Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):53-59
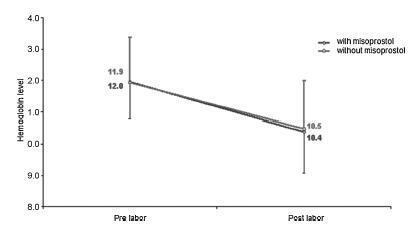
To evaluate blood loss during misoprostol-induced vaginal births and during cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction.
We conducted a prospective observational study in 101 pregnant women indicated for labor induction; pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were measured to estimate blood loss during delivery. Labor was induced by administering 25 μg vaginal misoprostol every 6 hours (with a maximum of 6 doses). The control group included 30 patients who spontaneously entered labor, and 30 patients who underwent elective cesarean section. Pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were evaluated using the analysis of variance for repeated measurements, showing the effects of time (pre- and postpartum) and of the group (with and withoutmisoprostol administration).
Therewere significant differences between pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels (p < 0.0001) with regard to misoprostol-induced vaginal deliveries (1.6 ± 1.4 mg/dL), non-induced vaginal deliveries (1.4 ± 1.0 mg/dL), cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction (1.5 ± 1.0 mg/dL), and elective cesarean deliveries (1.8 ± 1.1 mg/dL). However, the differences were proportional between the groups with and without misoprostol administration, for both cesarean (p = 0.6845) and vaginal deliveries (p = 0.2694).
Labor induction using misoprostol did not affect blood loss during delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(1):53-59
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000100008
PURPOSE: to study maternal (body composition and cardiovascular capacity) and perinatal (weight and prematurity) effects of hydrotherapy during pregnancy. METHODS: a prospective, random cohort study, with 41 low-risk pregnant women in their first pregnancy, practicing (study group, n=22) and not (control group, n=19) hydrotherapy. Anthropometric evaluation was used to assess lean mass, and absolute and relative body fat. Ergometric tests were used for maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max), stroke volume (SV) and cardiac output (CO). Perinatal results showed premature births and small for gestational age newborns. Initial and final indexes within and between groups were compared. Maternal variables were evaluated using the t test for dependent and independent values; the chi ² test was used to study proportions. RESULTS: there were no significant differences between the groups for maternal variables at the start and end of hydrotherapy. Comparison within each group confirmed the beneficial effect of hydrotherapy. In the study group, relative fat index was maintained at 29.0%; the control group showed an increase from 28.8% to 30.7%; the study group maintained VO2max at 35%, and increased SV from 106.6 to 121.5 and CO from 13.5 to 15.1; the control group showed a drop in VO2max and no change in SV and CO. There was no relationship between hydrotherapy and perinatal results. CONCLUSIONS: hydrotherapy adequately assisted metabolic and cardiovascular maternal adaptation to pregnancy and did not cause prematurity or weight loss in newborns.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(1):53-55
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000100008
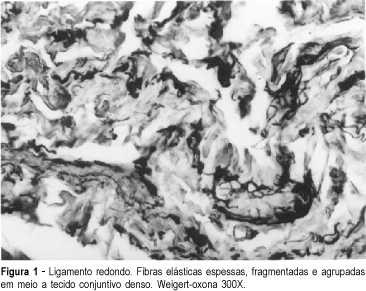
A case report of a young virgin patient with a second-degree uterine prolapse is presented. During the corrective surgery (Gillian surgery) samples of the ligaments and the pelvic fascia were obtained to evaluate the elastic fiber system. There were structural changes of the elastic fibers similar to ageing process, which promotes connective tissue weakness inducing a pelvic support defect.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):530-531
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800013
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):530-530
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):530-534
To evaluate the accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound in the diagnosis of intrauterine lesions, using hysteroscopy as the gold standard.
This was a prospective observational study with 307 patients. All patients underwent hysteroscopy after a previous transvaginal ultrasound to compare the results. The hysteroscopy was performed by experienced examiners, and transvaginal ultrasounds were performed in various public and private services, which is reflective of routine healthcare practices in obstetrics and gynecology. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the transvaginal ultrasound were calculated using hysteroscopy as the gold standard. The level of agreement between the two exams was calculated using the Kappa test.
Themean age was 56.55±12.3 years. For endometrial polyps, we observed a sensitivity of 39.8%, specificity of 72.7%, accuracy of 52.8%, and Kappa index of 0.11 (p=0.025). For fibroids, the sensitivity was 46.7%, specificity was 95.0%, accuracy was 87.9%, and Kappa index was 0.46 (p<0.001). For endometrial thickening, the sensitivity was 68.7%, specificity was 41.7%, accuracy was 47.6%, and Kappa index was 0.06 (p=0.126). For endometrial atrophy, we found a sensitivity of 6.7%, specificity of 99.3%, accuracy of 90.2%, and Kappa index of 0.10 (p=0.006). For the other findings, the sensitivity was 15.6%, specificity was 99.6%, accuracy was 87.3%, and Kappa index was 0.23 (P<0.001).
Our study demonstrated a low level of accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound for the diagnosis of endometrial lesions, when performed by a non-experienced professional. Thus, it is important to consider the use of hysteroscopy to avoid unnecessary and inappropriate treatments.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):530-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100003
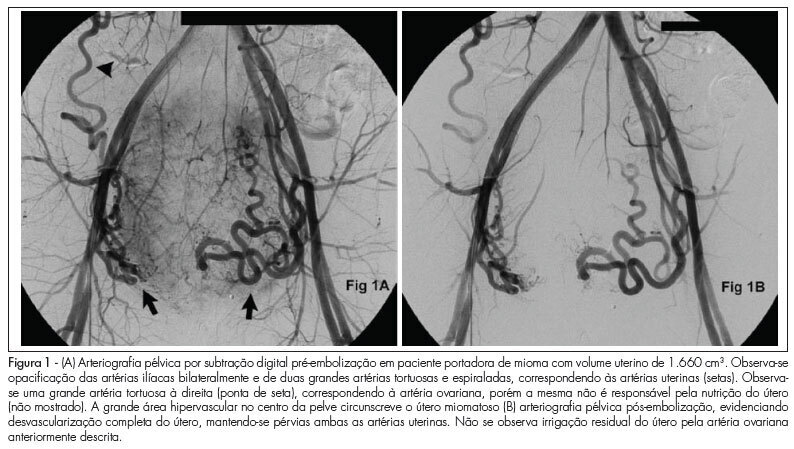
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effectiveness of uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) in patients with giant fibroids, with regard to both clinical outcomes and size reduction. METHODS: twenty-six patients with a mean age of 36.5 years, carrying symptomatic fibroids with a volume over 1,000 cm³, were referred for UFE. All patients had indication for percutaneous treatment. The procedures were performed under epidural anesthesia and sedation, using an institutional protocol. By unilateral femoral access, selective catheterization of uterine arteries and infusion of calibrated microspheres through microcatheter were carried out. Clinical evaluation was performed by means of regular outpatient gynecology consultation. All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before the procedure and 15 patients underwent control MRI after 6 months. RESULTS: technical success was 100%. There was no complication related to the procedures. Mean uterine volume of the 15 patients studied was 1,401 cm³ before embolization (min 1,045 cm³, max 2,137 cm³) and 799 cm³ after 6 months (525 cm³ min, max. 1,604 cm³), resulting in a total reduction of 42.9%. Clinical improvement was observed in 25 of 26 patients. One woman with uterine volume of 1,098 cm³ who developed necrosis and partial fibroid expulsion underwent myomectomy. Another patient was submitted to myomectomy six months after the procedure because she wanted to become pregnant, despite partial fibroid size reduction. One patient with a uterine volume of 2,201 cm³ required a second intervention to achieve an adequate angiographic result. No patient underwent hysterectomy. On average, 9.2 microsphere syringes were used per patient. CONCLUSION: embolization of giant uterine fibroids is a feasible procedure with acceptable clinical and radiological outcomes. It can be considered an option for patients who desire to preserve the uterus, and it may serve as adjuvant therapy for high-risk myomectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):530-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000900005
PURPOSE: to compare the incidence of preterm deliveries, and of low birth weight newborns, among primiparous adolescents, from two age groups. METHODS: this is a comparative, cross-sectional clinical study composed of 522 primiparous adolescents whose deliveries occurred at the gestational age of 25 to 42 weeks. The adolescents were divided into 2 groups according to their age; Gprec: from 10 to 15 complete years old (n=104); Gtard: from 16 to 19 complete years old (n=418). The research data were obtained by an individualized, confidential and ethical interview, soon after delivery; and by a written questionnaire with questions about the gestational age in complete weeks, and about the newborns birth weight. The gestational age was calculated at the delivery day, according to the date of the last trustworthy menstrual period, being also confirmed by the earliest pregnancy scanning or by Capurro's index, when there were any doubts about the previously described parameters. All newborns with gestational age under 37 weeks at birth were considered preterm babies. The newborn weight was taken by neonatologists immediately after delivery; all newborns with less than 2,500g were considered to be low weight babies. Thus, we compared prematurity rate and low birth weight among newborns from primiparous puerperal adolescents. The chi² test was used for the statistic analysis and the partition chi² test for the found differences. As the significancy level was 0.05 (alpha =5%), lower levels than that were considered significant. RESULTS: the prematurity rate was not significantly different between the two groups (5.8 and 2.6%). The incidence of low birth weight in Gprec (13.5%) was significantly higher than in Gtard (3.1%). CONCLUSIONS: the group with primiparous adolescents under 15 years old showed a significantly higher risk of low birth weight newborns. However, a statistically significant incidence of prematurity between the groups studied was not verified.