You searched for:"Roseli Mieko Yamamoto"
We found (41) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(6):324-330
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600002
PURPOSE: to compare the maternal factors, clinical aspects and perinatal results in placental abruption during two periods. METHODS: retrospective analysis of placental abruption cases that occurred from January 1, 1994 through December 31, 1997 (period 94-97), and from April 4, 2001 through March 3, 2005 (period 01-05), in singleton delivery with birthweight higher than 500 g and after 20 weeks of gestation. The following factors were analyzed: maternal age, previous obstetric history, prenatal care, premature rupture of membranes, obstetric and/or clinical intercurrent events, vaginal bleeding, uterine tonus, fetal anomaly, mode of delivery, hemoamnion and maternal complication (hysterectomy, uterine atony, disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute renal failure, and maternal death), and the perinatal results. RESULTS: the rate of placental abruption was 0.78% (60 cases) in the period 94-97 (n=7692 deliveries), and 0.59% (51 cases) in the period 01-05 (n=8644 deliveries), without significant difference. A significant difference was observed between the periods 94-97 and 01-05 regarding mean number of previous gestations (3.5±2.4 and 2.6±1.8, p=0.04), patients without prenatal care (13.3 and 2.0%, p=0.03) and maternal intercurrences (38.3 and 64.7%, p=0.01). No significant difference was observed related to vaginal bleeding, tonus abnormalities and perinatal results, between the periods, but a higher proportion of hemoamnion in 94-97 was found when compared to 01-05 (28.3 and 11.8%, p=0.03). CONCLUSIONS: in spite of obstetrical advances, maternal complications and perinatal results were similar in the analyzed periods. The severity and the unexpected results emphasize the importance of prevention and adequate control of associated factors, when this pathology is approached.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(7):352-357
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000700005
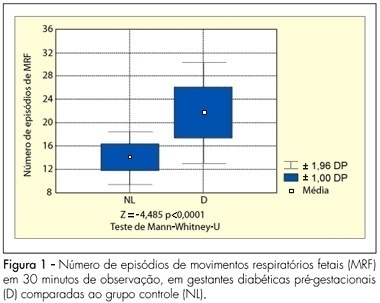
PURPOSE: to analyze the pattern of fetal breathing movements (FBM) in diabetic pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy. METHODS: sixteen pregestational diabetic and 16 nondiabetic (control group) pregnant subjects were included fulfilling the following criteria: singleton, between 36-40 weeks of gestation, absence of other maternal diseases and absence of fetal anomalies. The fetal biophysical profile (FBP) was performed to evaluate the following parameters: fetal heart rate, FBM, fetal body movements, fetal tone and amniotic fluid index. The FBM was evaluated for 30 minutes, period when the examination was integrally recorded in VHS video for posterior analysis of the number of FBM episodes, the duration of each episode and the fetal breathing movements index (BMI). The BMI was calculated by the formula: (interval of time with FBM/total time of observation) x 100. At the beginning and in the end of the FBP maternal glucose levels were checked. The results were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U-test and the Fisher exact test, adopting a level of significance of 5%. RESULTS: the glucose levels demonstrated significantly superior average in the diabetic group (113.3±35.3 g/dL) in relation to the normal group (78.2±14.8 g/dL, p<0.001). The average of the amniotic fluid index was higher in the group of the diabetic cases (15.5±6.4 cm) when compared with controls (10.6±2.0 cm; p=0.01). The average of the number of FBM episodes was superior in the diabetic ones (22.6±4.4) in relation to controls (14.8±2.3; p<0.0001). The average of the BMI in the diabetic patients (54.6±14.8%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (30.5±7.4%, p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: the elevated blood glucose levels can be associated with a different pattern in the FBM of diabetic mothers. The use of this parameter of the FBP, in the obstetric practice, must be considered with concern in diabetic pregnancies.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(6):353-363
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000600006
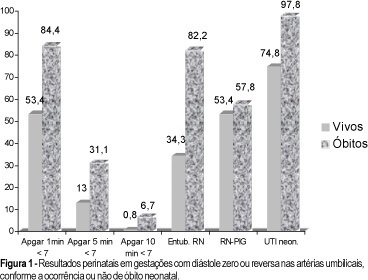
Purpose: to study the prognostic parameters for perinatal death in pregnancies with absent or reversed end-diastolic flow velocity on umbilical artery dopplervelocimetry. Methods: two hundred and four pregnancies were retrospectively reviewed. The methods used were cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and dopplervelocimetry of ductus venosus, fetal aorta, middle cerebral artery, umbilical arteries and uterine artery. The logistic regression model was applied to one hundred and seventy cases in order to determine the most accurate variable for predicting perinatal death. Results: the mortality rates were: 28 cases of intrauterine fetal death (13.7%) and 45 neonatal deaths (22.1%). A statistically significant correlation was found between death and the studied variables. The perinatal death rate in the group with birth weight below 1,000 g was 74.7%, and in the group with gestational age at delivery below 31 weeks it was 66.3%. By logistic regression, birth weight was the most accurate variable for predicting perinatal death, and a probability curve for death according to this variable was obtained. Conclusions: absent or reversed end-diastolic flow velocity in the umbilical arteries is a severe fetal condition, where the risk of perinatal death is mainly related to birth weight and a gestational age at delivery below 31 weeks.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(6):356-367
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2019;41(6):371-378
The aim of this study was to determine the content and face validity of the Mackey Childbirth Satisfaction Rating Scale (MCSRS) questionnaire cross-culturally adapted to Brazilian Portuguese.
The MCSRS is a questionnaire with 34 items related to childbirth satisfaction. The forward- and back-translated versions were compared with the original material, and 10 experts analyzed each item according to the following criteria: clarity, semantic equivalence, appropriateness, and cultural relevance. The final version was presented to 10 mothers for face validation to ensure the questionnaire would suit the target population.
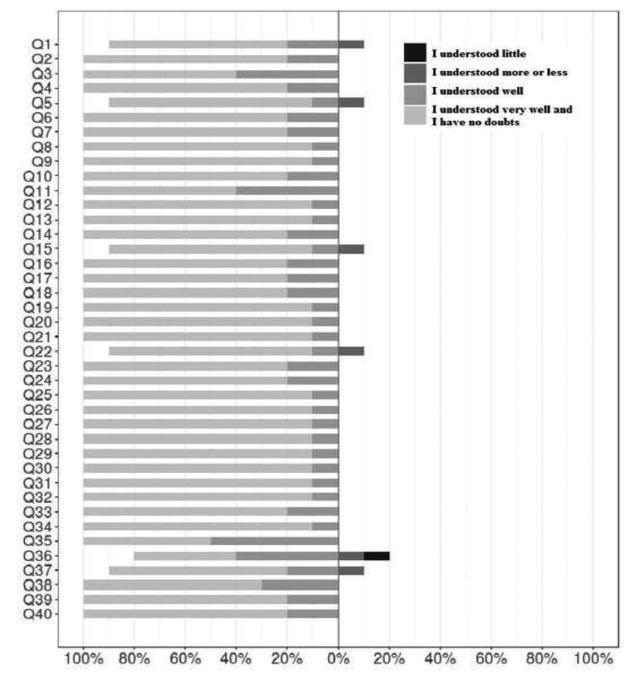
The total of 34 items assessed by experts for clarity, semantic equivalence, appropriateness, and relevance showed positive agreement of 0.85, 0.92, 0.97 and 0.97; negative agreement of 0.13, 0.09, 0.04 and 0.04; and total agreement of 0.75; 0.85, 0.94 and 0.94, respectively. Multilevel linear modeling was applied with crossed random effects and with nested random effects for each judge. The intercept of each criterion was as follows: clarity, 0.87; semantic equivalence, 0.92; appropriateness, 0.96; and cultural relevance, 0.96. The overall mean of agreement was 92.8%. The face validity measurement yielded 80% of agreement on the items, all of them clearly understood.
The final version of the Brazilian Portuguese MCSRS questionnaire had face and content validity confirmed. This instrument of evaluation of maternal satisfaction during childbirth was validated to be applied in the Brazilian female population.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(6):401-406
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000600007
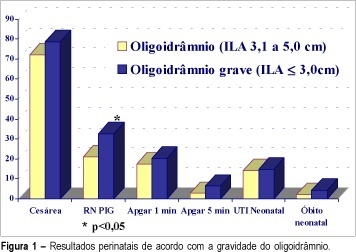
Purpose: to evaluate, in the high-risk pregnancies with oligohydramnios, the assessment tools for fetal well-being and perinatal results. Methods: five hundred seventy-two high-risk pregnancies were retrospectively analyzed. All of them presented with oligohydramnios established by AFI <=5.0 cm. Severe oligohydramnios was detected in 220 cases (AFI<=3,0 cm). The fetal well-being tests included: antepartum cardiotocography, biophysical profile score (BPS) and dopplervelocimetry of umbilical and middle cerebral arteries. Multiple gestation, fetal anomalies and premature rupture of membrane cases were excluded. Results: severe oligohydramnios was significantlly associated with abnormal and suspected cardiotocography results (23.2%), abnormal biophysical profile score (10.5%), abnormal results of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry (54.5%), small for gestational age infants (32.7%) and meconial amniotic fluid (27.9%) when compared to pregnancies with AFI between 3.1 and 5.0 cm. This group presented: abnormal or suspected cardiotocography results (13.9%), abnormal biophysical profile score (4.3%), abnormal results of middle cerebral artery dopplervelocimetry (33.9%), small for gestational age infants (21.0%) and meconial amniotic fluid (16.8%). Conclusion: the oligohydramnios severity in high-risk pregnancies allows to discriminate the cases that are related to adverse perinatal outcome.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(8):405-411
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800008
PURPOSE: the aim of this study was to describe perinatal and maternal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by sickle cell disease (SCD), comparing to pregnancies of women with sickle cell trait (SCT). METHODS: this was a retrospective cohort study, covering the period from March 2001 to April 2008, which included all pregnant women with SCD (n=42) followed up at a university hospital in the Southeast region of Brazil. The maternal and perinatal outcomes were compared to those of pregnant women with SCT (n=56) who were followed up at the same service. RESULTS:SCD-SS was diagnosed in 42 (82.4%) pregnant women and SC in 9 (17.6%). Mean (±SD) maternal age was significantly lower in the SCD group (26.0 years) compared to SCT women (28.7±7.1 years; p=0.018). The following maternal complications were more common among women with SCD in comparison to SCT: urinary tract infection (25.5 versus 8.9%; p=0.04), pneumonia (23.5 versus 1.8%; p=0.002), pulmonary hypertension (15.7 versus 0%; p=0.002), and blood transfusion during delivery or postpartum (33.3 versus 5.4%; p=0.001). Adverse perinatal outcome was more frequent in the SCD group compared to the SCT group: prematurity (49 versus 25%, p=0.01); mean gestational age at delivery (35.2 versus 37.9 weeks, p<0.001); fetal distress (56.9 versus 28.6%, p=0.006); birth weight <2,500 g (62.7 versus 17.9%, p<0.001); mean birth weight (2,183 versus 2,923 g, p<0.001), and small for gestational age infants (29.4 versus 10.7%, p=0.029). Two maternal deaths (3.9%) occurred in the group with SCD. CONCLUSION: Pregnant women with SCD are at greater risk for maternal morbidity and for adverse perinatal outcomes than women with SCT.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(9):420-425
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900002
PURPOSE: to compare the patterns of fetal heart rate (FHR) in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. METHODS: a prospective and comparative study performed between January 2008 and July 2009. The inclusion criteria were: singleton pregnancy, live fetus, pregnant women without clinical or obstetrical complications, no fetal malformation, gestational age between 24 and 27 weeks (2nd trimester - 2T) or between 36 and 40 weeks (3rd trimester - 3T). Computerized cardiotocography (System 8002 - Sonicaid) was performed for 30 minutes and the fetal biophysical profile was obtained. System 8002 analyzes the FHR tracings for periods of 3.75 seconds (1/16 minutes). During each period, the mean duration of the time intervals between successive fetal heart beats is determined in milliseconds (ms); the mean FHR and also the differences between adjacent periods are calculated for each period. The parameters included: basal FHR, FHR accelerations, duration of high variation episodes, duration of low variation episodes and short-term variation. The dataset was analyzed by the Student t test, chi-square test and Fisher's exact test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: eighteen pregnancies on the second trimester were compared to 25 pregnancies on the third trimester. There was a significant difference in the FHR parameters evaluated by computerized cardiotocography between the 2T and 3T groups, regarding the following results: mean basal FHR (mean, 143.8 bpm versus 134.0 bpm, p=0.009), mean number of transitory FHR accelerations > 10 bpm (3.7 bpm versus 8.4 bpm, p <0.001) and >15 bpm (mean, 0.9 bpm versus 5.4 bpm, p <0.001), mean duration of high variation episodes (8.4 min versus 15.4 min, p=0.008) and mean short - term variation (8.0 ms versus 10.9 ms, p=0.01). The fetal biophysical profile showed normal results in all pregnancies. CONCLUSION: the present study shows significant differences in the FHR characteristics when the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy are compared and confirms the influence of autonomic nervous system maturation on FHR regulation.