and IR. In face of that, the systematic IR evaluation in POS women may help to identify patients with cardiovascular risk.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1110-1116
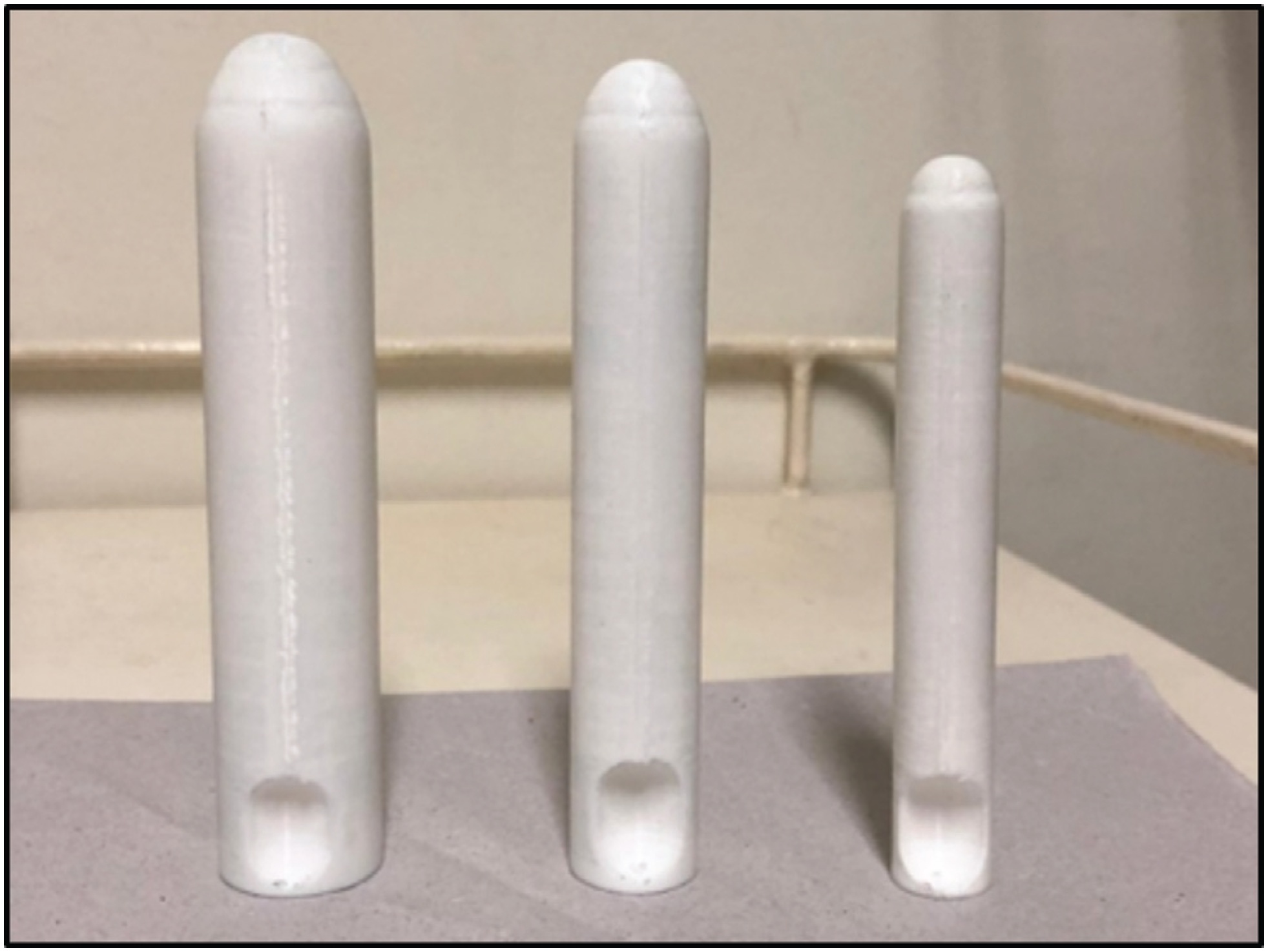
The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of vaginal molds, made with three-dimensional (3D) printing, for conservative treatment through vaginal dilation in patients with vaginal agenesis (VA).
A total of 16 patients with a diagnosis of VA (Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome, total androgen insensitivity syndrome, and cervicovaginal agenesis) from the Federal University of São Paulo were selected. Device production was performed in a 3D printer, and the polymeric filament of the lactic polyacid (PLA) was used as raw material. A personalized treatment was proposed and developed for each patient.
There were 14 patients who reached a final vaginal length of 6 cm or more. The initial total vaginal length (TVL) mean (SD) was 1.81(1.05) and the final TVL mean (SD) was 6.37 (0.94); the difference, analyzed as 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was 4.56 (5.27–3.84) and the effect size (95% CI) was 4.58 (2.88–6.28).
The 3D printing molds for vaginal dilation were successful in 87.5% of the patients. They did not present any major adverse effects and offered an economical, accessible, and reproducible strategy for the treatment of VA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1117-1121
Although obesity can result in high morbidity and mortality in surgical outcomes because of multiple comorbidities, determinants of outcome in obese patients who underwent endometrial cancer surgery remain unclear. The aim of this study is to assess the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and surgical outcomes in obese patients with endometrial cancer.
An institutional retrospective review of the demographic details, clinical characteristics, and follow-up data of 142 patients with endometrial cancer who underwent surgery during a 72-month period was performed. The patients were divided into three groups based on their BMI; patients with BMI < 25 were identified as normal weight, patients with BMI between 25 and 30 were accepted as overweight, and those with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 were identified as obese. The groups' demographic and clinical variables were compared.
Of the 142 patients, 42 were in the normal weight group, 55 in the overweight group, and 45 in the obese group. Age, surgical procedures, blood loss, preoperative health status, and metastatic lymph nodes did not show a significant difference between groups. However, surgery time and total lymph nodes were higher in the obese group. (p = 0.02, p = 0.00, and p = 0.00, respectively). Common complications were anemia, fever, intestinal injury, deep vein thrombosis, fascial dehiscence and urinary infection. There was no significant difference according to the complications.
Our results indicated that higher BMI was significantly associated with a longer duration of endometrial cancer surgery. Minimally invasive surgeries and conventional laparotomy could be performed safely in obese patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):112-116
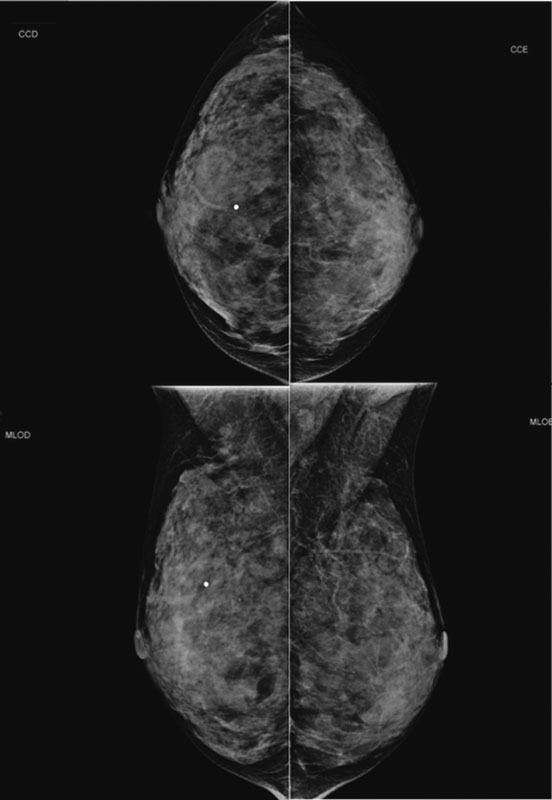
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and accounts for 1 to 2% of all breast cancers. LCIS diagnosis currently remains one of the major identifiable risk factors for subsequent breast cancer development. Imaging methods are becoming increasingly sensitive, and the consequent detection of small lesions and subtle abnormalities increases the chance of detection of in situ and invasive carcinomas, leading to a reduction in mortality. This report describes a case of a palpable complaint with abnormal imaging findings, including a solid LCIS mass.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(3):112-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000300003
PURPOSE: to compare the lamellar body number density (LBND) count in amniotic fluid using the fluorescent polarization (FP) test as a diagnostic parameter for the assessment of fetal pulmonary maturity. METHOD: this was an analytical, controlled cross-sectional study conducted on 60 pregnant women from March 2002 to December 2007. Amniotic fluid specimens were obtained by amniocentesis or at the time of caesarean section, and submitted to the LBND and FP tests (TDxFLM®, Abbott Laboratories), the latter considered to be a reference test, and compared in terms of the presence or absence of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Cut-off values for maturity were established at 30,000 lamellar bodies/µL for the LBND test and 55 mg/g albumin for the FP test. Maternal and perinatal characteristics and neonatal evolution were evaluated, and the performance of the diagnostic tests regarding fetal pulmonary maturity was determined. In the statistical analysis, descriptive measures were used and the sensitivity, specificity and positive and predictive values of the tests were determined with the level of significance set at p<0.05. RESULTS: maternal age ranged from 15 to 34 years (mean: 26.6 years) and gestational age ranged from 24.3 to 41.6 weeks (mean: 35.1 weeks). RDS was diagnosed in 35.1% of neonates. Perinatal characteristics such as weight, Apgar score, and RDS incidence were compared to the results of the LBND and FP tests and a significant correspondence (p<0.05) was observed between the groups of neonates clinically classified as mature and immature in both tests. The tests were concordant in 68.3% of the cases. Comparison of the PF and LBND tests revealed 100% specificity for both and a higher specificity for the LBND test (73.1% as opposed to 51.9% for the PF test). The gold standard for the determination of fetal maturity is the occurrence of RDS. The positive predictive value of the LBND test was higher (36.4%) than that of the FP test (24.2%) (p<0.05) and the negative predictive value was 100% for both tests. CONCLUSIONS: the present study demonstrated that the LBND test has 100% sensitivity and higher specificity than the reference test (FP). In addition, the LBND test is considered to be rapid, accessible, inexpensive and feasible for the Brazilian reality, and it can be used as a reliable test for the prediction of fetal pulmonary maturity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):112-121
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200007
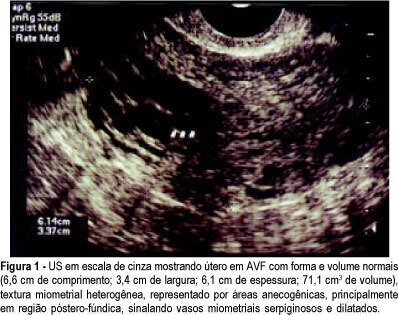
PURPOSE: to investigate the presence and outcome of uterinevascular malformations (UVAM) after gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). METHODS: retrospective study of 2764 patients with GTD diagnosed from 1987 to 2004. All patients were followed up annually at the "Santa Casa da Misericórdia" Trophoblastic Disease Center (Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil) with transvaginal ultrasonography (US) and color Doppler imaging. Seven patients had a final diagnosis of UVAM based on ultrasonographic analysis - pulsatility index (PI), resistance index (RI), peak systolic velocity (PSV) - and pelvic magnetic nuclear resonance (MNR) findings. Negative beta-hCG values were of utmost importance to establish differential diagnosis with persistent GTD. RESULTS: the incidence of UVAM after GTD was 0.2% (7/2764). US features of UVAM: PI mean 0.44±0,058 (extremes: 0.38-0.52); RI mean 0.36±0.072 (extremes: 0.29-0.50); PSV mean 64.6±23.99 cm/s (extremes: 37-96). MNR image showed a bulky uterus, myometrial inhomogeneity, serpiginous flow-related signal voids, and prominent parametrial vessels. The most common UVAM clinical presentation was vaginal hemorrhage, present in 52.7% (4/7). Pharmacological management with 150 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate was employed to control bleeding, after hemodynamic stabilization. These patients are still being followed and remain asymptomatic nowadays. Two patients with persistent UVAM became pregnant and had successful outcomes. CONCLUSION: patients with antecedent of GTD presenting transvaginal bleeding and negative beta-hCG may be considered to have UVAM and should be investigated through US with Doppler velocimetry. Conservative management is a valuable option in many of the acquired UVAM after GTD.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1122-1125
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1126-1133
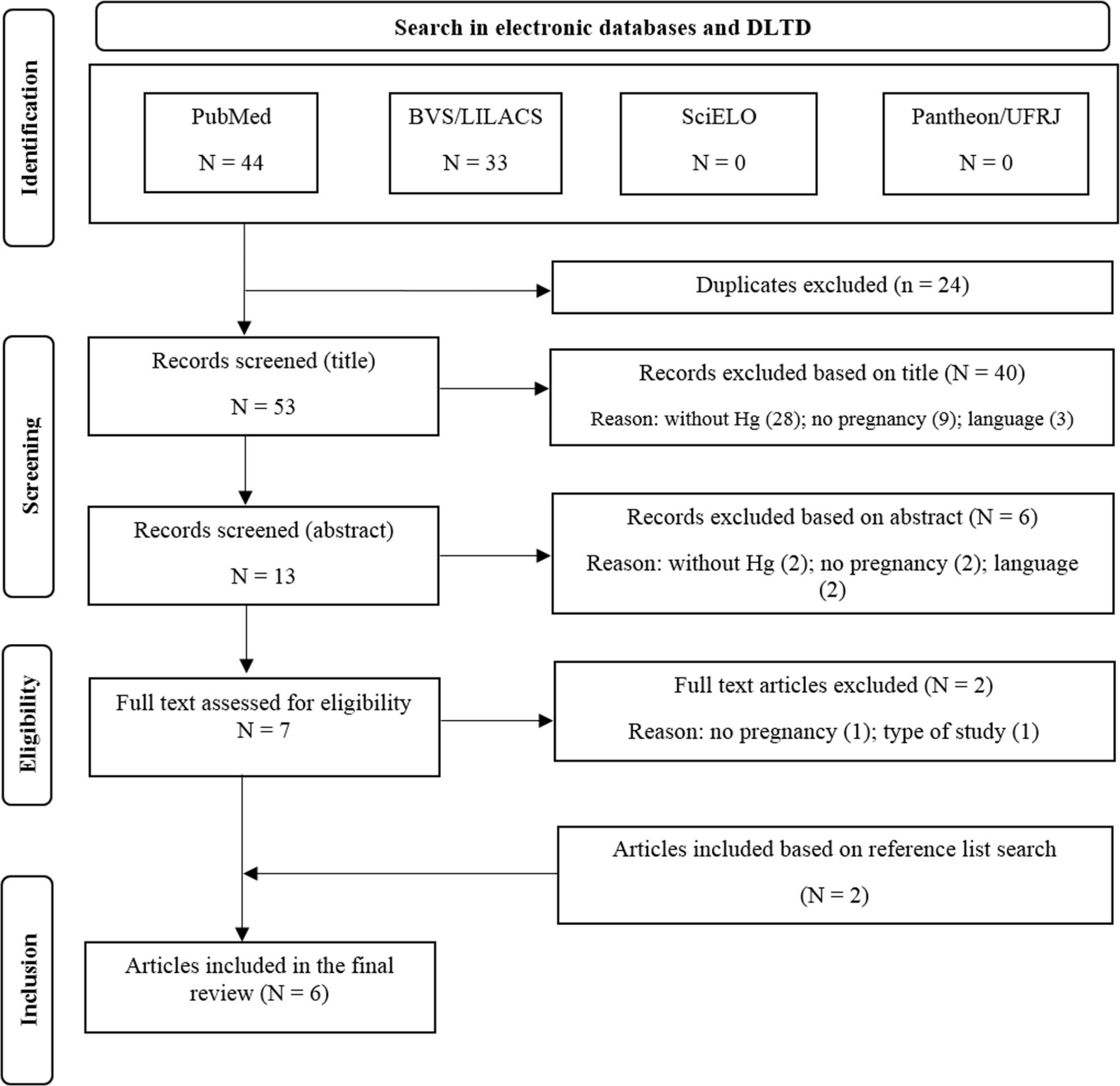
The present review aimed to synthesize the evidence regarding mercury (Hg) exposure and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP).
The PubMed, BVS/LILACS, SciELO and UFRJ's Pantheon Digital Library databases were systematically searched through June 2021.
Observational analytical articles, written in English, Spanish, or Portuguese, without time restriction.
We followed the PICOS strategy, and the methodological quality was assessed using the Downs and Black checklist.
We retrieved 77 articles, of which 6 met the review criteria. They comprised 4,848 participants, of which 809 (16.7%) had HDP and 4,724 (97.4%) were environmentally exposed to Hg (fish consumption and dental amalgam). Mercury biomarkers evaluated were blood (four studies) and urine (two studies). Two studies found a positive association between Hg and HDP in the group with more exposure, and the other four did not present it. The quality assessment revealed three satisfactory and three good-rated studies (mean: 19.3 ± 1.6 out 28 points). The absence or no proper adjustment for negative confounding factor, such as fish consumption, was observed in five studies.
We retrieved only six studies, although Hg is a widespread toxic metal and pregnancy is a period of heightened susceptibility to environmental threats and cardiovascular risk. Overall, our review showed mixed results, with two studies reporting a positive association in the group with more exposure. However, due to the importance of the subject, additional studies are needed to elucidate the effects of Hg on HDP, with particular attention to adjusting negative confounding.