You searched for:"Luiz Carlos Zeferino"
We found (27) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(8):408-414
the aim of this study was to evaluate the pattern of human papillomavirus (HPV) detection in an 11.3-year post-vaccination period in a cohort of adolescent and young women vaccinated or not against HPV 16/18.
a subset of 91 women from a single center participating in a randomized clinical trial (2001-2010, NCT00689741/00120848/00518336) with HPV 16/18 AS04- adjuvanted vaccine was evaluated. All women received three doses of the HPV vaccine (n = 48) or a placebo (n = 43), and cervical samples were collected at 6-month intervals. Only in this center, one additional evaluation was performed in 2012. Up to 1,492 cervical samples were tested for HPV-DNA and genotyped with polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The vaccine group characteristics were compared by Chi-square or Fisher exact or Mann-Whitney test. The high-risk (HR)-HPV 6-month-persistent infection rate was calculated. The cumulative infection by HPV group was evaluated by the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test.
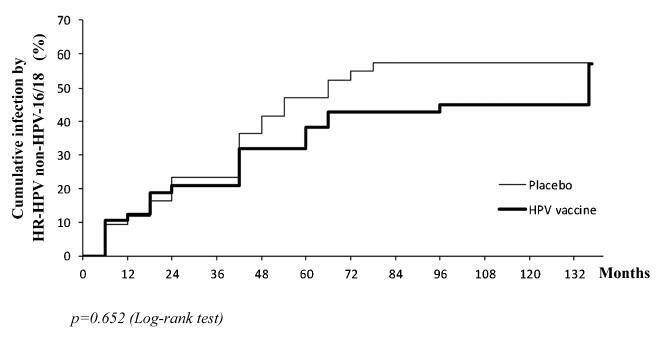
the cumulative infection with any type of HPV in an 11.3-year period was 67% in the HPV vaccine group and 72% in the placebo group (p = 0.408). The longitudinal analysis showed an increase of 4% per year at risk for detection of HR-HPV (non-HPV 16/ 18) over time (p = 0.015), unrelated to vaccination. The cumulative infection with HPV 16/18 was 4% for the HPV vaccine group and 29% for the placebo group (p = 0.003). There were 43 episodes of HR-HPV 6-month persistent infection, unrelated to vaccination.
this study showed themaintenance of viral detection rate accumulating HR-HPV (non-HPV-16-18) positive tests during a long period post-vaccination, regardless of prior vaccination. This signalizes that the high number of HPV-positive testsmay be maintained after vaccination.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(1):42-47
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100008
Breast cancer is the principal cause of death from cancer in women. Molecular studies of breast cancer, based in the identification of the molecular profiling techniques through cDNA microarray, had allowed defining at least five distinct sub-group: luminal A, luminal B, HER-2-overexpression, basal and " normal" type breast-like. The technique of tissue microarrays (TMA), described for the first time in 1998, allows to study, in some samples of breast cancer, distinguished by differences in their gene expression patterns, which provide a distinctive molecular portrait for each tumor and the basis for and improved breast cancer molecular taxonomy. Another important implication is that genetic profiling may lead to the identification of new target for therapy and better predictive markers are needed to guide difficult treatment decisions. Additionally, the current pathology classification system is suboptimal, since patients with identical tumor types and stage of disease present different responses to therapy and different overall outcomes. Basal breast tumor represents one of the most intriguing subtypes and is frequently associated with poor prognosis and absence of putative therapeutic targets. Then, the purpose of this review was to resume the most recent knowledge about the breast carcinoma classification and characterization.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1999;21(8):431-437
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000800002
Purpose: to evaluate risk factors and papillomavirus (HPV) associated lesions in male partners of women with genital intraepithelial neoplasia. Patients and Methods: three hundred and thirty-seven men were evaluated by urethral cytology, peniscopy, and biopsy, if necessary. We analyzed the results and the relations to age, educational level, smoking, contact time with the present partner, age at first intercourse, number of partners, previous sexually transmitted diseases (STD), circumcision, peniscopic findings, and female lesion grade. Results: peniscopy was positive in 144 (42,7%) and HPV infection was diagnosed in 105 (31,2%). Smoking, contact time with the present partner up to 6 months, and more than one previous sexual partner were associated with HPV lesions (p<0,05). The urethral cytology was suspect in 4,2% and smoking, positive peniscopy or biopsy and partners of women with high-grade lesion (p<0,05) were associated with the diagnosis. 72.1% of 229 biopsies were positive, independently of the peniscopic findings and women's lesion grade. Conclusions: HPV infection was diagnosed in 31.2% and was associated with smoking, contact time with the present partner up to 6 months and more than one previous sexual partner, but not with the female lesion grade, educationa level, previous STD, circumcision and peniscopic findings.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(8):479-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800007
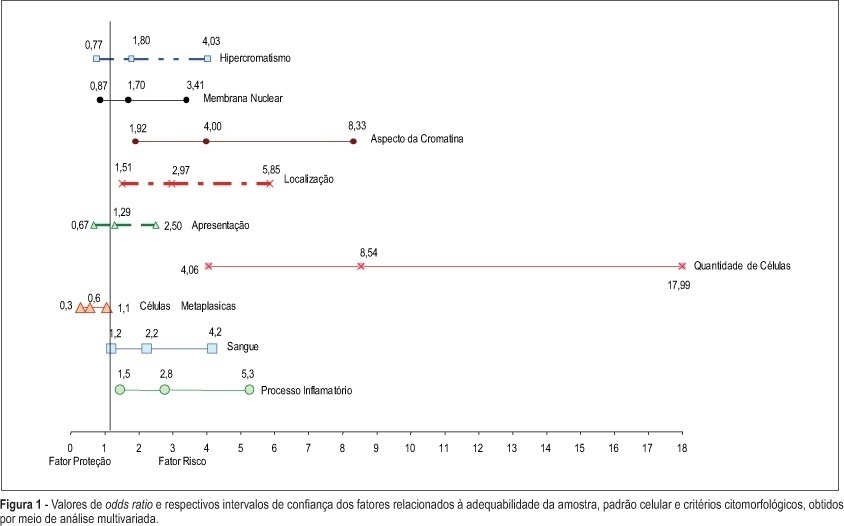
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether factors related to the adequacy of the sample, cell pattern and cytomorphological criteria are associated with false-negative (FN) results of cervical cytopathology during routine examinations. METHODS: this is a case-control study in which the study group included 100 cytopathologic smears with FN results detected during systematic internal quality control consisting of 100% rapid review. For each FN result detected, two smears with a true-positive diagnosis were identified by the same cytotechnician and these constituted the control group, making a total sample size of 300 smears. The variables were established in accordance with the criteria defined for the analysis of sample adequacy, cell pattern and cytomorphological analyzed criteria. The results were evaluated using bivariate analysis and logistic regression with stepwise variable selection criteria expressed in OR (95%). RESULTS: the number of atypical cells, the appearance of nuclear chromatin, and the distribution and presentation of atypical cells in the smear were the variables that showed the greatest risk for FN results with OR of 9.6, 4.2, 4.4, and 3.6, respectively. Inflammatory processes and the presence of blood in the smear were also identified as variables that influence the risk of FN results. CONCLUSIONS: the majority of the factors associated with FN results are dependent on the conditions and techniques of sample collection, since in the majority of cases, the lesion may not be adequately represented in the smear. Confounding factors such as blood and inflammatory processes may also impair analysis. With respect to cytomorphological alterations, thin chromatin strand was the variable that indicated the greatest risk of FN results.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1998;20(10):565-569
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000004
Purpose: to estimate the duration of cervical neoplasia from human pappilomavirus (HPV) infection to advanced invasive carcinoma, using as paremeter the mean age of the women at diagnosis. Methods: this cross-sectional study included 1,177 women with HPV infection, 1,561 with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and 773 with invasive carcinoma. Results: the mean ages of CIN 1 and CIN 2 on diagnosis were not statistically different. The mean duration of CIN 2 was 2.2 years. The mean duration of CIN 3 was 10.3 years, with 4.1 years as severe dysplasia and 6.2 years as carcinoma in situ (CIS). The mean duration of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions was 12.5 years. The duration means of invasive carcinoma stages Ia, Ib and II were 3.0, 2.7 and 3.7 years, respectively. Conclusions: according to the results, CIN 1 and CIN 2 may arise directly from HPV infection and most of these lesions are transient. CIS presented the longest duration and the mean asymptomatic period of cervical neoplasia is 18.2 years. These results were discussed considering the present knowledge of the natural history of cervical carcinoma and other studies on duration of this neoplasia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2019;41(10):579-580
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2019;41(12):710-717
To identify the biomarkers of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in early luminal breast cancer.
A cross-sectional study that included all patients with early or locallyadvanced luminal breast cancer submitted to neoadjuvant chemotherapy between 2013 and 2014. Demographic, clinic and pathologic data were retrieved from patient records. The expressions of the estrogen receptor (ER), the progesterone receptor (PR), and Ki67 were analyzed by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The status of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) was evaluated by IHC and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). Independent predictors of clinic and pathologic response were evaluated by stepwise logistic regression models and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
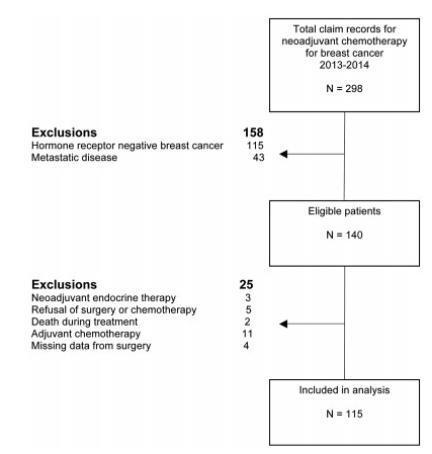
Out of 298 patients identified, 115 were included in the analysis. Clinical complete response (cCR) was observed in 43.4% of the patients (49/113), and pathologic complete response (pCR) was observed in 7.1% (8/115) of the patients. The independent predictors of cCR were premenopausal status (p < 0.001), low PR expression (≤ 50% versus > 50%; p = 0.048), and Ki67 expression ≥ 14% (versus < 14%; p = 0.01). Patients with cCR were more commonly submitted to breast conserving surgery (34.7% versus 7.8%; p < 0.001). Increasing cut-off points for Ki67 expression were associated with an increase in specificity and a decrease in sensitivity to identify patients with cCR.
Premenopausal status, lower PR expression and higher Ki67 expression were associated with a higher rate of cCR to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in luminal breast cancer.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(9):721-725
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900008
PURPOSE: to analyze the association between bacterial vaginosis (BV), high-risk HPV DNA, and Pap smear abnormalities in women submitted to diathermic conization for the treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN 2 or 3). METHODS: a descriptive clinical study with 81 women submitted to diathermic conization for the treatment of CIN 2 or 3. Initial Pap smear was performed by the time of the biopsy and was also used to verify the presence of BV. Prior to conization, samples for the detection of high-risk HPV DNA through hybrid capture II (HC II) were collected. A control visit was scheduled for four months after the conization to repeat these tests. Twenty-seven women were found to have BV and 54 were not. Statistical analysis comprised odds ratios (OR) to assess the correlations between BV and HPV detection before and after diathermic conization and cytological abnormalities. All analyses were performed with a 95% confidence interval (95% CI). RESULTS: high-risk HPV DNA detection before conization was identical in both groups (89%). After conization, HPV DNA detection decreased to 26 and 18% in the groups with and without BV, respectively (OR=1.5; 95% CI 0.5 to 4.6). In addition, 41% of the women with BV and 20% without BV showed Pap smear abnormalities (OR=2.7; 95% CI 1.0 to 7.4). Regarding these 22 women with Pap smear abnormalities approximately four months after the diathermic conization, 83% of the BV group tested positive for HPV DNA compared with 50% in the group without BV (OR=5.0; IC 95% 0.5 a 52.9). CONCLUSION: women with BV presented more Pap smear abnormalities after conization when compared to the women without BV, although this was not statistically significant. This association was not related to high-risk HPV DNA.