Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):357-359
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(8):357-362
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000800004
PURPOSE: To establish reference values for the first trimester uterine artery resistance index (UtA-RI) and pulsatility index (UtA-PI) in healthy singleton pregnant women from Northeast Brazil. METHODS: A prospective observational cohort study including 409 consecutive singleton pregnancies undergoing routine early ultrasound screening at 11 - 14 weeks of gestation was performed. The patients responded to a questionnaire to assess maternal epidemiological characteristics. The left and right UtA-PI and UtA-RI were examined by color and pulsed Doppler by transabdominal technique and the mean UtA-PI, mean UtA-RI and the presence of bilateral protodiastolic notching were recorded. Quartile regression was used to estimate reference values. RESULTS: The mean±standard deviation UtA-RI and UtA-PI were 0.7±0.1 and 1.5±0.5, respectively. When segregated for gestation age, mean UtA-PI was 1.6±0.5 at 11 weeks, 1.5±0.6 at 12 weeks, 1.4±0.4 at 13 weeks and 1.3±0.4 at 14 weeks' gestation and mean UtA-RI was 0.7±0.1 at 11 weeks, 0.7±0.1 at 12 weeks, 0.6±0.1 at 13 weeks and 0.6±0.1 at 14 weeks' gestation. Uterine artery bilateral notch was present in 261 (63.8%) patients. We observed that the 5th and 95th percentiles of the UtA-PI and UtA-RI uterine arteries were 0.7 and 2.3 and, 0.5 and 0.8, respectively. CONCLUSION: Normal reference range of uterine artery Doppler in healthy singleton pregnancies from Northeast Brazil was established. The 95th percentile of UtA-PI and UtA-RI values may serve as a cut-off for future prediction of pregnancy complications studies (i.e., pre-eclampsia) in Northeast Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):357-359
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):357-360
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600009
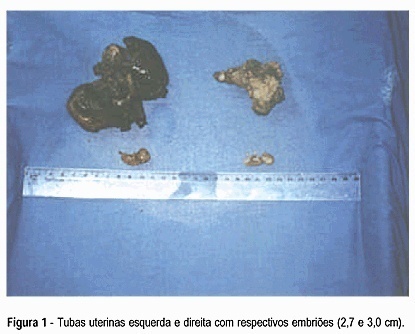
Bilateral ectopic pregnancy is the most unusual twin gestation considering that less than 250 cases have been reported in the literature. Our case fulfills the diagnostic criterion determined by Norris9 which requires demonstration of chorionic villi in each fallopian tube. We report the case of a 36-year-old multiparous woman who had an hemorrhagic acute abdomen. A laparotomy performed under general anesthesia revealed hemoperitoneum of 1.8 liters and both swelled tubes with laceration of their walls, besides two embryos with 2,7 and 3,0 cm in length free in the intra-abdominal blood. A literature review on bilateral ectopic pregnancy is presented.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):357-365
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600011
The multiple factors involved in maternal complications and maternal mortality make the task of their long-term control difficult and time-consuming. Professional care for pregnant women and/or those in labor certainly represents a key point for obtaining good outcomes, either maternal or perinatal. From the starting point that an adequate professional medical care for delivery has the capacity of decreasing the occurrence of complications associated with maternal morbidity and mortality, the evidence regarding some interventions included in this care is summarily presented. The evidence derived from studies performed with a strong methodological and scientific approach, mainly randomized controlled trials, on interventions to reduce complications and maternal mortality. These main interventions basically refer to: institutional care to is focused delivery, skilled professional care, use of traditional birth attendants in some contexts, use of appropriate technologies including partograph, place of birth, position for delivery, use of episiotomy, type of delivery, use of oxytocin during the active phase of labor, performance of push efforts during the second stage, active management of the third stage, and prophylaxis for post-partum hemorrhage. Although the effect of avoiding maternal death is difficult to be evaluated due to its low frequency, its rational and standardized use, through manuals and guidelines for intervention care, has a positive effect on the quality of care for childbirth. This is part of the human and technical context of the right that every woman has to the best possible care in this so special moment of her life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):357-361
To study a sample of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients for their gynecological/obstetric history and compare them to controls to determine their influences on number of pregnancies, menarche, menopause and reproductive years following RA onset.
This is a cross-sectional study of 122 RA patients and 126 controls. Patients and controls were questioned about age of menarche, age of menopause, number of pregnancies and abortions. Reproductive years were calculated as the difference between age at menopause and age at menarche. For comparison, we used the Mann-Whitney, unpaired t, chi-squared, and Spearman tests. The adopted significance was 5%.
In the RA patients with disease beginning in the postmenopausal years, the period of reproductive years (age at menopause - age of menarche) showed a positive correlation with age at disease onset (rho=0.46; 95% confidence interval [CI]=0.20- 0.55 with p=0.0008). The number of pregnancies was higher in patients with postmenopausal disease onset when compared with those with premenopausal disease onset (median of 3 with interquartile range [IQR]=2-4 versus median of 2 with IQR=1-3; p=0.009), and RA patients had more pregnancies than controls (p=0.0002).
The present study shows that, in our population, the duration of reproductive years and the number of pregnancies are linked to the onset of RA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):358-368
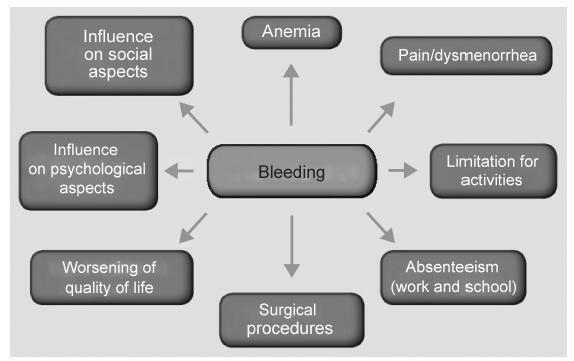
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a frequent condition in Gynecology. It may impact physical, emotional sexual and professional aspects of the lives of women, impairing their quality of life. In cases of acute and severe bleeding, women may need urgent treatment with volumetric replacement and prescription of hemostatic substances. In some specific cases with more intense and prolonged bleeding, surgical treatment may be necessary. The objective of this chapter is to describe the main evidence on the treatment of women with abnormaluterinebleeding, both acuteand chronic.Didactically,thetreatmentoptions were based on the current International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) classification system (PALM-COEIN). The etiologies of PALM-COEIN are: uterine Polyp (P), Adenomyosis (A), Leiomyoma (L), precursor and Malignant lesions of the uterine body (M), Coagulopathies (C), Ovulatory dysfunction (O), Endometrial dysfunction (E), Iatrogenic (I), and Not yet classified (N). The articles were selected according to the recommendation grades of the PubMed, Cochrane and Embase databases, and those in which the main objective was the reduction of uterine menstrual bleeding were included. Only studies written in English were included. All editorial or complete papers that were not consistent with abnormal uterine bleeding, or studies in animal models, were excluded. The main objective of the treatment is the reduction of menstrual flow and morbidity and the improvement of quality of life. It is important to emphasize that the treatment in the acute phase aims to hemodynamically stabilize the patient and stop excessive bleeding, while the treatment in the chronic phase is based on correcting menstrual dysfunction according to its etiology and clinical manifestations. The treatment may be surgical or pharmacological, and thelatterisbasedmainlyonhormonaltherapy,anti-inflammatorydrugsandantifibrinolytics.