You searched for:"Antonio Fernandes Moron"
We found (33) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(3):193-200
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300004
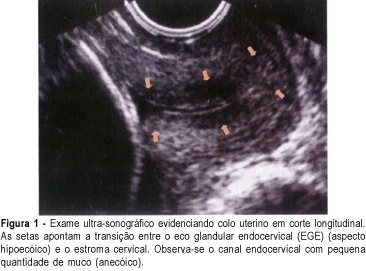
PURPOSE: to verify the prevalence of two sonographic findings, the cervical gland area (CGA) feature and the cervical length of less than 20 mm, and to compare these with the risk for premature delivery in pregnant women between 21 and 24 weeks' gestation. METHOD: this was a prospective, cross-sectional study in which 361 women were consecutively examined by transvaginal ultrasonography. Müllerian or other malformations, multiple gestations, fetal death, olygo- or polyhydramnios, marginal placenta previa, and conization, cerclage, amputation or other surgical procedures in the cervix, prior to or during pregnancy, were exclusion criteria. After the abdominal ultrasonographic morphological examination, we used transvaginal ultrasonography to measure the cervical length and to observe the presence of hyper- or hypoechoic area next to the endocervical canal, a feature characteristic of endocervical epithelium glands which is called CGA (cervical gland area). Qualitative variables are expressed as absolute and relative frequency. Quantitative variables are expressed as mean, median, standard deviation, minimum, and maximum values. Association between qualitative variables was detected by the c² test or by the Fisher exact test. For each variable, the relative risk and the 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated. Logistic regression analysis was used to calculate the predictive values for premature delivery. Significance level was 95% (alpha = 5%), with descriptive (p) values equal or lower than 0.05 considered significant. RESULTS: spontaneous preterm delivery occurred in 5.0% of the patients. Cervical length was up to 20 mm in 3.3% of all studied patients and in 27.8% of those who delivered spontaneously before the end of the pregnancy. Absence of the CGA was detected in 2.8% of all patients and in 44.4% of the women who eventually developed spontaneous preterm labor. There was a statistically significant association of absence of CGA with short cervical length (p<0.001). Absence of CGA was strongly associated with spontaneous preterm delivery (relative risk of 28.57, 95% CI 14.40-56.68). CONCLUSION: the absent CGA feature is a new morphological ultrasonographic parameter that is useful in the prediction of spontaneous preterm delivery in single gestations. Our results show that the parameter can be used as an indicator of risk for premature delivery, to be confirmed by future research.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(5):229-233
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500005
PURPOSE: to assess a possible association between polymorphism of the progesterone receptor gene (PROGINS) and recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA). METHODS: in this case-control study, 85 women with at least three previous spontaneous abortions without an identifiable cause (RSA Group) and 157 women with at least two previous term pregnancies without pathologies and no previous miscarriage (Control Group) were selected. An amount of 10 mL of peripheral blood was collected by venipuncture and genomic DNA was extracted by the DTAB/CTAB method, followed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) under specific conditions for this polymorphism and by amplification by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The bands were visualized with an ultraviolet light transilluminator and the gels were photographed. Differences in the PROGINS genotype and allele frequencies between groups were analyzed by the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. The Odds Ratio (OR) was also used, with 95% confidence intervals 95%CI. RESULTS: PROGINS genotypic frequencies were 72.3% T1T1 and 27.7% T1T2 for the RSA group and 764% T1T1, 22.3% T1T2 and 1.3% T2T2 for the control group. There were no differecnes between groups when the genotype and allele frequencies were analyzed: respectively p=0.48 (OR: 0.8) and p=0.65 (OR: 0.9). CONCLUSIONS: our results suggest that PROGINS polymorphism is not associated with RSA.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(5):235-248
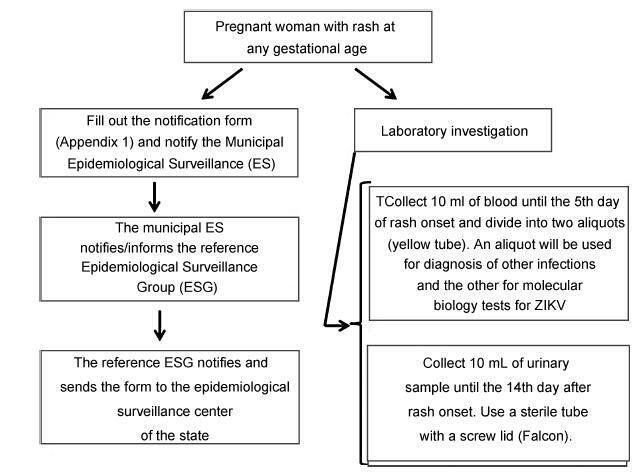
From the discovery of the Zika virus (ZIKV) in 1947 in Uganda (Africa), until its arrival in South America, it was not known that it would affect human reproductive life so severely. Today, damagetothe central nervous system is known to be multiple, and microcephaly is considered the tip of the iceberg. Microcephaly actually represents the epilogue of this infection’s devastating process on the central nervous system of embryos and fetuses. As a result of central nervous system aggression by the ZIKV, this infection brings the possibility of arthrogryposis, dysphagia, deafness and visual impairment. All of these changes of varying severity directly or indirectly compromise the future life of these children, and are already considered a congenital syndrome linked to the ZIKV. Diagnosis is one of the main difficulties in the approach of this infection. Considering the clinical part, it has manifestations common to infections by the dengue virus and the chikungunya fever, varying only in subjective intensities. The most frequent clinical variables are rash, febrile state, non-purulent conjunctivitis and arthralgia, among others. In terms of laboratory resources, there are also limitations to the subsidiary diagnosis. Molecular biology tests are based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)with reverse transcriptase (RT) action, since the ZIKV is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. The RT-PCR shows serum or plasma positivity for a short period of time, no more than five days after the onset of the signs and symptoms. The ZIKVurine test is positive for a longer period, up to 14 days. There are still no reliable techniques for the serological diagnosis of this infection. If there are no complications (meningoencephalitis or Guillain-Barré syndrome), further examination is unnecessary to assess systemic impairment. However, evidence is needed to rule out other infections that also cause rashes, such as dengue, chikungunya, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, and herpes. There is no specific antiviral therapy against ZIKV, and the therapeutic approach to infected pregnant women is limited to the use of antipyretics and analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided until the diagnosis of dengue is discarded. There is no need to modify the schedule of prenatal visits for pregnant women infected by ZIKV, but it is necessary to guarantee three ultrasound examinations during pregnancy for low-risk pregnancies, and monthly for pregnant women with confirmed ZIKV infection. Vaginal delivery and natural breastfeeding are advised.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2015;37(6):249-251
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005308
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(5):281-286
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500005
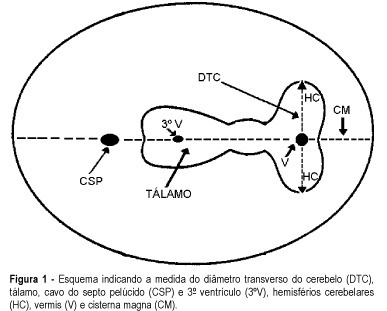
Purpose: to evaluate the effectiveness of the transverse cerebellar diameter (TCD), by ultrasonography, in the evolution of the fetal growth, and to relate it to gestational age, biparietal diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC) and femur length (FL). Method: a prospective and longitudinal study was performed on 254 pregnant women considered of low risk, with a gestational age from 20 to 40 weeks. Only 55 pregnant women were included in the study, according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. All the examinations, 217 ultrasonographic evaluations, were done by the author (LN), at least three and at most six examinations for each pregnant woman being accomplished at an interval of one to five weeks. Normality patterns were established between the 10 and 90 percentiles for each gestational age and confirmed postnatally. Results: the transverse cerebellar diameter presented a good correlation with the gestational age either as a dependent variable (R² = 0.90) or as an independent variable (R² = 0.92). A significant relationship was found in the evaluation of the fetal growth between the TCD and the several fetal parameters: BPD and HC (R² = 0.92), FL (R² = 0.90) and AC (R² = 0.89). Conclusions: the transverse cerebellar diameter is a parameter that should be used in the follow-up of development and of fetal growth because of the ascending pattern of its growth curve. Any up- or downward alteration in the growth curve can be useful for the detection of deviations of fetal growth.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(5):291-298
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000500004
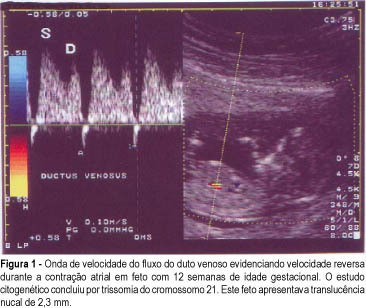
Objective: to study the value of Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus and of the umbilical artery and vein, in the screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10-14 weeks of gestation. Patients and Methods: a total of 314 fetuses were studied consecutively. In 112 cases a cytogenetic study was performed on material obtained from a biopsy of the chorionic villus, and in 202 cases the postnatal phenotype was used as a basis for the result. In addition to the routine ultrasonographic examination, all the fetuses were submitted to measurement of the nuchal translucency thickness and to Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery and vein, particularly of the ductus venosus. For statistical analysis the Fisher exact test and the Mann-Whitney test were used. Results: twenty-three cases of chromosomal abnormalities occurred. Of these abnormal cases, the ductus venosus blood flow during atrial contraction was absent (1 case) and reverse (22 cases), sensitivity was 92%. In the group of normal fetuses (289 cases), 6 evaluations demonstrated alterations in the Doppler of the ductus venosus (specificity of 97.6%, positive and negative predictive values of 76.7% and 93.3%, respectively); the false-positive rate was 2.4%. In reference to the umbilical vein and umbilical artery, there was no statistically significant difference between the abnormal and the normal group. Conclusion: The only parameter of Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery and vein which contributed to the detection of aneuploidies was the accidental discovery of the reverse blood flow in both vessels. Although our favorable results demonstrated that the Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus is effective in detecting aneuploidies, this conclusion, however, is preliminary and needs further investigation.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(6):340-344
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600004
PURPOSE: the study the effects of maternal cigarette smoking during pregnancy on placental maturation (calcifications) and the placental-uterine circulation, evaluated through umbilical and uterine Doppler. METHODS: prospective cohort study involving 244 pregnant women, 210 of them non-smokers and 34 smokers. Participants were submitted to four serial sonograms. The first was performed up to the 16th week of pregnancy to determine gestational age, and the other three at 28, 32 and 36 weeks for fetal biometry, evaluation of placental texture and Doppler studies of the uterine and umbilical arteries. Premature placental calcification was defined as grade III before 36 weeks. The chi2 and Fisher exact tests were used to compare placental grading, and the Mann-Whitney test to evaluate the resistance index of uterine and umbilical arteries. RESULTS: the frequency of grade III placenta and the resistance of the uterine arteries did not differ significantly between smokers and non-smokers, at all gestational ages. Umbilical artery Doppler was significantly higher in smokers than in non-smokers at 32 weeks. CONCLUSIONS: no association was found between cigarette smoking and premature placental calcification. Smoking was associated with increased umbilical artery resistance at 32 weeks.