You searched for:"ALESSANDRA CRISTINA MARCOLIN"
We found (21) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(1):54-60
Scientific information on the impact of the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) on the health of pregnant women, fetuses and newborns is considered of limited confidence, lacking good-quality evidence, and drawing biased conclusions. As a matter of fact, the initial impressions that the evolution of COVID-19 was no different between pregnant and non-pregnant women, and that SARS-CoV-2 was not vertically transmitted, are confronted by the documentation of worsening of the disease during pregnancy, poor obstetric outcomes, and the possibility of vertical transmission. The present article aims to compile the data available on the association of COVID-19 and reproductive events, from conception to birth.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(9):609-614
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000900007
Purpose: the objective of the present study was to determine the number and type of deliveries, category of admission to the hospital, occupation and obstetrical diagnosis for adolescents from the municipality of Ribeirão Preto, from January 1992 to December 1996. Methods: the information obtained from hospital discharge forms was analyzed at the Hospital Data Processing Center. The 6.04a-text processor Epi-Info System, a data bank and statistics for epidemiology produced by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (Atlanta, GA, USA), and Dbase IV were used to process the information. The association between variables was tested by the chi² test, with the level of significance set at 5%. The analyzed parameters were: number and type of delivery, category of hospital admission, occupation and obstetric diagnosis. Results: a total of 42,969 deliveries occurred during the study period, among which 7,134 (16.6%) corresponded to adolescent deliveries. An increase in the number of deliveries by girls in this age range occurred over the years, from 1,225 in 1992 to 1,538 in 1996. Deliveries were reported starting from 12 years of age, with a gradual increase in this number, especially after 14 years of age, when a 104.2% increase occurred for deliveries at this age, followed by 48.8% at 15 years, 36.1% at 16 years, 14.0% at 17 years, 52.8% at 18 years, and with practically no increase among 19-year-old girls. The highest number of deliveries (5,709) was recorded for the unified health system category of admission, followed by 1,277 deliveries for the prepaid category and 148 deliveries for the private category. With respect to occupation, 14.1% of the patients belonged to the economically active population, while 85.8% did not. Of the total deliveries, 59.2% were normal, 5.6% were forceps deliveries, and 35.2% were cesarean sections. The most frequent obstetrical diagnoses were: problems of fetus or placenta affecting maternal management (7.9%), fetus-pelvis disproportion (6.0%), problems with the amniotic cavity and membranes (5.0%), hypertension complicating delivery and puerperium (3.5%), and premature or false labor (3.4%). Conclusions: most deliveries were normal and occurred more frequently at the end of adolescence, especially among girls belonging to the unified health system. There was a predominance of adolescents not belonging to the economically active population. Some obstetrical complications were diagnosed at the time of resolution of pregnancy.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(10):672-675
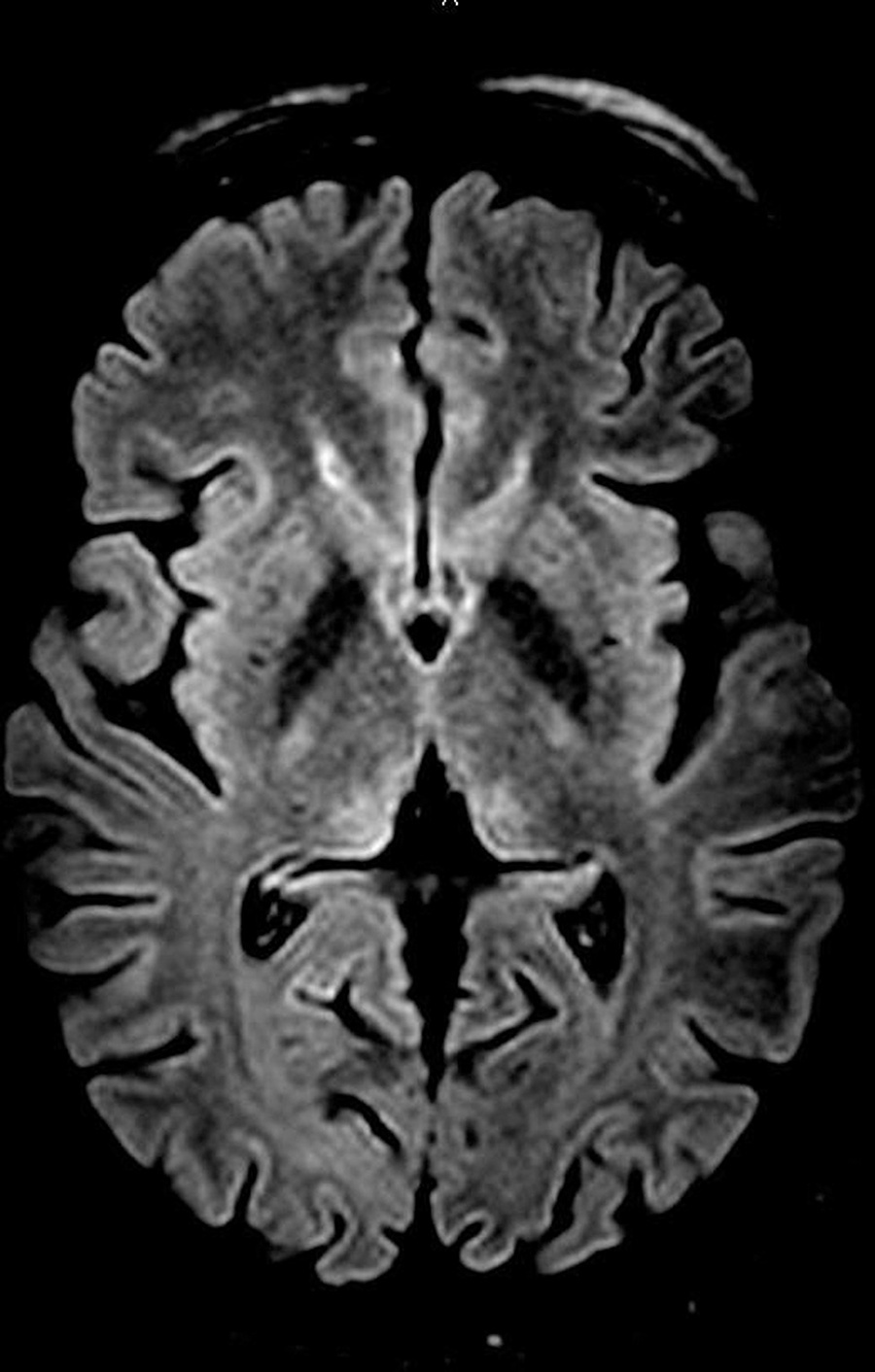
Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) is an acute neurological disorder resulting from vitamin B1 deficiency, which is common in chronic alcoholism. We report a rare case of WE due to hyperemesis gravidarum in a 25-year-old pregnant patient at 13 weeks and 5 days of gestation. Initially, the disease manifested as weakness, mental confusion, anterograde amnesia, and visual and auditory hallucinations. The diagnosis was established after the detection of suggestive findings of WE in the thalamus by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and a rapid improvement in the patient's clinical status subsequent to treatment with thiamine. Hyperemesis is a rare cause of WE, which makes the reported case important in the literature and reinforces the need for attention in clinical practice to rare but important complications of this common condition (hyperemesis gravidarum).
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(2):93-100
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200008
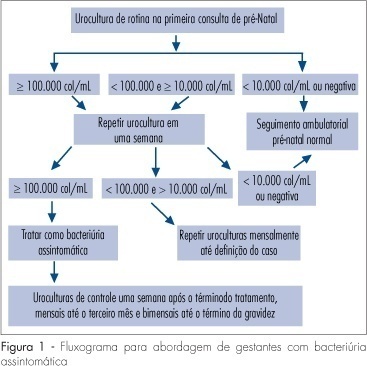
Several factors cause urinary tract infection (UTI) to be a relevant complication of the gestational period, aggravating both the maternal and perinatal prognosis. For many years, pregnancy has been considered to be a factor predisposing to all forms of UTI. Today, it is known that pregnancy, as an isolated event, is not responsible for a higher incidence of UTI, but that the anatomical and physiological changes imposed on the urinary tract by pregnancy predispose women with asymptomatic bacteriuria (AB) to become pregnant women with symptomatic UTI. AB affects 2 to 10% of all pregnant women and approximately 30% of these will develop pyelonephritis if not properly treated. However, a difficult to understand resistance against the identification of AB during this period is observed among prenatalists. The diagnosis of UTI is microbiological and it is based on two urine cultures presenting more than 10(5) colonies/mL urine of the same germ. Treatment is facilitated by the fact that it is based on an antibiogram, with no scientific foundation for the notion that a pre-established therapeutic scheme is an adequate measure. For the treatment of pyelonephritis, it is not possible to wait for the result of culture and previous knowledge of the resistance profile of the antibacterial agents available for the treatment of pregnant women would be the best measure. Another important variable is the use of an intravenous bactericidal antibiotic during the acute phase, with the possibility of oral administration at home after clinical improvement of the patient. At our hospital, the drug that best satisfies all of these requirements is cefuroxime, administered for 10-14 days. Third-generation cephalosporins do not exist in the oral form, all of them involving the inconvenience of parenteral administration. In view of their side effects, aminoglycosides are considered to be inadequate for administration to pregnant women. The inconsistent insinuation of contraindication of monofluorinated quinolones, if there is an indication, norfloxacin is believed to be a good alternative to cefuroxime. In cases in which UTI prophylaxis is indicated, chemotherapeutic agents are preferred, among them nitrofurantoin, with care taken to avoid its use at the end of pregnancy due to the risk of kernicterus for the neonate.