You searched for:"Lúcia Costa-Paiva"
We found (16) results for your search.Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):335-342
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700008
PURPOSE: To evaluate whether climacteric women undergoing liver transplantation had higher prevalence of decreased bone mass than those without any liver disease. METHODS: A cross-sectional study with 48 women receiving follow-up care at a university hospital in Southeastern Brazil, from February 4th 2009 to January 5th 2011, was conducted. Of these women, 24 were 35 years or older and had undergone liver transplantation at least one year before study entry. The remaining 24 women had no liver disease and their ages and menstrual patterns were similar to those of transplanted patients. Laboratorial tests (follicle-stimulating hormone and estradiol) and bone density measurements of the lumbar spine and femur (equipment Hologic, Discovery WI) were performed. Statistical analysis was carried out by Fisher's exact test, simple Odds Ratio (OR), and multiple logistic regression. RESULTS: Mean age of the women included in the study was 52.8 (±10.7) years-old, 27.1% were premenopausal and 72.9% were peri/postmenopausal. Approximately 14.6% of these women exhibited osteoporosis and 35.4% had low bone mass. The following items were associated with decreased bone mass: being postmenopausal (OR=71.4; 95%CI 3.8 - 1,339.7; p<0.0001), current age over 49 years-old (OR=11.4; 95%CI 2.9 - 44.0; p=0.0002), and serum estradiol levels lower than 44.5 pg/mL (OR=18.3; 95%CI 3.4 - 97.0; p<0.0001). Having a history of liver transplantation was not associated with decreased bone mass (OR=1.4; 95%CI 0.4 - 4.3; p=0.56). CONCLUSION: Liver transplantation was not associated with decreased bone mass in this group of climacteric women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(10):439-441
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):467-472
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005094
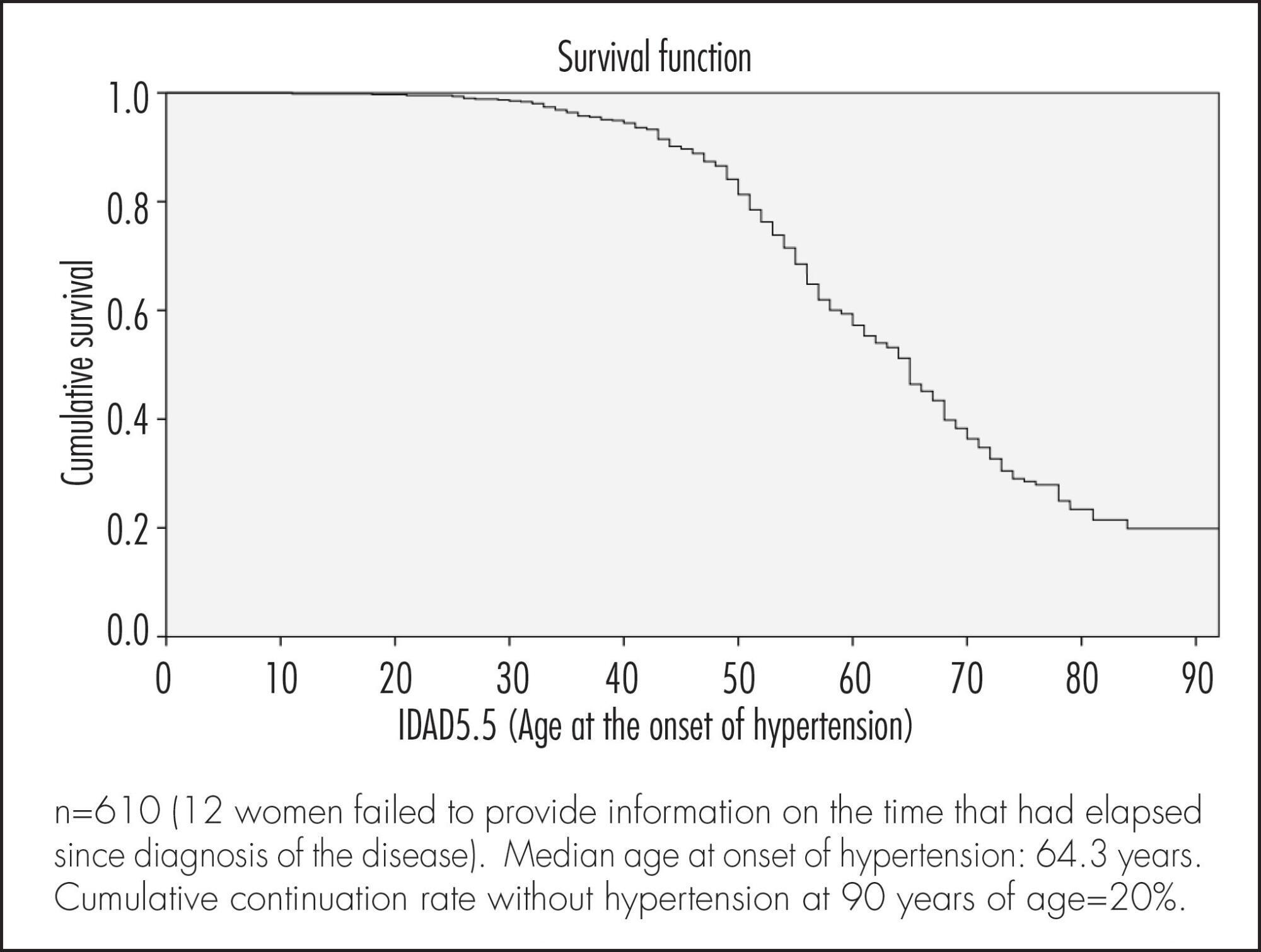
To evaluate factors associated with hypertension in Brazilian women of 50 years of age or more.
A cross-sectional population based study using self-reports. A total of 622 women were included. The association between sociodemographic, clinical and behavioral factors and the woman's age at the onset of hypertension was evaluated. Data were analyzed according to cumulative continuation rates without hypertension, using the life-table method and considering annual intervals. Next, a Cox multiple regression analysis model was adjusted to analyze the occurrence rates of hypertension according to various predictor variables. Significance level was pre-established at 5% (95% confidence level) and the sampling plan (primary sampling unit) was taken into consideration.
Median age at onset of hypertension was 64.3 years. Cumulative continuation rate without hypertension at 90 years was 20%. Higher body mass index (BMI) at 20–30 years of age was associated with a higher cumulative occurrence rate of hypertension over time (coefficient=0.078; p<0.001). Being white was associated with a lower cumulative occurrence rate of hypertension over time (coefficient= -0.439; p=0.003), while smoking >15 cigarettes/day was associated with a higher rate over time (coefficient=0.485; p=0.004).
The results of the present study highlight the importance of weight control in young adulthood and of avoiding smoking in preventing hypertension in women aged ≥50 years.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):476-485
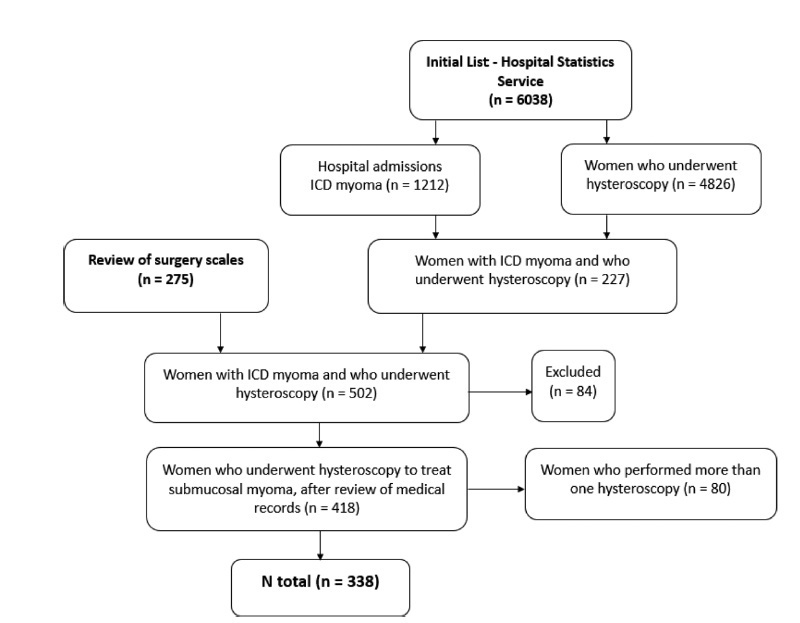
To evaluate the factors associated with complete myomectomy in a single surgical procedure and the aspects related to the early complications.
A cross-sectional study with women with submucous myomas. The dependent variables were the complete myomectomy performed in a single hysteroscopic procedure, and the presence of early complications related to the procedure.
We identified 338 women who underwent hysteroscopic myomectomy. In 89.05% of the cases, there was a single fibroid to be treated. According to the classification of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d’Obstétrique, FIGO, in French),most fibroids were of grade 0 (66.96%), followed by grade 1 (20.54%), and grade 2 (12.50%). The myomectomies were complete in 63.31% of the cases, and the factors independently associated with complete myomectomy were the diameter of the largest fibroid (prevalence ratio [PR]: 0.97; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.96-0.98) and the classification 0 of the fibroid according to the FIGO (PR: 2.04; 95%CI: 1.18-3.52). We observed early complications in 13.01% of the hysteroscopic procedures (4.44% presented excessive bleeding during the procedure, 4.14%, uterine perforation, 2.66%, false route, 1.78%, fluid overload, 0.59%, exploratory laparotomy, and 0.3%, postoperative infection). The only independent factor associated with the occurrence of early complications was incomplete myomectomy (PR: 2.77; 95%CI: 1.43-5.38).
Our results show that hysteroscopic myomectomy may result in up to 13% of complications, and the chance of complete resection is greater in small and completely intracavitary fibroids; women with larger fibroids and with a high degree of myometrial penetration have a greater chance of developing complications from hysteroscopic myomectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(10):496-502
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001000005
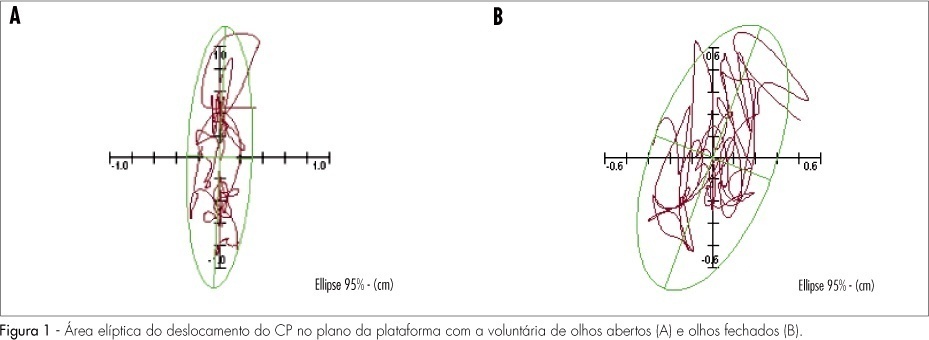
PURPOSE: to evaluate the rate of fall and its association with stabilometric parameters in postmenopause women, with or without osteoporosis. METHODS: transversal cohort study including 266 over 60-year-old women with and without osteoporosis, with at least 12 months of amenorrhea. The women were interviewed about the occurrence of falls in the previous 12 months, and about clinical and sociodemographic information. The osteoporosis diagnosis was done through bone densitometry and the postural stability evaluated through a stabilometric platform. For statistical analysis, mean, standard deviation, percentage, Mann-Whitney test, χ2 and Odds Ratio, and Spearman's correlation coefficient have been calculated. RESULTS: women with osteoporosis presented lower body mass index (BMI), lower schooling, shorter hormonal therapy and sooner menopause onset. The rate of fall was significantly higher in the group of women with osteoporosis (51.1%) (p<0.01), that presented an adjusted risk of 1.9 (1.3 to 3.4) times higher of falls and 3.2 (1.2 a 8.2) times higher of recurrent falls than the group without osteoporosis. Women with osteoporosis presented higher amplitude of Y axis oscillation in the open-eye test, than women without osteoporosis. The adjusted correlation analysis between stabilometric parameters and falls has not shown any significant correlation. CONCLUSIONS: women with post-menopausal osteoporosis present higher rate of falls and higher risk of recurrent falls, as compared with women without osteoporosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):497-502
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100004
PURPOSE: To analyze the prevalence of and factors associated with fragility fractures in Brazilian women aged 50 years and older. METHODS: This cross-sectional population survey, conducted between May 10 and October 31, 2011, included 622 women aged >50 years living in a city in southeastern Brazil. A questionnaire was administered to each woman by a trained interviewer. The associations between the occurrence of a fragility fracture after age 50 years and sociodemographic data, health-related habits and problems, self-perception of health and evaluation of functional capacity were determined by the χ2 test and Poisson regression using the backward selection criteria. RESULTS: The mean age of the 622 women was 64.1 years. The prevalence of fragility fractures was 10.8%, with 1.8% reporting hip fracture. In the final statistical model, a longer time since menopause (PR 1.03; 95%CI 1.01-1.05; p<0.01) and osteoporosis (PR 1.97; 95%CI 1.27-3.08; p<0.01) were associated with a higher prevalence of fractures. CONCLUSIONS: These findings may provide a better understanding of the risk factors associated with fragility fractures in Brazilian women and emphasize the importance of performing bone densitometry.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):507-512
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of osteoporosis in climacteric women and analyze the influence of general and reproductive risk factors on bone mineral density. METHODS: a cross-sectional study with the evaluation of the 473 hospital records of climacteric women followed up at the Menopause Outpatient Facility of CAISM/Unicamp, between 03/28/2000 and 04/17/2001. These women were at least 12 months in amenorrhea and presented the results of a bone densitometry study performed at the Nuclear Medicine Department of HC/Unicamp. The following variables were evaluated: age, color, body mass index, level of education, smoking, use of medication, age at menopause, parity, use and length of hormone replacement therapy and its effect on bone mineral density. Statistical analyses were performed using logistic regression ajusted by age and hormone replacement therapy use. RESULTS: the mean age of the studied women was 53.9 years (± 7.1 SD) with mean age at menopause being 45.9 years (± 6.9 SD). Osteoporosis occurred in 14.7% and osteopenia in 38% of the cases in the lumbar vertebrae (L2-L4 interspace) and in 3.8 and 32.7% in the femur, respectively. Logistic regression adjusted to age and hormone therapy showed an association between the following variables: level of education, age at menopause and body mass index. CONCLUSION: there was a high prevalence of osteoporosis and osteopenia in the studied population. Advanced age, lower level of education, late menarche, early menopause and lower body mass index were identified as risk factors for developing decreased bone mass in the studied population.
Summary