Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):242-252
Evaluate the effect of combined training on body image (BI), body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer. As also the relationship of BI with body composition and functional capacity.
This was a Controlled Clinical Trial study, this study including 26 patients with breast cancer (30 to 59 years). The training group (n = 13) underwent 12 weeks of training, including three 60-min sessions of aerobic exercise and resistance training, and two sessions of flexibility training per week; each flexibility exercise lasted 20s. The Control Group (n = 13) received only the standard hospital treatment. Participants were evaluated at baseline and after 12 weeks. BI (primary outcomes) was assessed using the Body Image After Breast Cancer Questionnaire; Body composition was estimated with the indicators: Body mass index; Weight, Waist hip Ratio; Waist height ratio; Conicity index; Reciprocal ponderal index; Percentage of fat; Circumference of the abdomen and waist; Functional capacity by cardiorespiratory fitness (cycle ergometer) and strength (manual dynamometer). The statistic was performed in the Biostatistics and Stata 14.0 (α = 5%).
The patients in the training group showed a reduction in the limitation dimension (p = 0.036) on BI, However, an increase in waist circumference was observed in both groups. In addition an increase in VO2max (p < 0.001) and strength in the right (p = 0.005) and left arms (p = 0.033).
Combined training demonstrates to be an effective and non-pharmacological strategy to patients with breast cancer, with improvement on BI and functional capacity, changing related variables negatively when there is no physical training.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):242-242
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400013
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):242-242
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):242-248
To analyze the factors associated with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in women with cervical cancer (CC) in a single center in Rio de Janeiro, state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
A cross-sectional study in women with a diagnosis of CC followed-up in the gynecology outpatient clinic of the Hospital do Câncer II (HCII, in the Portuguese acronym) of the Instituto Nacional de Câncer (INCA, in the Portuguese acronym). The data were collected from March to August 2015. Women with palliative care, communication/cognition difficulty, undergoing simultaneous treatment for other types of cancer, or undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy were excluded. For the evaluation of the HRQoL, a specific questionnaire for women with CC was used (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Cervix Cancer [FACT-Cx]). The total score of the questionnaire ranges from 0 to 168, with higher scores indicating a better HRQoL.
A total of 115 women were included in the present study, with a mean age of 52.64 years old (standard deviation [SD] = 12.13). The domains of emotional (16.61; SD = 4.55) and functional well-being (17.63; SD = 6.15) were those which presented the worst scores. The factors that had an association with better HRQoL in women with CC were having a current occupation, a longer time since the treatment and diagnosis, and women who had undergone hysterectomy.
Considering the domains of HRQoL of the women treated for cervical cancer, a better score was observed in the domains of physical and social/family wellbeing. For most domains, better scores were found between those with a current occupation, with a longer time after the diagnosis and treatment, and among those who had undergone a hysterectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):242-250
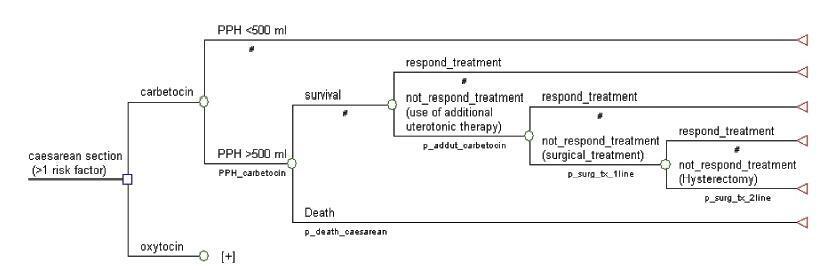
To assess the cost-effectiveness of carbetocin versus oxytocin for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) due to uterine atony after vaginal delivery/ cesarean section in women with risk factors for bleeding.
A decision treewas developed for vaginal delivery andanother one for cesarean, in which a sequential analysis of the results was obtained with the use of carbetocin and oxytocin for prevention of PPH and related consequences. A third-party payer perspective was used; only directmedical costs were considered. Incremental costs and effectiveness in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were evaluated for a one-year timehorizon. The costs were expressed in 2016 Colombian pesos (1 USD = 3,051 Col$).
In the vaginal delivery model, the average cost of care for a patient receiving prophylaxis with uterotonic agents was Col$ 347,750 with carbetocin and Col$ 262,491 with oxytocin,while theQALYs were 0.9980 and 0.9979, respectively. The incremental costeffectiveness ratio is above the cost-effectiveness threshold adopted by Colombia. In the model developed for cesarean section, the average cost of a patient receiving prophylaxis with uterotonics was Col$ 461,750 with carbetocin, and Col$ 481,866 with oxytocin, and the QALYs were 0.9959 and 0.9926, respectively. Carbetocin has lower cost and is more effective, with a saving of Col$ 94,887 per avoided hemorrhagic event.
In case of elective cesarean delivery, carbetocin is a dominant alternative in the prevention of PPH compared with oxytocin; however, it presents higher costs than oxytocin, with similar effectiveness, in cases of vaginal delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(4):243-246
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000400007
Purpose: to evaluate the possibility and accuracy of fetal karyotyping in pleural effusions. Methods: we studied fifteen fetuses with unilateral or bilateral pleural effusions. All of these fetuses underwent intrauterine thoracocentesis guided by ultrasound examinations. The gestational age varied from 19 to 34 weeks. A morphogenetic ultrasound examination was performed in each case by the authors in order to identify associated structural anomalies. When the cellular cultures of pleural effusion samples were negative, an alternative karyotype was obtained by cordocentesis. A fetal lymphocyte culture was made of pleural effusion samples for karyotype in a similar technique as for fetal blood. Results: the fetal karyotype was successful in 12 cases. There were 4 abnormal results, all of them were Down syndromes, and in the other 8 cases the chromosomal analyses were normal. The fetal karyotype was confirmed and compared by newborn blood chromosomal analysis, genetic evaluation or necropsy. There were no maternal or fetal side effects related to the procedure. Conclusions: the fetal karyotyping performed in pleural effusions obtained by intrauterine thoracocentesis proved to be highly efficient and safe. It must be the method of choice for rapid karyotyping in fetuses with pleural edema.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):243-243
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):243-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400011