You searched for:"Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon"
We found (21) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(8):375-378
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(7):401-411
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700002
Purpose: to analyze the relationship between White's classification and the histopathological, changes occurring in the placentas of diabetic pregnant women, performing a qualitative comparison of histopathological changes in the placentas of nondiabetic pregnant women with those in diabetic ones (classes A and A/B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH), studying the influence of the quality of glycemic control and of gestational age on placental changes in the three groups of diabetic pregnant women. Patients and methods: specimens of placentas were collected from all diabetic pregnant women seen between 1991 and 1996 in the Maternity Section of the Hospital das Clínicas, Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, stained using the hematoxylin-eosin technique, and submitted to a histopathological examination. The quality of glycemic control was analyzed by the glycemia average of gestation and classified as adequate or inadequate, with a limit of 120 mg/dl. Gestational age was individualized as term and preterm. Results: forty-two newborns (43.3%) were born at term and the remaining were preterm (56.7%). The prematurity rate was higher for women with clinical diabetes (classes B and C; D to FRH). Some histopathological alterations were observed only in placentas from diabetic pregnant women: cystoid degeneration, chorial edema, intima edema, dysmaturity, Hofbauer cell hyperplasia, villitis, ghost cells, two vessels in the umbilical cord, and endarteritis. Conclusions: histopathological changes in the placentas of pregnant women with gestational diabetes (classes A and A/B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH) were similar to those in the nondiabetic ones, and, therefore, were independent of White's clinical classification. The histopathological changes in the placentas of pregnant women with gestational diabetes (classes A and A and B), clinical, short duration (classes B and C), and clinical with vasculopathy (classes D to FRH) were not related to gestational age at birth and to the quality of glycemic control of the mother. The comparison between histopathological changes and the increased number of preterm newborns in clinical diabetes, class D to FRH, suggest early placental ageing in clinical diabetes patients.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(1):53-59
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000100008
PURPOSE: to study maternal (body composition and cardiovascular capacity) and perinatal (weight and prematurity) effects of hydrotherapy during pregnancy. METHODS: a prospective, random cohort study, with 41 low-risk pregnant women in their first pregnancy, practicing (study group, n=22) and not (control group, n=19) hydrotherapy. Anthropometric evaluation was used to assess lean mass, and absolute and relative body fat. Ergometric tests were used for maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max), stroke volume (SV) and cardiac output (CO). Perinatal results showed premature births and small for gestational age newborns. Initial and final indexes within and between groups were compared. Maternal variables were evaluated using the t test for dependent and independent values; the chi ² test was used to study proportions. RESULTS: there were no significant differences between the groups for maternal variables at the start and end of hydrotherapy. Comparison within each group confirmed the beneficial effect of hydrotherapy. In the study group, relative fat index was maintained at 29.0%; the control group showed an increase from 28.8% to 30.7%; the study group maintained VO2max at 35%, and increased SV from 106.6 to 121.5 and CO from 13.5 to 15.1; the control group showed a drop in VO2max and no change in SV and CO. There was no relationship between hydrotherapy and perinatal results. CONCLUSIONS: hydrotherapy adequately assisted metabolic and cardiovascular maternal adaptation to pregnancy and did not cause prematurity or weight loss in newborns.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(10):571-574
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(10):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000003
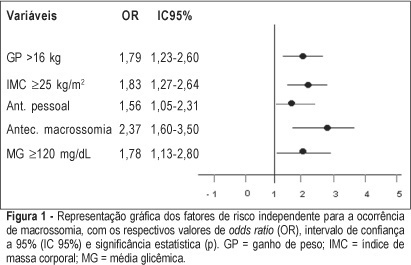
PURPOSE: to identify risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia. METHODS: retrospective study, control-case, including 803 pairs of mothers and newborns belonging to this specific population, divided into two groups - macrosomic (cases, n=242) and non-macrosomic (controls, n=561). Variables regarding age, parity, weight and body mass index (BMI), weight gain (WG), diabetes history, high blood pressure and tabagism, diabetes type and classification, and glycemic control indicators in the third trimester were compared. The means were evaluated by the F test and the categorized variables were submitted to univariate analysis using the chi² test. The significative results were included in the multiple regression model for the identification of macrosomia independent risk considering OR, 95% CI and p value. The statistical significance limit of 5% was established for all analyses. RESULTS: there was a significative association between macrosomia and WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², personal, obstetric and macrosomic history, classification in the Rudge groups (IB and IIA + IIB), glycemic mean (GM) >120 mg/dL and postprandial glycemic mean >130 mg/dL in the third trimester. In the multiple regression analysis, WG >16 kg (OR=1,79; 95% CI: 1,23-1.60), BMI >25 kg/m² (OR=1.83; 95% CI: 1.27-2.64), personal history of diabetes (OR=1.56; 95% CI: 1.05-2.31) and of macrosomia (OR=2.37; 95% CI: 1.60-3.50) and GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester (OR=1.78; 95% CI: 1.13-2.80) confirmed to be independent risk factors for macrosomia in these pregnancies. CONCLUSION: WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester and personal history of macrosomia and diabetes were identified as risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):647-654
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900005
PURPOSE: to study the effects of physiotherapeutic techniques applied by the Multidisciplinary Program of Preparation for the Childbirth and Maternity on musculoskeletal discomforts during pregnancy. METHODS: prospective cohort study, with 71 low-risk nulliparous women, distributed according to participation (study: n=38) or not (control; n=33). The Multidisciplinary Program of Preparation for Childbirh and Maternity had 10 meetings (18th to 38th week), with educational, physiotherapeutic, and interaction activities. Occurrence, characteristics, and evolution of musculoskeletal discomforts were compared by means of a specific questionnaire, both at the beginning and at the end of the program. The average of results of the initial assessment was compared through analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the F test. For the study between proportions in the beginning and at the end of the program the c² was used. The statistical significance was determined at 5% of limit (p<0.05). RESULTS: at the beginning of the program, 63.6% of the pregnant women of the control group and 84.2% of the study group reported musculoskeletal symptoms (p=0.05), characterized by back and posterior pelvic pain. In the control group, light intensity (18.2%) and serious intensity pain (18.4) were predominant, while in the study group, the serious was 36.8%, and the isolated or associated was 31.6%. At the end, the control group showed symptoms of serious intensity (60.6%), with daily frequency (42.4%) and length of more than 3 h (69.7%; p<0.05). The study group reported light intensity (57.9%) and bimonthly frequency (50.0%) with a maximum length of one hour (55.3%) (p<0.05). Symptom evolution was also differentiated and there were worsening in 63.6% of pregnant women of the control group and improvement in 65.8% of participants of the program (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the physiotherapeutic techniques of the Multidisciplinary Program of Preparation for Childbirth and Maternity were related to a decrease in intensity, frequency and length and to a better evolution of musculoskeletal discomforts during pregnancy.
Summary
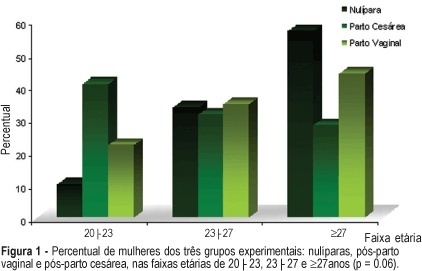
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):677-682
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100008
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of the delivery route on pelvic floor (PF) muscle strength. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate PF muscle strength by the pelvic floor strength evaluation (PFSE) test and perineometer in primiparous patients aged 20 to 30 years 4 to 6 months after delivery. The categorization was: zero lack of muscle contraction; one - weak contraction; two - moderate contraction not sustained for 6 s and three - normal contraction sustained for 6 s. A total of 94 patients were divided into there groups based on prior delivery route. They were: 32 patients with vaginal delivery with singleton cephalic presentation; 32 patients with cesarean delivery, and 30 nulliparous patients as a control group. The independent variable was delivery route and the dependent one was the muscle strength of the PF. Comparison between contraction levels was performed by Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn multiple comparison tests and the influence of delivery method was tested by chi2. Confidence interval of 95% was obtained for relative risk (RR) of Pf muscle strength changes and kappa statistics. RESULTS: the 1st and 3rd quartiles of delivery route regarding PF muscle strength were lower (p=0.01) for vaginal delivery (2.0;1-2) and intermediate for cesarean section (2.0;2-3) compared to the nulliparous (3.0;2-3) by the PFSE test and perineometer. RR of the altered examination was increased after vaginal delivery (RR=2.58; CI 95%: 1.32-5.04, p=0.002); (RR=2.31; CI 95%: 1.24-4.32, p=0.005), and after cesarean section (RR=1.56; CI 95%: 0.94-2.57, p= 0.12); (RR=1.38; CI 95%: 0.85-2.23, p=0.29) by AFA and perineometer, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: vaginal delivery decreased PF muscle strength when compared with cesarean delivery and control groups.