You searched for:"Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori"
We found (29) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(9):452-458
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900003
PURPOSE: to evaluate and to compare the effectiveness of oxybutynin, electrostimulation (ES) and pelvic floor training (PFT) in the management of women with detrusor overactivity. METHODS: a total of 64 women, 35 to 80 years old, were enrolled in this randomized prospective trial. Patients were randomized in three groups: Oxybutynin (n=22), ES (n=21) and PFT (n=21). There were no statistical differences between the three groups with regards to race (p=0.948), age (p=0.747), hormonal status (p=0.813), time of symptomatology (p=0.789), previous surgery for urinary incontinence (p=0.993), or body mass index (p=0.897). Patients were assessed before and after treatment by urodynamic test, a seven-day voiding diary, and subjective response. The duration of the treatment was twelve weeks. For statistical analyses, the Pearson chi2, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the paired t-test were used. RESULTS: there was a decrease in the urge-incontinence episodes and in the number of pads required in all groups (p<0.05). There was reduction in the frequency of micturition in the Oxybutynin Group (p=0.014). Oxybutynin and ES Groups had reduction in nocturia episodes (p=0.003 and p=0.036, respectively). There were no significant differences in improvement between the three groups (p>0.05). Urgency was resolved in 14 (63.6%), 11 (52.4%) and 12 (57.1%) patients of the Oxybutynin, ES and PFT Groups, respectively, without differences among the groups (p=0.754). Subjectively, 17 (77.3%), 11 (52.4%) and 16 (76.2%) women who had accomplished oxybutynin, ES and PFT, respectively, were satisfied, without differences among the groups (p = 0.142). Urodynamic was normal in 8 (36.4%), 12 (57.1%) and 11 (52.4%) patients of the Oxybutynin, ES and PFT Groups, respectively. This urodynamic analysis revealed no differences between the three groups (p=0.358). The reduction of urge-incontinence correlated with patient satisfaction (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: treatments were equally effective; reduction of urge-incontinence was correlated with patient satisfaction.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(8):468-475
To investigate the effects of preoperative fasting abbreviation with a carbohydrate and protein-enriched solution, on postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) incidence in gynecological surgery patients, a population naturally at risk for such unpleasant episodes.
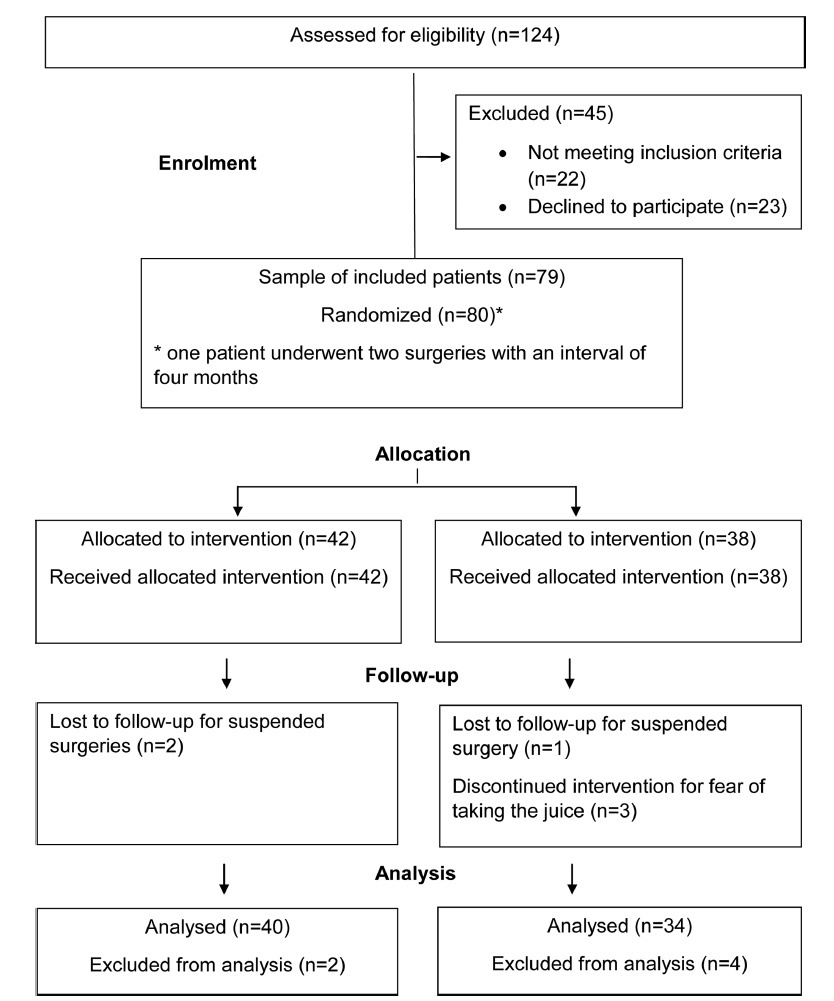
The present prospective double-blind randomized study was performed at The Hospital Municipal e Maternidade Dr. Odelmo Leão Carneiro (HMMOLC, in the Portuguese acronym), in Uberlândia, state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, in partnership with the Gynecology Department of the Universidade Federal de São Paulo (UNIFESP), approved by the Human Research EthicsCommittee ofUNIFESP and theboard ofHMMOLC, and included in the Brazil Platform and in the Brazilian Clinical Trial Registry. After signing the consent form, 80 women, who were submitted to gynecological surgery in the period from January to June 2016,were randomized into 2 groups: control group (n= 42) and juice group (n= 38). They received, respectively, 200mL of inert solution or liquid enriched with carbohydrate and protein 4 hours presurgery. The incidence, frequency and intensity of PONV were studied using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), with statistical analysis performed by the software IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).
The incidence of nausea and vomiting was lower than in the literature, to this population, with 18.9% (14/74) for the control group and 10.8% (8/74) for the juice group, respectively, with no statistically significant difference between the groups.
The incidence of nausea and vomiting was lower than in the literature, but it cannot be said that this is due to the abbreviation of fasting. It can provide greater comfort, with the possibility of PONV prevention in patients at risk for these episodes.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2012;34(11):505-510
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100005
PURPOSE: To investigate the effect of adding biofeedback (BF) to the training of pelvic floor muscles (PFMT) for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). METHODS: A prospective pilot study, randomized and controlled with women with SUI without sphincter deficiency, detected by urodynamic study and who performed the correct PFM contraction. Women with neuromuscular disorders and grade III and IV genital prolapse were excluded. Forty women were randomized into a Control Group and BF Group. The PFMT protocol with BF equipment consisted of three sets of ten slow contractions (tonic), with a holding time of six to eight seconds at each contraction followed by a rest period of equal duration. After each sustained contraction, they performed three to four fast contractions (phasic) in the supine and standing position twice a week, for a total of 12 sessions. We evaluated the effect of adding BF to PFMT on quality of life using King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ) regarding urinary symptoms based on a voiding diary and regarding the function of pelvic floor muscles by digital palpation. The evaluation was performed initially and after 12 treatment sessions. Data are reported as mean and standard deviation. The Mann-Whitney test was used for the analysis of homogeneity and to determine differences between groups, and the Wilcoxon test was used to determine possible differences between the times of observation, with the level of significance set at 0.05. RESULTS: A significant decrease in the scores of the domains assessed by the KHQ was observed in the comparison between groups, except for the general health domain (BF Group: 32.8±26.9 versus Control Group: 48.4±29.5, p<0.13). Accordingly, there was improvement in PFM function after treatment in the BF Group, regarding power (4.3±0.8, p= 0.001), endurance (6.0±2.2, p<0.001) and fast (9.3±1.9, p=0.001). When comparing the groups, the BF Group showed a positive result regarding power (BF Group 4.3±0.8 versus Control Group 2.5±0.9, p<0.001), endurance (6.0±2.2 BF Group versus Control Group 2.7±1.9, p<0.001) and fast (BF Group 9.3±1.9 versus Control Group 4.6 ± 3.2, p<0.001). Reduction of nocturnal urinary frequency (1.2±1.2 versus 0.7±0.9, p=0.02) and of effort urine loss (1.5±1.4 versus 0.6±0.8, p=0.001) was observed in the BF Group. CONCLUSION: The addition of BF to the PFMT for the treatment of SUI, applied according to the protocol described, improved PFM function, reduced urinary symptoms, and improved of the quality of life.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(5):511-518
The Burch procedure (1961) was considered the gold standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) before the midurethral slings (MUSs) were introduced, in 2001.
This historical perspective of the Burch’s timeline can encourage urogynecological surgeons to master the Burch technique as one of the options for surgical treatment of SUI.
Criteria A bibliographic search was performed in the PubMed and National Library of Medicine (NIH) databases with the terms Burch colposuspension AND history AND stress urinary incontinence in the last 20 years. The original article by Burch (1961) was included. The references were read by three authors. The exclusion criterion was studies in non-English languages. Biomedical Library Special Collections were included as historical relevant search.
Some modifications of the technique have been made since the Burch procedure was first described. The interest in this technique has been increasing due to the negative publicity associated with vaginal synthetic mesh products. Twenty-nine relevant articles were included in the present review article, and numerous trials have compared Burch colposuspension with MUS.
This historical perspective enables the scientific community to review a standardized technique for SUI. Burch colposuspension should be considered an appropriate surgical treatment for women with SUI, and an option in urogynecological training programs worldwide.

Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(10):519-524
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000005
PURPOSE: to identify the impact of pelvic reconstructive surgery on female sexual function, as well as the changes in vaginal anatomy, and to detect possible correlations between them. METHODS: a prospective, descriptive study, including 43 sexually active women with genital dystopy, undergoing surgery for pelvic organ prolapse, conducted between October 2004 and September 2006. The women completed the same multiple-choice questionnaire regarding sexual function, and analogic scales to quantify the degree of desire, arousal and satisfaction, and were clinically assessed using the pelvic organ prolapse quantification (POP-Q) staging system, before the surgery and three and six months after it. Statistical analysis was performed through the Bowker test for symmetry, Wilcoxon test, Student t test, chi2 and analysis of variance (ANOVA) as appropriate, with statistical significance set at 5% (p<0.05). RESULTS: all 43 women completed the follow-up at three and six months after the surgery, but two of them lost their partners after the surgery. Quality of sexual life improved significantly (p=0.03). Symptoms such as dyspareunia (25.6% before versus 17.1% after surgery), discomfort (27.9 versus 0%), embarrassment (20.9% versus 0%) and fear (2.3% versus 0%) significantly improved (p<0.001). Analogical scales scores regarding desire (5 versus 7, p=0.001), arousal (6 versus 8, p<0.001) and satisfaction with sexual life (5 versus 7, p<0.001) also improved. There was a statistically significant improvement (p<0.001) of the POP-Q stages after the surgery. However, there was no statistically significant correlation between changes in vaginal dimensions and changes in sexual function. CONCLUSIONS: after pelvic reconstructive surgery, there was a significant improvement in the quality of sexual life and of the POP-Q stages. However, there was no correlation between them.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(10):534-540
The presence of bacteria in urine is called bacteriuria, which may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The manipulation of the urinary tract during urodynamic study (UDS), which is an invasive procedure, can result in urinary tract infection (UTI). Studies on the use of prophylactic antibiotics for UDSs are contradictory. Some investigators concluded that they were valuable and others did not. The objective of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis before UDS. This is a placebo-control randomized double-blind study.
Two-hundred and seventeen women affected by urinary incontinence were eligible for this study. All patients had presented negative urine culture previous to the UDS. They were randomized in four groups: group A received placebo, group B received 500 mg of levofloxacin, group C received 80 mg trimethoprim and 400 mg sulfamethoxazole and group D received 100 mg of nitrofurantoin. A urine culture was performed 14 days after the UDS.
We observed asymptomatic bacteriuria after the UDS in five patients in group A, one in group B, one in group C and one in group D. Only one patient on group A had symptomatic bacteriuria.We didn’t observe statistical difference between the groups. When we recategorized the patients in two groups, the incidence of bacteriuria was significantly higher in the placebo group compared with the antibiotic group.
The conclusion is that antibiotic prophylaxis before the UDS did not reduce the incidence of UTI in women within the target population.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(1):54-62
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000100010
Female lower urinary tract symptoms are nonspecific and a clinical evaluation is required to establish the correct diagnosis. Such evaluation should consist of a structured micturition history or questionnaire, physical examination, micturition diary, pad test, and urodynamic evaluation. Urodynamic investigation was developed as an extension of patient history and physical examination in order to reveal the etiology of the patient's complaints. The goal of the present article is to review clinical and subsidiary diagnosis of urinary incontinence.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(9):573-577
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000900002
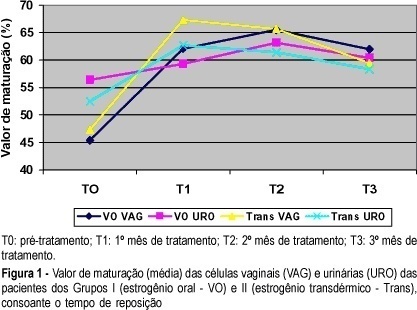
Objective: to study the effects of oral or transdermal estrogen replacement on the lower urinary tract and vagina in postmenopausal women. Methods: we studied 25 postmenopausal women evaluating the oral or transdermic estrogen replacement effects on the vaginal cells and urinary sediment during 3 months. The patients were randomly distributed into 2 groups: Group I, n = 14, treated orally with 0.625 mg equine conjugated estrogen plus 5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate, daily for 3 months; Group II, n = 11, treated transdermally with 50 mug 17-ß-estradiol, once a week, plus 5 mg medroxyprogesterone. Daily, for 3 months, urinary samples were collected from the first miction in the morning after urogenital antisepsis into sterile tubes. The sample was centrifuged and the sediment was smeared. Vaginal and urinary smears were then fixed in absoluted alcohol and stained by the method of Shorr. Results: the patients who used the oral route presented maturation of the vaginal cells (from 45.4 to 65.5% after 2 months of treatment, maintaing 62% afterwards) but this did not occur with urinary cells (56.4 before treatment versus 60.4% at the end of the period). The transdermal route promoted maturation of vaginal and urinary cells. Conclusion: we have concluded that transdermal estrogens have satisfactory effects both on vaginal and urethral sites. However, with the oral route we did not find the expected results in the urinary tract in all cases.