Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):513-519
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800003
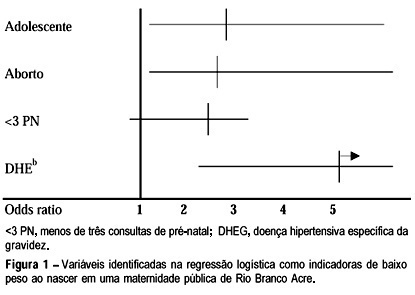
Purpose: to study pregnancy in adolescent women as a possible risk factor for low birth weight. Material and Methods: a cross-wide study was performed on 562 adolescent and non-adolescent mothers who were interviewed during the first 24 h after delivery in the period from January 10,2002, to March 25, 2002, in a public maternity hospital located in Rio Branco, Acre State, Brazil. Those who delivered dead fetuses, whose babies died after being born, or had twins were excluded from the study. Results: among the 562 mothers who were studied, 37.0% (n=208) were teenagers (16±1.6 years), and 63.0% (n=354) were 20 or more years old (22.9±6.3 years). The average weight of the newborns was statistically higher (p<0.010) among the adult mothers (3,158.64±626.50 g) than among the adolescent mothers (3,019.93±587.43 g). When the 32 (5.7%) premature newborn babies (<37 week's pregnancy) were excluded, there was also a significantly greater proportion (p<0.007) of newborns with low weight (<2,500 g) among the adolescent mothers (11.9%) than among the non-adolescent ones (5.5%). The analysis of logistic regression showed an increased risk for newborns with low weight among the adolescent mothers (OR=2.99; 1.47-6.07), as well as for abortion (OR=2.78; 1.23-6.30) and pregnancy - induced hypertensive disorders (OR=5.16; 1.65-16.12). Conclusions: the present study shows that associated with the psychosocial, familial, and economic impact, already reported in the literature, pregnancy in adolescents is associated with deleterious effects on the conceptus, which requires a cohort study to assess the repercussions at both the medium- and long-term.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(10):513-526
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001000008
The present context of medical practice demands from the obstetrician and gynecologist broad understanding of the scientific and technological advances of the area. The main purpose of prenatal evaluation is to identify fetuses at risk for adverse events or death, for preventive action to avoid mishappenings. The determination of fetal biophysical profile reaches its maximum efficiency when applied within the clinical context of each case. In high risk gestations, the Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery has shown to be useful to improve perinatal outcome. In the fetal growth deficit, due to severe placentary insufficiency, Doppler velocimetry of the venous duct has been showing to be an important tool in handling of the cases before the 34th week of gestation. Although no test itself is considered the best to evaluate the fetus's prenatal vitality, the joint analysis of all methods may lead to a better understanding of the fetal response to hypoxia.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):514-518
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005007
To describe the epidemiologic and obstetric characteristics of women with recurrent miscarriages.
A descriptive and analytical study whose inclusion criterion was every woman that was attended at the clinic for recurrent miscarriage (loss group), between January 2006 and December 2010. Patients that did not live in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil, and those who were not reached by telephone or whose number was not included in the medical record were not included. The Control Group consisted of 204 pregnant women seen at the low-risk prenatal care unit between May 2007 and April 2008. Women who did not accept to be interviewed and those with obstetric risk were excluded from the Control Group. The analyzed variables were: age, education, occupation, marital status, alcohol consumption, body mass index, obstetric history and the gestational age when the losses occurred. The SPSS 18.0 program was used for statistical analysis. Means and standard deviations of continuous variables were compared using the Student's t-test and the frequencies of the nominal variables were compared by the χ2 test.
The mean age of women in the loss group was higher than in the Control Group (32.3±6.3 versus 26.5±6.4 years old, p<0.01). Consumption of alcoholic beverages predominated in the loss group (36.9 versus 22.1%, p=0.01), as well as marital status (93.2 versus 66.7% were married or living in a stable union, p<0.01). The pre-pregnancy body mass index was higher in the loss group (26.9 versus 23.5%, p<0.01). Regarding obstetric history, 103 women with recurrent miscarriage reported 334 pregnancies. Fifty-six of them had 2 or more miscarriages in the first quarter and in 31 of them, 2 or more pregnancies progressed to late abortions/extremely preterm infants.
Some risk factors were identified in women with recurrent losses, such as more advanced age and higher body mass index. These observations agree with more recent proposals regarding recurrent losses that consider the inclusion of losses in various gestational ages.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):515-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900003
PURPOSE: the technological improvements in image quality have increased the importance of ultrasound as an imaging method in the study of breast pathologies. The need for a standardized method for lesion characterization, description and reporting in image analysis motivated the development of a breast sonographic report classification system. METHODS: the classification grouped the breast sonographic images in five classes: I - normal; II - benign; III - indeterminate, IV - suspect, and V - highly suspect. The used morphologic ultrasound features were shape, border, contour, echogenicity, echotexture, sound transmission, orientation, and secondary signals. The gold standard test, in the study of 450 lesions, considered sonographic follow-up of the lesions for a period from 6 to 24 months and the histopathology of surgical cases. RESULTS: breast sonographic classification for the diagnosis of breast cancer showed a sensitivity of 90.2% (CI: 82.8-94.9%), a specificity of 96.2% (CI: 94.0-97.6%), a positive predictive value of 84.1% (CI: 76.0-89.9%), and a negative predictive value of 97.8% (CI: 95.9-98.9%), obtaining an accuracy of 95.1%. CONCLUSIONS: the adoption of a sonographic classification system results in the standardization and optimization of the reports. It also aids the comparison with clinical findings, histopathological tests and breast images, avoiding unnecessary procedures and therefore leading to more adequate therapeutical management.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(11):516-519
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005454
To investigate the frequencies of polymorphic allele and genotypes for the LT-α gene, position +252 (rs909253), in Brazilian women with preeclampsia.
This is a case-control study, in which 30 women with preeclampsia, classified according to the criteria of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program, and 115 women in the control group, with at least two healthy pregnancies, were selected. Peripheral blood was collected, and DNA was extracted, followed by genotyping, using specific primers and restriction analysis. The genotypes obtained were AA, AG and GG. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 association test. The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium was tested using the Haploview Program.
The results showed no association between genotypes and preeclampsia development (χ2=2.0; p=0.4). When the AG and GG genotypes were grouped according to allele G presence or absence (genotype AA), the data showed that the presence of allele G was not significantly different between cases (women with preeclampsia) and controls (χ2=0.0; p=1.0). The LT-α gene polymorphism, position +252 (rs909253), seems not to be an important candidate for the development of preeclampsia. Other inflammatory genes should be researched, and studies involving gene-environment interactions should be performed, in order to reach a better understanding of the etiology of the preeclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):516-516
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):516-522
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100007
PURPOSE: To analyze the impact of vaginal delivery after a previous cesarean section on perinatal outcomes. METHODS: Case-control study with selection of incident cases and consecutive controls. Maternal and perinatal variables were analyzed. We compared secundiparas who had a vaginal delivery after a previous cesarean delivery (VBAC) (n=375) with secundiparas who had a second cesarean section (CS) (n=375). Inclusion criteria were: secundiparas who underwent a cesarean section in the previous pregnancy; singleton and term pregnancy; fetus in vertex presentation, with no congenital malformation; absence of placenta previa or any kind of bleeding in the third quarter of pregnancy. RESULTS: The rate of vaginal delivery was 45.6%, and 20 (5.3%) women had forceps deliveries. We found a significant association between VBAC and mothers younger than 19 years (p<0.01), Caucasian ethnicity (p<0.05), mean number of prenatal care visits (p<0.001), time of premature rupture of membranes (p<0.01), labor duration shorter than 12 hours (p<0.04), Apgar score lower than seven at 5th minute (p<0.05), fetal birth trauma (p<0.01), and anoxia (p<0.006). In the group of newborns delivered by cesarean section, we found a higher frequency of transient tachypnea (p<0.014), respiratory disorders (p<0.048), and longer time of stay in the neonatal intensive care unit (p<0.016). There was only one case of uterine rupture in the VBAC group. The rate of neonatal mortality was similar in both groups. CONCLUSIONS: Vaginal delivery in secundiparas who had previous cesarean sections was associated with a significant increase in neonatal morbidity. Further studies are needed to develop strategies aimed at improving perinatal results and professional guidelines, so that health care professionals will be able to provide their patients with better counseling regarding the choice of the most appropriate route of delivery.