Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):303-309
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600003
PURPOSE: to diagnose intrauterine growth restriction (IGR) and its connection with early neonatal morbidity and mortality, through Roher's ponderal index (PI). METHODS: this was a retrospective, descriptive study of transversal cohort, in which 2741 newborns (NB) were included, 2053 of them from healthy pregnant women, 228 from women with mild pregnancy-related hypertension, 52 from those with severe pregnancy-related hypertension, 25 from those with mild pregnancy-related hypertension that evolved to eclampsia, 136 from those with premature membrane rupture, and 247 from women who smoked along gestation. Roher's PI was calculated by the equation: PI = weight/height ³ x 100 and the values 2.25 and 3.10 of Lubchenco's 10 and 90 percentiles were used to classify the types of IGR. IGR was classified as asymmetric for NB with PI < 2.25 and weight lower than percentile 10, as symmetric, with PI from 2.25 to 3.10 and weight lower than percentile 10, and adequate for gestational age with PI from 2.25 to 3.10, and weight from 10 to 90 percentiles. Statistical analysis was performed using the non-paired t test, the non-parametric chi2 test and Fisher's exact test, with significance set at a value of p<0.05. RESULTS: low birth weight (< 2,500 g) was present in 3.6% (100/2741) of the cases, while the rate of IGR diagnosed through PI was 15.7% (430/2741), 14.0% being asymmetric and 1.7% symmetric. The most frequent complication among the asymmetric IGRNB was transient tachypnea (8.3%), followed by asphyxia (5.7%) and infection (2.6%). Transient tachypnea was present in 6.5% of symmetric IGRNB, followed by asphyxia (4.3%), meconium aspiration syndrome (2.2%), hypoglycemia (2.2%) and infection (2.2%). Early neonatal death was similar for NB with restricted IGR and adequate IGR for gestational age, both groups reaching a rate of 0.3%. CONCLUSIONS: Rohrer's PI was able to diagnose the different IGR patterns, which would not be known if the birth weight had been calculated in terms of gestational age. The asymmetric NB presented a higher incidence of transient tachypnea and asphyxia, without statistical significance in relation the other IGR patterns. The frequency of early neonatal death was similar for the asymmetric and adequate for gestational age NB groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):303-308
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600002
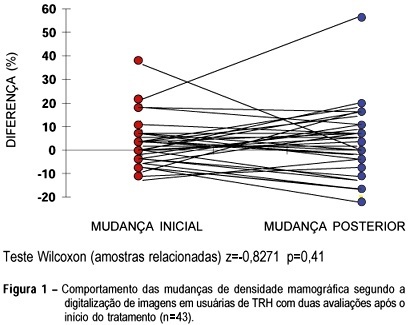
Objective: to compare mammographic density changes, case by case, according to image digitization in three consecutive evaluations of users or nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy (HRT). Methods: 59 postmenopausal women were evaluated, 43 being users of cyclic or continuous estro-progestin hormonal replacement therapy, and 16 nonusers. The criteria of inclusion were: amenorrhea for at least 12 months, a normal mammographic examination at the beginning of the HRT (users) or the clinical follow-up without HRT (nonusers), at two incidences (mediolateral and craniocaudal). The following variables were used for the evaluation of mammary density: initial change - the difference between the first mammography after HRT performed in 12 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT-and final change - the difference between the second mammography after HRT performed in 24 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT. Wilcoxon and c² tests were used in order to evaluate the differences in mammographic density changes. Results: more than half (56.3%) of the women, HRT users with initial increase in mammographic density remained with the increase after the final evaluation. This finding was not significant (p=0.617). In the same group, the initial nonincrease was significantly associated with the final nonincrease (p=0.017). Among the nonusers, all breasts that were not totally fat at the initial evaluation presented a mammographic density decrease at the final evaluation. Conclusions: the majority of HRT users presenting mammographic density increase at the first evaluation, after approximately one year of use, remained with the increase at a second evaluation. After some time, the nonusers tended to present a significant mammographic density decrease (p=0.003).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(6):303-309
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000600007
PURPOSE: Due to the scarce information available in Brazil in relation to the number of women who initiated the use of combined oral contraceptives and prematurely discontinued, the objective was to assess the reasons for discontinuation of the use of several combined oral contraceptives among Brazilian women living in urban areas. METHODS: A cross-sectional study with 400 gynecologists registered withy the Brazilian Federation of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Each physician interviewed 10 non-pregnant, not breastfeeding, not amenorrheic women aged 18 to 39 years who consulted requesting combined oral contraceptive (COC) with a questionnaire at the beginning of use and at six months later. The questionnaire included sociodemographic data, type of COC chosen or prescribed and reasons for discontinuation when it occurred during follow-up. The strategy of selection allowed the inclusion of women from different socioeconomic strata, however, only those attended at private or insurance offices. The sample size was estimated at 1,427 women. RESULTS: A total of 3,465 interviews were conducted at the first visit and 1,699 six months later. The women were 20 to 29 years old, 57.3% were single and an equal proportion of 45.0% attended high school or college. Most (60.7%) were nulligravidas and among those who had used some contraceptive before, 71.8% had used a COC. Among the more prescribed or chosen COC the most prevalent were monophasic with ethynil estradiol (20 µg) and regarding progestin the most prevalent was with gestodene (36.5%) followed by a COC with drosperinone (22.0%). At six months 63.5% still used COC. Among those who discontinued the main reasons were wishing to become pregnant (36.5%) and side effects (57.3%) and the most prevalent were headache (37.6%), weight gain (16.6%) and irregular bleeding (23.6%). CONCLUSIONS: The continuation rate of COC was low at six months and this study could contribute to a better counseling on the part of physicians of patients who initiate COC about side-events that are rare, minimal and temporary and about the benefits of COC use.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):303-309
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005012
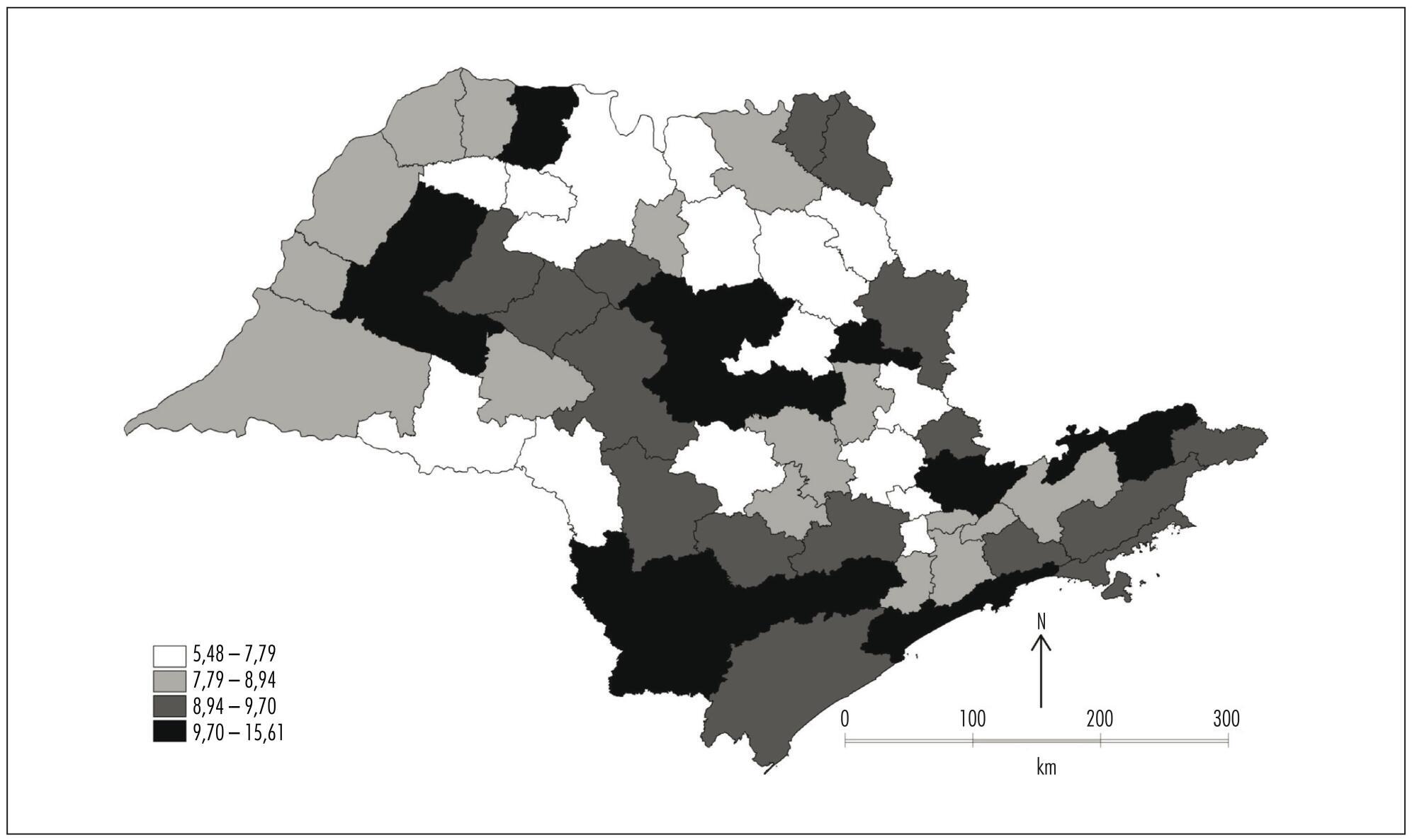
To identify spatial patterns of neonatal mortality distribution in the micro regions of São Paulo State and verify the role of avoidable causes in the composition of this health indicator.
This ecological exploratory study used neonatal mortality information obtained from Information System and Information Technology Department of the Brazilian National Healthcare System (DATASUS) in the period between the years 2007 and 2011. The digital set of micro regions of São Paulo State was obtained from Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Moran Indexes were calculated for the neonatal mortality total rate and rate from avoidable causes; thematic maps were constructed with these rates, as well as the difference between them; and the Box Map was built.
The overall neonatal mortality rate was 8.42/1,000 live births and neonatal mortality rate from avoidable causes of 6.19/1,000 live births. Moran coefficients (I) for these rates were significant (p-value<0.05) - for the total rate of neonatal mortality I=0.11 and for mortality from preventable causes I=0.19 -, and neonatal deaths were concentrated in southwest region and the Vale do Paraíba. If preventable causes were abolished, there would be a significant reduction in the average rate of overall neonatal mortality, from 8.42 to 2.23 deaths/1,000 live births, representing a decline of 73%.
This study demonstrated that neonatal mortality rate would be close to the rates of developed countries if avoidable causes were abolished.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):303-311
The lack of data on the impact of hyperglycemia and obesity on the prevalence of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence (PSUI) led us to conduct a cross-sectional study on the prevalence and characteristics of PSUI using validated questionnaires and clinical data.
This cross-sectional study included 539 women with a gestational age of 34 weeks who visited a tertiary university hospital between 2015 and 2018. The main outcome measures were the prevalence of PSUI, the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire Short Form (ICIQ-SF), and the Incontinence Severity Index (ISI) questionnaires. The women were classified into four groups: normoglycemic lean, normoglycemic obese, hyperglycemic lean, and hyperglycemic obese. The differences between groups were tested using descriptive statistics. Associations were estimated using logistic regression analysis and presented as unadjusted and adjusted odds ratios.
Prevalence rates of PSUI were no different between groups. However, significant difference in hyperglycemic groups worse scores for severe and very severe PSUI. When adjusted data for confound factors was compared with normoglycemic lean group, the hyperglycemic obese group had significantly higher odds for severe and very severe forms of UI using ICIQ-SF (aOR 3.157; 95% CI 1.308 to 7.263) and ISI (aOR 20.324; 95% CI 2.265 to 182.329) questionnaires and highest perceived impact of PSUI (aOR 4.449; 95% CI 1.591 to 12.442).
Our data indicate that obesity and hyperglycemia during pregnancy significantly increase the odds of severe forms and perceived impact of PSUI. Therefore, further effective preventive and curative treatments are greatly needed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):303-304
The COVID-19 outbreak is increasing around the world in the number of cases, deaths, and affected countries. Currently, the knowledge regarding the clinical impact of COVID-19 on maternal, fetal, and placental aspects of pregnancy is minimal. Although the elderly and men were the most affected population, in previous situations, such as the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic and the Ebola epidemic, pregnant women were more likely to develop complications than nonpregnant women. There are unanswered questions specific to pregnant women, such as whether pregnant women are more severely affected and whether intrauterine transmission occurs. Additional information is needed to inform key decisions, such as whether pregnant health care workers should receive special consideration, whether to separate infected mothers and their new borns, and whether it is safe for infected women to breastfeed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):304-310
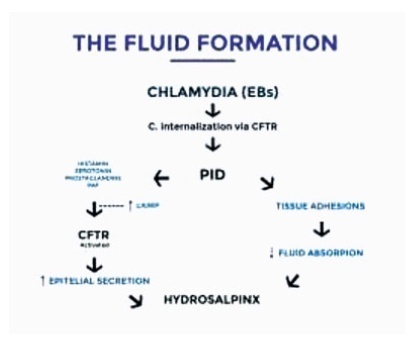
Hydrosalpinx is a disease characterized by the obstruction of the salpinx, with progressive accumulation in the shape of a fluid-filled sac at the distal part of the tuba uterina, and closed to the ovary. Women with hydrosalpinges have lower implantation and pregnancy rates due to a combination of mechanical and chemical factors thought to disrupt the endometrial environment. Evidence suggests that the presence of hydrosalpinx reduces the rate of pregnancy with assisted reproductive technology. The main aim of the present is review to make an overview of the possible effects of hydrosalpinx on in vitro fertilization (IVF).We conducted a literature search on the PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Google Scholar data bases regarding hydrosalpinx and IVF outcomes. Hydrosalpinx probably has a direct toxic effect on sperm motility and on the embryos. In addition, the increasing liquid inside the salpinges could alter the mechanisms of endometrial receptivity. The window of endometrial receptivity is essential in the implantation of blastocysts, and it triggers multiple reactions arising from the endometrium as well as the blastocysts. Hydrosalpinx could influence the expression of homeobox A10 (HOXA10) gene, which plays an essential role in directing embryonic development and implantation. Salpingectomy restores the endometrial expression of HOXA10; therefore, it may be one mechanism by which tubal
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):304-309
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500007
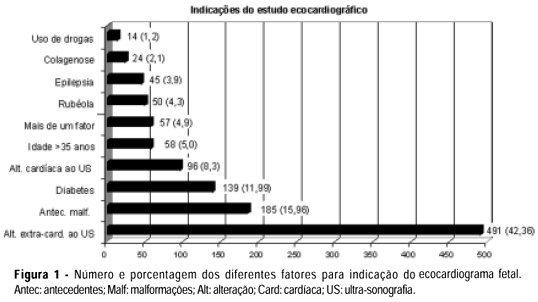
PURPOSE: to analyze the results of a screening and diagnostic program of arrhythmias and congenital heart disease in a reference hospital and the relevance of early diagnosis in the fetal and neonate evolution. METHODS: cardiac evaluation of 1159 fetuses was done in two different levels. Level I: by morphological ultrasound examination with the objective to detect the existence of either arrhythmias or structural cardiac malformations. Level II: by fetal echocardiography to establish the differential diagnosis. The results of level I in the arrhythmia group were compared with those of level II, and in the group with malformations the results of both levels were confronted with the neonate echocardiogram or necropsy. The kappa index was calculated to evaluate the concordance between the two levels. RESULTS: all detected arrhythmias in level I were confirmed in level II, there were no false negative cases and five patients with severe arrhythmia required pharmacological therapy. The diagnosis of structural malformation by level I had sensitivity of 72% and specificity of 98% and there were 28% of false-positive cases. In level II, the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnosis of congenital heart disease were 100 and 99%, respectively. The kappa index was 57% and indicated a moderate degree of concordance between the two levels. Fifty-one percent of the fetuses with diagnosis of cardiac malformations required pharmacological or invasive intervention immediately after birth. CONCLUSION: morphological ultrasound examination is a important tool in the screening of arrhythmias and congenital heart defects during fetal life. The sensitivity and specificity of the fetal echocardiogram were very high and the early diagnosis made it possible to treat the fetus with severe cardiac disease either during pregnancy or immediately after birth.