Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):531-531
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):531-531
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):531-535
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):531-538
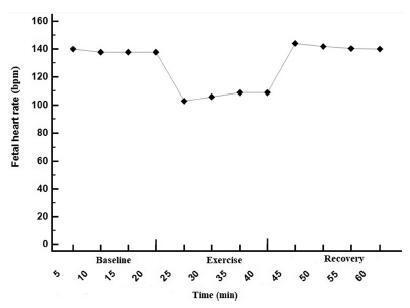
To determine the effect of treadmill walking on maternal heart rate (MHR) and cardiotocographic parameters (basal fetal heart rate [FHR], active fetal movements [AFM], number of accelerations and decelerations, and short-term variation [STV] and long-term variation [LTV] of fetal heart rate) in pregnant women at 36 weeks.
A nonrandomized, open clinical trial involving 88 healthy pregnant women submitted to moderate intensity walking and computed cardiotocography in 3 20- minute periods (resting, treadmill walking, and postexercise recovery).
The mean FHR decreased during walking (resting: 137 bpm; treadmill: 98 bpm; recovery: 140 bpm; p<0.001), with bradycardia occurring in 56% of the fetuses in the first 10minutes of exercise, and in 47% after 20minutes. Bradycardia was not detected in the other phases. The mean STV and HV were 7.9, 17.0, and 8.0 milliseconds (p<0.001) and 7.6, 10.8 and 7.6 bpm (p=0.002) in the resting, walking and recovery phases, respectively. Themean number of fetalmovements in 1 hour was 29.9, 22.2 and 45.5, respectively, in the 3 periods (p<0.001). In overweight/obese women, the mean FHR was lower (p=0.02). Following the logistic regression analysis, two variables remained significantly associated with bradycardia: maternal fitness in the 28th week of pregnancy (protective effect) and maternal weight (increased risk).
In healthy fetuses, physical exercise proved to be safe, since, although FHR and AFM decreased during treadmill walking, an increase in SVT and LTV was observed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(11):531-537
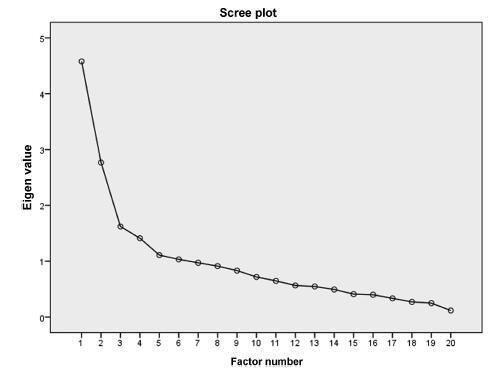
To analyze the internal consistency and the construct validity of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) State-Anxiety (S-Anxiety) scale for pregnant women during labor.
A study of measurement property including 150 pregnant women aged between 15 and 45 years old, during the first period of labor and with term pregnancies. The questionnaire used was the STAI S-Anxiety scale. In order to assess the internal consistency, Cronbach’s α was calculated through an exploratory factor analysis. The correlation between the factors was calculated using the Pearson coefficient. The state of significance used for this analysis was 0.05.
The STAI S-Anxiety scale used in the context of labor showed two factors represented as the absence (factor 1) and the presence of anxiety (factor 2); item 4 (“I regret it”) did not show a representative value. Both factors showed high indications of Cronbach’s α, varying from 0.830 for factor 1, and 0.723 for factor 2. In the results of the Pearson coefficient between the two factors, a significant but weak correlation was observed (r = -0.188; p = 0.021).
The STAI S-Anxiety scale used in pregnant women during labor presented appropriate values of internal consistency; however, item 3 did not show a significant factorial value. Therefore, this questionnaire must be applied cautiously and carefully without the use of the item 4 in the clinical practice and in researches about labor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):531-534
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(10):532-537
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000007
PURPOSE: to determine the effects of soy-derived isoflavone on hot flashes, menopausal symptoms, and endometrial thickness in postmenopausal women. METHODS: this double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study involved 90 postmenopausal patients aged 45-60 years old attended at the Outpatient Menopause Clinic. All patients had been experiencing hot flashes accompanied or not by other hypo-estrogenic symptoms. Patients were randomized to receive either two soy capsules containing 50 mg of soy-derived isoflavone or two identical placebo capsules, twice a day for 12 weeks in a double-blind fashion. Each patient was observed for 12 weeks, with two evaluations being made, one at baseline and the other at the end of the study. At each time point, the patients were given a diary to record the severity of the climacteric symptoms experienced, assessed with a modified Kupperman index, using a 100 mm Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). The intensity of hot flashes was also assessed separately. The patients were also submitted to a transvaginal echography for the measurement of endometrial thickness. Yates chi2, ANOVA or t de Student and Mann-Whitney were used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: no significant difference was detected in the Kupperman index (64 versus 82, p>0,05) or in the hot flashes (20 versus 20, p>0,05) between the isoflavone and placebo groups. No significant difference was either detected concerning the Kupperman index and hot flashes before and after treatment, when the two groups were analyzed separately. No difference was detected in the endometrial thickness either in the isoflavone or the placebo group (0.28 versus 0.26 mm, respectively, p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: our results indicate that 100 mg of isoflavone are not more effective than placebo in reducing hot flashes and hypo-estrogenic symptoms in postmenopausal women and present no effect on the endometrium thickness.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):532-539
The present article seeks to consolidate existing knowledge on breastfeeding during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Articles from 2020 and 2021 collected from the PubMed, CAPES, Virtual Health Library, Google Scholar, SciELO, and UpToDate databases were analyzed. Books and government documents published in the last decade (2010-2020) were also consulted.
Sixteen works were used in the present study. The date of publication and discussion of SARS-CoV-2 transmission through breastmilk were the inclusion criteria. Thus, articles containing repeated information or with no relevance to add to the production were excluded. Data collection comprised critical reading and synthesis of the main information obtained on the subject, which were performed for the preparation of the present study. The research took place in the period from March 27 to April 2, 2021.
Breast milk has diverse benefits for both the nursing mother and the infant. The presence of viral RNA by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR) in milk from disease-positive mothers has been detected in a few cases, and infant infections in these conditions suggest oral transmission of maternal or third-party origin. The virulence of the novel coronavirus in human milk is not confirmed, while significant amounts of exclusive antibodies are.
Lactation in the context of COVID-19 has shown greater benefits than risks of vertical transmission. Therefore, it should be encouraged when possible.