You searched for:"Manoel João Batista Castello Girão"
We found (31) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(7):327-333
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000700004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the clinical and epidemiological risk factors for endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women with endometrial polyps, as well as the genetic polymorphism of the progesterone receptor (PROGINS). METHODS: a case-control study was designed with 160 postmenopausal women with endometrial polyps, compared to a normal Control Group of 400 postmenopausal women. The genotyping of PROGINS polymorphism was determined by the polymerase chain reaction. Clinical and epidemiological data were compared between benign endometrial polyps and 118 of the control subjects. Variables were also compared with regard to benign and malignant endometrial polyps. RESULTS: comparison of the epidemiological variables between groups showed a significant difference for age, ethnicity, time since menopause, parity, tamoxifen use, hypertension and breast cancer, all of them more prevalent in the polyp group. After adjustment for age, statistical significance remained only for parity (OR=1.1), hypertension (OR=2.2) and breast cancer (OR=14.4). There were six cases of malignant polyps (3.7%). The frequency of bleeding was 23.4% for benign polyps and 100% for malignant polyps, with large polyps being detected in 54.6% of the benign cases and in 100 of the malignnat ones. The frequency of arterial hypertension was 54.5% for benign polyps and 83.3% for the malignant ones. The frequency of PROGINS T1/T1, T1/T2 and T2/T2 polymorphism was 79.9%, 19.5% and 0.6%, respectively, for the polyp group, and 78.8%, 20.8% and 0.5% for the Control Group. CONCLUSIONS: elderly age, hypertension, and breast cancer were significantly associated with endometrial polyps. The presence of PROGINS polymorphism was not significantly associated with endometrial polyps. The incidence of malignant polyps was low and strongly associated with bleeding, large-sized polyp and arterial hypertension.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 1999;21(1):33-37
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000100006
Purpose: to evaluate the agreement between the urodynamic and ultrasonography diagnoses of urinary incontinence, as well as to correlate the variables of both examinations. Methodology: three hundred eighty-one patients with urine loss were selected, from the Sectior of Urogynecology and Vaginal Surgery of the Division of Gynecology, Escola Paulista de Medicina - Federal University of São Paulo. All of them were submitted to urodynamic study, according to the standardization of the International Society of Continence, and to ultrasonography of the bladder neck, with a 6 MHz trasvaginal transducer. We analyzed the maximum closing urethral pressure (MCUP) and the etiological diagnosis of the urine loss. In the ultrasonography, the position of the bladder neck was evaluated in relation to the inferior border of the pubic symphysis, and its mobility as well as the diameter of the urethra and bladder neck. The women were categoriaed according to the urodynamic study in to stress urinary incontinence, detrusor instability and mixed urinary incontinence. Results: 1) the bladder neck, at rest was most frequently above the inferior border of the pubic symphysis and, during effort, below or at the height of the bony reference, in the three groups; 2) the mobility of the bladder neck was similar in the groups; 3) there was no significant correlation between MCUP and the diameter of the urethra and of the bladder neck. Conclusion: we deem that ultrasonography of the bladder neck is always a complement to the clinical evaluation and the urodymanic study.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2009;31(7):353-360
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000700006
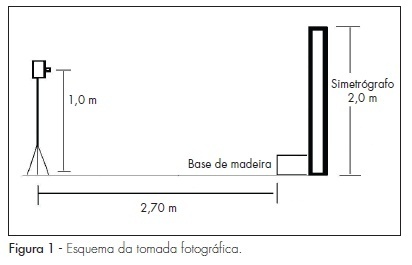
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate by photogrammetry, postural changes in women with chronic pelvic pain. METHODS: thirty women with complaint of chronic pelvic pain and 37 without it, in a total of 67 women, were evaluated. The evaluation was realized through anamnesis, fixed markers in defined anatomical sites, and frontal, posterior, left and right lateral photographies. Photo analysis has been done by the software CorelDraw®, version 11.0. Quantitative values for postural analysis of the ankle, the knee in the saggittal plan, pelvis, lumbar lordosis, thoracic kyphosis, adducted/abducted scapula, shoulders, head and third finger on the floor test were obtained. The qualitative variables studied were the knee (varus, valgus or normal), the presence or not of winged scapula and leveling of shoulders. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 16.0 was used for the statistical analyses. Fisher's exact test and Monte-Carlo method were used to compare the qualitative variables, and for the quantitative data, t or Mann-Whitney test was used. The comparisons among continuous data, corrected for possible confusion variables were realized by the univariate covariance analysis. Significance level was established at 0.05 or 5%. RESULTS: there were significant differences between cases and controls for protruded head (47.5 and 52.0º, respectively; p<0.0001) and for protruded shoulders (1.9 and 1.6 cm, respectively; p=0.03). The other variables did not show significant differences. CONCLUSIONS: based on these results, attention to head and shoulder posture, to antalgic postures and to the emotional factor is recommended. Women with chronic pelvic pain should be treated, taking into consideration individual muscle-skeletal changes, and social and emotional conditions.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(6):365-370
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000600002
Purpose: to study the relationship between pelvic floor function and bladder neck mobility in women with and without stress urinary incontinence (SUI), in menacme and postmenopausal. Methods: sixty-one SUI patients were evaluated; 31 of them were in menacme and of these 17 had SUI and 14 did not have any complaint; 30 were postmenopausal and of these, 15 with SUI and 15 without SUI. Simple cystometry and empty supine stress test were performed in those who had urinary incontinence complaint. Bladder neck mobility was studied by ultrasound and by the Q-tip test. To study pelvic floor function, vaginal cones and digital palpation were used. Results: the bladder neck position in the incontinent women (Groups A and C), determined by ultrasound or the Q tip-test, was --11.8 cm in Group A and --12.5 cm in Group C, lower than the continent women, in whom the bladder neck was at +4.4 cm in Group B and +2.3 cm in Group D. There were no differences in bladder neck mobility among the continent menacme (9.1 cm) and postmenopausal (9.5 cm) groups. Also there were no differences among the incontinent groups (17.1 cm for Group A and 16.6 cm for Group C). The bladder neck mobility was greater in the incontinent women (A and C). Continent women had better results on evaluation of pelvic floor muscles than the incontinent ones, even using vaginal cones or digital palpation, and these results were not dependent on the hormonal status. Conclusion: a positive correlation was found between the Q-tip tests and ultrasound, and between test with vaginal cones and digital palpation. No significant correlation was found between pelvic floor function and bladder neck mobility.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(9):441-442
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2009;31(9):447-452
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000900005
PURPOSE: to compare the effects of functional electrostimulation of the pelvic floor and therapy with cones in women with stress urinary incontinence (SUI). METHODS: randomized clinical study for which 45 patients with SUI were selected. The effects of functional electrostimulation of the pelvic floor were evaluated in the SUI treatment of 24 women, with the use of clinical data (micturition diary, pad test and a questionnaire about quality of life - I-QoL). The patients were submitted to two 20' weekly sessions for four consecutive months, under the supervision of a physiotherapist. The electrode used had 10 cm length and 3.5 cm width with a double metallic ring and a cylindrical shape, positioned in the medium third of the vagina. The electric parameters used were: intensity varying from 10 to 100 mA and 50 Hz of fixed frequency, with pulse duration of 1 ms. Also, we evaluated 21 patients who were submitted to vaginal cone treatment. The cone therapy was done with two 45 minute sessions per week. The cones' weight varied from 20 to 100 gr. RESULTS: there was no difference between the outcomes of electrostimulation of the pelvic floor and the vaginal cones for the treatment of SUI (p>0.05). After four months, there was a significant improvement in the I-QoL index of the patients treated both with electrostimulation (40.3 versus 82.9) or with the cones (47.7 versus 84.1). There was a significant decrease in pad weight in both groups, measured before and after the treatment (28.5 and 32 g versus 2.0 and 3.0 g for the electrostimulation and cone group, respectively). Finally, there was a significant decrease in the number of urinary leakage evaluated by the micturition diary in both groups (p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: both electrostimulation and vaginal cones were effective in the treatment of women with SUI.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(9):452-458
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900003
PURPOSE: to evaluate and to compare the effectiveness of oxybutynin, electrostimulation (ES) and pelvic floor training (PFT) in the management of women with detrusor overactivity. METHODS: a total of 64 women, 35 to 80 years old, were enrolled in this randomized prospective trial. Patients were randomized in three groups: Oxybutynin (n=22), ES (n=21) and PFT (n=21). There were no statistical differences between the three groups with regards to race (p=0.948), age (p=0.747), hormonal status (p=0.813), time of symptomatology (p=0.789), previous surgery for urinary incontinence (p=0.993), or body mass index (p=0.897). Patients were assessed before and after treatment by urodynamic test, a seven-day voiding diary, and subjective response. The duration of the treatment was twelve weeks. For statistical analyses, the Pearson chi2, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the paired t-test were used. RESULTS: there was a decrease in the urge-incontinence episodes and in the number of pads required in all groups (p<0.05). There was reduction in the frequency of micturition in the Oxybutynin Group (p=0.014). Oxybutynin and ES Groups had reduction in nocturia episodes (p=0.003 and p=0.036, respectively). There were no significant differences in improvement between the three groups (p>0.05). Urgency was resolved in 14 (63.6%), 11 (52.4%) and 12 (57.1%) patients of the Oxybutynin, ES and PFT Groups, respectively, without differences among the groups (p=0.754). Subjectively, 17 (77.3%), 11 (52.4%) and 16 (76.2%) women who had accomplished oxybutynin, ES and PFT, respectively, were satisfied, without differences among the groups (p = 0.142). Urodynamic was normal in 8 (36.4%), 12 (57.1%) and 11 (52.4%) patients of the Oxybutynin, ES and PFT Groups, respectively. This urodynamic analysis revealed no differences between the three groups (p=0.358). The reduction of urge-incontinence correlated with patient satisfaction (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: treatments were equally effective; reduction of urge-incontinence was correlated with patient satisfaction.
Summary
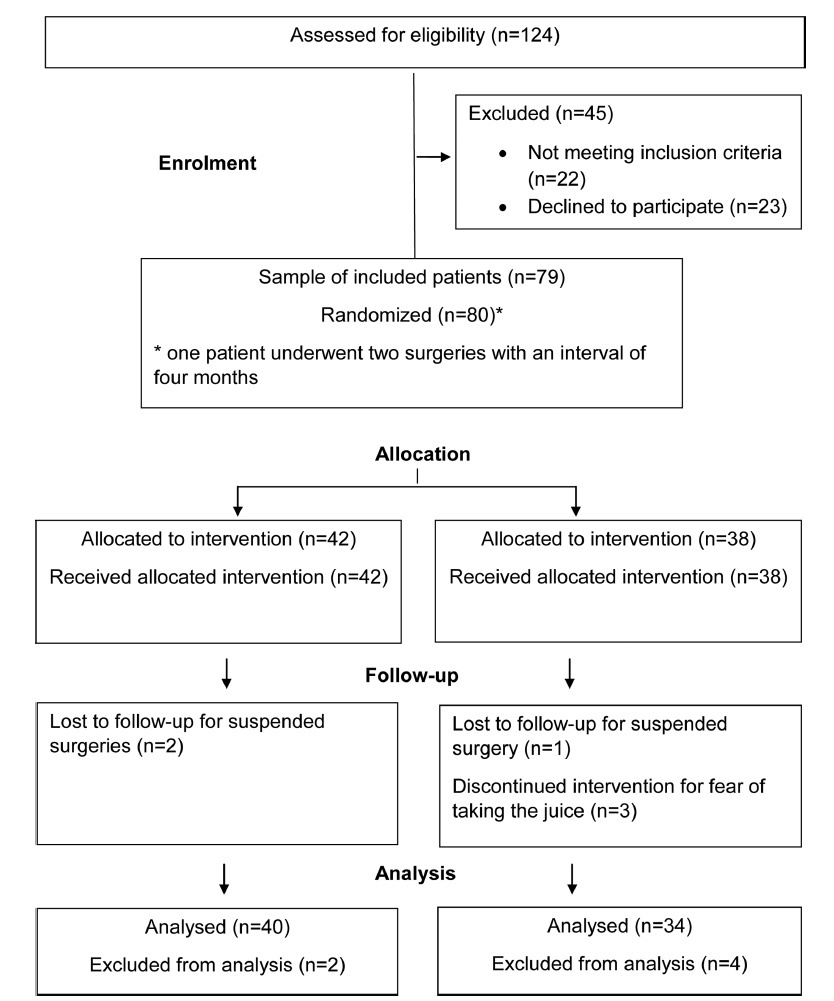
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(8):468-475
To investigate the effects of preoperative fasting abbreviation with a carbohydrate and protein-enriched solution, on postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) incidence in gynecological surgery patients, a population naturally at risk for such unpleasant episodes.
The present prospective double-blind randomized study was performed at The Hospital Municipal e Maternidade Dr. Odelmo Leão Carneiro (HMMOLC, in the Portuguese acronym), in Uberlândia, state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, in partnership with the Gynecology Department of the Universidade Federal de São Paulo (UNIFESP), approved by the Human Research EthicsCommittee ofUNIFESP and theboard ofHMMOLC, and included in the Brazil Platform and in the Brazilian Clinical Trial Registry. After signing the consent form, 80 women, who were submitted to gynecological surgery in the period from January to June 2016,were randomized into 2 groups: control group (n= 42) and juice group (n= 38). They received, respectively, 200mL of inert solution or liquid enriched with carbohydrate and protein 4 hours presurgery. The incidence, frequency and intensity of PONV were studied using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), with statistical analysis performed by the software IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).
The incidence of nausea and vomiting was lower than in the literature, to this population, with 18.9% (14/74) for the control group and 10.8% (8/74) for the juice group, respectively, with no statistically significant difference between the groups.
The incidence of nausea and vomiting was lower than in the literature, but it cannot be said that this is due to the abbreviation of fasting. It can provide greater comfort, with the possibility of PONV prevention in patients at risk for these episodes.