Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):316-316
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):316-316
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):316-322
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the relationship between renal transplantation and pregnancy through the analysis of clinical and obstetric intercurrent events and perinatal outcomes. METHODS: a retrospective series of 39 cases of pregnancy in 37 women with renal transplantation from January 1997 to December 2003 was evaluated. A control group consisted of 66 pregnant women with no previous clinical pathologies. This group received prenatal care and these patients delivered during 2002 and 2003. Preeclampsia, premature rupture of membranes, premature delivery, and intrauterine growth restriction were used to compare these variables. Demographic characteristics of these groups were related to the mean age at conception, ethnic characteristics and obstetric past. Regarding renal transplantation the type of donator and used immunosuppressive drugs were evaluated. The studied clinical variables were chronic hypertension, anemia and urinary tract infection. The interval between the surgery and conception, occurrence of dysfunction, rejection and loss of the allograft were characteristcs related to the allograft. Obstetric variables were related to the type of delivery, incidence of preeclampsia and premature rupture of membranes. Perinatal outcomes were premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction and these results were compared with renal function. The used statistical methods were the chi2 and Fisher's exact tests. The significance level was fixed always as less than or equal to 0.05 (5%). RESULTS: the mean age at conception was 27 years. The live donator was the most frequent among the patients. Among the immunosuppressive drugs, cyclosporine was the most used. Chronic hypertension occurred in 82% of the cases, anemia in 77% and urinary tract infection in 38.5%. The incidence of renal dysfunction was 47.4% and preeclampsia was the main cause. The loss of the renal transplantation occurred in 10.2%. Delivery by cesarean section was performed in 53.8% of the patients, and the main causes were hypertensive syndromes. Preeclampsia occurred in 28.2%. Among the perinatal outcomes, premature delivery occurred in 46.1% of the cases, with a significant relation to creatinine level greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL at the start of prenatal care. Another observed intercurrent event was intrauterine growth restriction, which occurred in 41.0%, and here we found no relation between this event and creatinine levels. CONCLUSIONS: young patients constituted the study group. Chronic hypertension, anemia and urinary tract infection were very common. Renal dysfunction was frequent and must be investigated during prenatal care. There were four cases of loss of the transplant due to clinical or obstetric causes. Cesarean delivery had the highest incidence, but vaginal delivery should be the first choice in these cases. Preeclampsia occurred very frequently and this complication should be considered as a high risk. Preterm delivery and intrauterine growth restriction were the main perinatal complications. Premature deliveries before 37 weeks of gestation were related to allograft function.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):316-322
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700005
PURPOSE: To compare the metabolic parameters, body composition and muscle strength of women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) to those of women with ovulatory menstrual cycles. METHODS: A case-control study was conducted on 27 women with PCOS and 28 control women with ovulatory cycles, aged 18 to 27 years with a body mass index of 18 to 39.9 kg/m², who did not practice regular physical activity. Serum testosterone, androstenedione, prolactin, sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), insulin and glycemia levels were determined. Free androgen index (FAI) and resistance to insulin (by HOMA) were calculated. The volunteers were submitted to evaluation of body composition based on skin folds and DEXA and to 1-RM maximum muscle strength tests in three exercises after familiarization procedures and handgrip isometric force was determined. RESULTS: Testosterone levels were higher in the PCOS group than in the Control Group (68.07±20.18 versus 58.20±12.82 ng/dL; p=0.02), as also were the FAI (282.51±223.86 versus 127.08±77.19; p=0.01), insulin (8.41±7.06 versus 4.05±2.73 µIU/mL; p=0.01), and HOMA (2.3±2.32 versus 1.06±0.79; p=0.01), and SBHG levels were lower (52.51±43.27 versus 65.45±27.43 nmol/L; p=0.04). No significant differences in body composition were observed between groups using the proposed methods. The PCOS group showed greater muscle strength in the 1-RM test in the bench press (31.2±4.75 versus 27.79±3.63 kg; p=0.02), and leg extension exercises (27.9±6.23 versus 23.47±4.21 kg; p=0.02) as well as handgrip isometric force (5079.61±1035.77 versus 4477.38±69.66 kgf/m², p=0.04). PCOS was an independent predictor of increase muscle strength in bench press exercises (estimate (E)=2.7) (p=0.04) and leg extension (E=3.5) (p=0.04), and BMI in the exercise of isometric handgrip (E=72.2) (p<0.01), bench press (E=0.2) (p=0.02) and arm curl (E=0.3) (p<0.01). No association was found between HOMA-IR and muscle strength. CONCLUSIONS: Women with POS showed greater muscle strength, with no difference in body composition, and IR was not associated with muscle strength performance. Muscle strength may be possibly related to high levels of androgens in these women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(7):317-322
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000700006
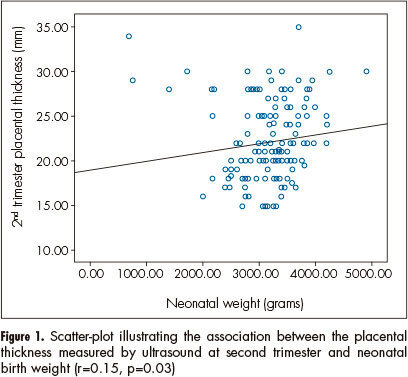
PURPOSE: To investigate relationship between placental thickness during the second and third trimesters and placental and birth weights. METHODS: From January 2011 to June 2012, a total of 250 singleton pregnant women presented at our antenatal clinic were enrolled in this prospective study. All recruited women were assessed at the 1st trimester screening for baseline demographic and obstetric data. The placental thickness was measured trans-abdominally by placing the ultrasound transducer perpendicularly to the plane of the placenta, in the area of the cord insertion at second and third trimester. Pearson's correlation analysis was used to establish the degree of relationship between placental thickness and birth and placental weights. RESULTS: Of 250 recruited participants, 205 women were able to complete the study. The mean age of cases was 26.4±5.1. Values of mean birth and placental weights were 305.56±657.0 and 551.7±104.8 grams respectively. Ultrasonographic measures of placental thickness in second and third trimester and changes between them were 21.68±4.52, 36.26±6.46 and 14.67±5.67 mm respectively. There was a significant positive correlation between placental thickness and birth weight in the second and third trimesters (r=0.15, p=0.03; r=0.14, p=0.04 correspondingly). CONCLUSION: According to our study, birth weight has a positive relation with both second and third trimester placental thickness; however, placental thickness change could not predict low birth weight.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):317-324
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in post menopausal women, and inflammation is involved in the atherosclerosis process.
to assess whether dietary pattern, metabolic profile, body composition and physical activity are associated with low-grade chronic inflammation according to highsensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels in postmenopausal women.
ninety-five postmenopausal participants, with no evidence of clinical disease, underwent anthropometric, metabolic and hormonal assessments. Usual dietary intake was assessed with a validated food frequency questionnaire, habitual physical activity was measured with a digital pedometer, and body composition was estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis. Patients with hs-CRP ≥ 10 mg/L or using hormone therapy in the last three months before the study were excluded from the analysis. Participants were stratified according to hs-CRP lower or ≥3 mg/L. Sedentary lifestyle was defined as walking fewer than 6 thousand steps a day. Two-tailed Student's t-test, Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U or Chi-square (x 2) test were used to compare differences between groups. A logistic regression model was used to estimate the odds ratio of variables for high hs-CRP.
participants with hs-CRP ≥ 3 mg/L had higher body mass index (BMI), body fat percentage, waist circumference (WC), triglycerides, glucose, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (p = 0.01 for all variables) than women with hs-CRP <3 mg/L. Also, women with hs-CRP ≥3 mg/L had a higher glycemic load diet and lower protein intake. Prevalence of sedentary lifestyle (p < 0.01) and metabolic syndrome (p < 0.01) was higher in women with hs-CRP ≥3 mg/L. After adjustment for age and time since menopause, the odds ratio for hs- CRP ≥3 mg/L was higher for sedentary lifestyle (4.7, 95% confidence interval [95%CI] 1.4-15.5) and carbohydrate intake (2.9, 95%CI 1.1-7.7).
sedentary lifestyle and high-carbohydrate intake were associated with low-grade chronic inflammation and cardiovascular risk in postmenopause.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):317-323
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400009
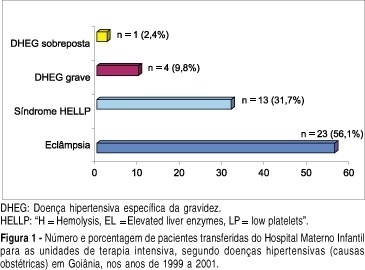
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the epidemiological and parturitional aspects of obstetric patients admitted to intensive care units (ICU), and analyze the frequency of intensive support needed by them. METHODS: observational and descriptive study of all obstetric patients' transfers to ICU from the Hospital Materno Infantil of Goiânia-Go, from January 1999 to December 2001. The analysis has included variables as maternal age, parity, obstetric and non-obstetric indications for ICU admissions, moment of transfer, mode of delivery, maternal death, and the frequency of ICU utilization per 1,000 deliveries (IDR - imminent death ratio). The statistical analysis was performed by the chi2 test or the Fisher exact test and a significant difference was set at a level of 5%. RESULTS: over the 36-month period analyzed, 86 pregnancy-associated ICU admissions were identified (among 4,560 deliveries). Of the 86 patients, 52.33% (n=45) were nulliparae and 63 (73.26%) were between 19 and 35 years old. Hypertensive disorders accounted for 41 (57.75%) of the admissions and hemorrhage for 14 (19.72%). Eclampsia (n=23), HELLP syndrome (n=13) and premature abruptio placentae (n=5) were the most common obstetric indications for ICU admissions. Maternal cardiac disorders accounted for 4 cases of non-obstetric indications. There was a predominance of postpartum transfers (82.35%). Fifty-five (72.37%) patients needed delivery by caesarian section. The average time spent in the UCI by those patients was 5.1 days. Maternal mortality found in this study was 24.29%, hypertensive disorders being responsible for 52.94% (9/17) of all obstetric-associated deaths. There were no significant statistical differences (p=0.81) regarding these obstetric-associated deaths and their causes (hypertensive disorders, hemorrhage or infections) or even regarding maternal deaths and duration of stay (< or > 48 hours) in the ICU (p=0.08). The IDR found was 18.8 per 1,000 deliveries. CONCLUSIONS: the need of intensive care estimated by IDR was 18.8 per 1,000 deliveries, the pregnancy-induced hypertension being responsible for the majority of the indications for maternal transfers.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):317-321
This study aimed to evaluate and validate the qualitative human chorionic gonadotropin β subunit (β-hCG) test of the vaginal fluid washings of pregnant women with premature rupture of fetal membranes (PROM).
Cross-sectional study of pregnant women between gestational weeks 24 and 39 who underwent consultations in one of our institutions. They were divided into two groups: group A (pregnant women clinically diagnosed with PROM) and group B (pregnant women without loss of amniotic liquid). The patients were subjected to a vaginal fluid washing with 3 mL of saline solution, which was aspirated subsequently with the same syringe. The solution was immediately sent to the laboratory to perform the vaginal β-hCG test with cut-off points of 10 mIU/mL (β-hCG-10) and/or 25 mIU/mL (β-hCG-25).
The β-hCG-10 test of the vaginal secretion was performed in 128 cases. The chi-squared test with Yates’ correction showed a statistically significant difference between the 2 groups (p = 0.0225). The sensibility, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy parameters were 77.1%, 43.6%, 52.3%; 70.4%; and 58.6% respectively. The β-hCG-25 test of the vaginal washing was performed in 49 cases. The analysis by Fisher’s exact test showed a statistically significant difference between the groups (p = 0.0175). The sensibility, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy parameters were 44.4%, 87.1%, 66.6%; 72.9%; and 71.4% respectively.
The β-hCG-25 test showed better accuracy for the diagnosis of PROM, and can corroborate the early diagnosis of PROM because it is a simple and quick exam.